Summary
Background and objectives
There are conflicting research results about the survival differences between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, especially during the first 2 years of dialysis treatment. Given the challenges of conducting randomized trials, differential rates of modality switch and transplantation, and time-varying confounding in cohort data during the first years of dialysis treatment, use of novel analytical techniques in observational cohorts can help examine the peritoneal dialysis versus hemodialysis survival discrepancy.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements
This study examined a cohort of incident dialysis patients who initiated dialysis in DaVita dialysis facilities between July of 2001 and June of 2004 and were followed for 24 months. This study used the causal modeling technique of marginal structural models to examine the survival differences between peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis over the first 24 months, accounting for modality change, differential transplantation rates, and detailed time-varying laboratory measurements.
Results
On dialysis treatment day 90, there were 23,718 incident dialysis—22,360 hemodialysis and 1,358 peritoneal dialysis—patients. Incident peritoneal dialysis patients were younger, had fewer comorbidities, and were nine and three times more likely to switch dialysis modality and receive kidney transplantation over the 2-year period, respectively, compared with hemodialysis patients. In marginal structural models analyses, peritoneal dialysis was associated with persistently greater survival independent of the known confounders, including dialysis modality switch and transplant censorship (i.e., death hazard ratio of 0.52 [95% confidence limit 0.34–0.80]).
Conclusions
Peritoneal dialysis seems to be associated with 48% lower mortality than hemodialysis over the first 2 years of dialysis therapy independent of modality switches or differential transplantation rates.
Introduction
The number of patients requiring maintenance dialysis treatment continues to increase (1,2). The choice of dialysis modality has become an important decision that not only affects the programs funding renal replacement therapy but also influences patients’ quality of life and survival (3). The major dialysis modality (>90%) in the United States has been in-center hemodialysis (HD), despite the rising costs that increased from $64,000 per patient in 2003 to $82,285 in 2009. During the same period, annual expenses for peritoneal dialysis (PD) per patient had increased from $47,000 to $61,588 (3,4). However, in 2008, only about 6% of dialysis patients in the United States received PD modality (5,6). Obtaining the best-practice evidence on which modality is the best for a particular patient and for how long has been fraught with difficulties and mixed results.
Although randomized controlled studies are the best to compare outcomes of different dialysis modalities, many patients, when properly educated, would not agree to randomization. A randomized controlled trial attempted in The Netherlands in 1997–2000 was stopped prematurely because of insufficient enrolment (7). We are aware of only one randomized controlled study to compare HD with PD currently underway in China, the results of which may not be available for some time (8).
Most of the recent observational studies infer that the survival of PD patients equates or even surpasses the survival of HD patients (6,9). However, virtually all observational studies have had methodological limitations in addition to nonrandom assignment of dialysis modality, such as suboptimal adjustment for differential modality switch over time (because PD patients are more likely to switch to HD than HD patients are likely to switch to PD over time), inability to account for time-varying confounding by laboratory values, which are both the results and determinants of dialysis treatment choices, and inappropriate adjustment for the differential longitudinal censorship of transplantation across modalities (8). The latter may be a major challenge in such studies, especially because PD patients are much more likely to receive a kidney transplant during the first 2 years of dialysis therapy.
Inverse probability of treatment-weighted marginal structural model (MSM) is a statistical technique that allows for adjusting for repeatedly measured confounders by creating the inverse probability of treatment weights that accounts for the effect of time-dependent cofounding. With sufficient confounding control (an unverifiable assumption) and in the absence of measurement error, MSM can potentially yield estimates comparable with those estimates in randomized trials by simulating randomization in observational data (10). We examined the comparative effect of PD versus HD with mortality during the first 2 years of dialysis treatment in a large nationally representative cohort of incident dialysis patients. We used MSM to account for transplant censorship, modality changes over time, and time-varying laboratory measures during each calendar quarter. We hypothesized that a choice of initial dialysis modality and a decision to switch from one modality to another affect survival of incident dialysis patients.
Materials and Methods
Dialysis Patients
We linked the databases from the US Renal Data System (USRDS) and DaVita, Inc., a large provider of dialysis treatment in the United States, using unique identifiers to identify a cohort of incident dialysis patients. Dates of dialysis initiation, death, and transplantation were collected from the USRDS as well as information about comorbidities and employment status at baseline. The DaVita database provided all other information about the patients who received dialysis in DaVita clinics between July 1, 2001 and June 30, 2006. The date of enrollment in a DaVita clinic, dialysis treatment data, and laboratory measurements during the cohort period were also extracted. Patients with a discordance of >90 days between the date of first dialysis initiation from the USRDS and DaVita data were excluded. From the DaVita dataset, we extracted the information about the calendar quarter in which each patient entered the cohort, reached day 90 on dialysis, and patient died or transplanted. Laboratory measurements were extracted and averaged for each calendar quarter. Information about demographic characteristics and insurance at baseline was also obtained.
A total of 59,062 incident dialysis patients were identified in DaVita dialysis clinics during the 5 years (July of 2001 to June of 2006). We restricted the cohort to 23,718 incident dialysis patients, including 22,360 HD and 1,358 PD patients, with no missing data on dialysis modalities and key predictors who initiated dialysis between July 1, 2001 and June 30, 2004; therefore, every patient could potentially stay in the cohort for at least eight calendar quarters (2 years) with all laboratory data (i.e., until June 30, 2006).
Modality Switch and Informative Censorship
Using USRDS records, we determined the duration of dialysis treatment and status for each patient (death, transplant, and changes in dialysis modality) during each of the 20 calendar quarters, even if they transferred to a non-DaVita dialysis center. Hence, we assumed no loss to follow-up, and the only informative censoring event considered was kidney transplantation. Patients were censored on day of death or transplantation. For censored patients, we added days from the concluding quarter to its preceding quarter and counted any event that occurred (death or transplantation) as occurring in the latter quarter if the patient contributed less than 45 days to the last calendar quarter. This calculation was done to make cohort quarters more commensurate to quarters used in the conventional Cox analysis, where person-time and not calendar time was used.
Laboratory Measures
Blood samples were drawn using uniform techniques in all dialysis clinics and transported to DaVita Laboratory in Deland, FL within 24 hours.
Statistical Methods
We created Kaplan–Meier survival curves to compare the survival between PD and HD patients after adjusting for age, sex, race, and diabetes. We also examined survival stratifying separately on diabetes and heart failure status and adjusting for age, sex, and race. Additionally, we compared survival between PD and HD patients, separating those patients who never changed the initial modality from the patients who had at least one modality change during the cohort time.
The MSM using the inverse probability weights (IPWs) was used to determine the effects of dialysis modality on mortality during the first 2 years while accounting for the history of dialysis modalities during this time period as well as the time spent under each modality (11,12). IPWs were estimated by combining the inverse probability of treatment weights (IPTWs) and inverse probability of censoring weights (IPCWs). The IPTW (or IPCW) was computed from the ratio of the estimated probabilities of treatment (or censorship) using baseline covariates (numerator) to the estimated probabilities of treatment (or censorship) using baseline and time-dependent covariates (denominator). Two logistic regressions were fitted to estimate the numerator and denominator of the IPTW. We used baseline covariates to predict the probability of dialysis modality at day 90 for the numerator and baseline and time-dependent covariates, which included history of dialysis modality (and laboratory parameters in models where laboratory data were included), to predict modality at any given quarter after day 90 during the first 2 years of dialysis treatment for the denominator. The second set was for the IPCW to account for the informative censoring from receiving a kidney transplant. This set was fitted using two similar logistic models, also including dialysis modality (in both numerator and denominator) and modality at the previous quarter (denominator) as predictors of receiving kidney transplantation at any given quarter after reaching day 90 on dialysis.
We created three different models of IPWs using increasing numbers of covariates for estimation. For model 1, the IPTWs were calculated using age at baseline and modality from the prior quarter as the time-dependent predictor. For model 2, the IPTWs were calculated using age, sex, race (non-Hispanic whites versus others), and diabetes at baseline; for model 3, the same was used with addition of baseline and time-dependent measurements for serum levels of albumin and hemoglobin, because they were considered important predictors that may be associated with choice of dialysis modality as well as mortality (13,14). IPCWs were calculated similarly, but person-time starting from the time of dialysis initiation and dialysis modality for each quarter were added to the models as important predictors of transplantation. We then created stabilized IPWs by combining the two weights as described elsewhere (12). Each stabilized IPW had a mean of around one.
We used three levels of adjustment for all models. (1) We used IPW-only adjusted models. (2) To overcome possible residual confounding from the variables already included in the IPWs, we further adjusted for baseline variables used to estimate IPWs. (3) We also added additional variables to the third level of adjustment, such as marital status, employment, baseline comorbidities (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cancer, hypertension, ability to ambulate, congestive heart failure, and atherosclerotic heart disease), and baseline serum levels of ferritin, calcium, and phosphorus. These additional predictors, although important predictors of mortality, were not good predictors of dialysis modality or transplantation.
We performed additional analyses, where we fitted conventional Cox proportional hazard models to compare the mortality patterns with the MSMs. All descriptive and multivariate statistics were performed using SAS, version 9.3 (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC).
Results
Table 1 shows patients’ characteristics on dialysis initiation across modality status on day 90, modality switch over time, and transplantation status. Additionally, the detailed characteristics of the total HD and PD cohorts at baseline and patients who switched modality are shown in Supplemental Table 1. Of 23,718 incident dialysis patients, 1629 patients were transplanted during their first 2 years of dialysis, including 1385 HD and 244 PD patients, resulting in transplant rates of 6% and 18%, respectively. Among the patients undergoing HD at day 90, 6% switched modality at least one time during 2 years, whereas the modality switch rate was 57% among PD patients. Patients who never changed modality and did not undergo transplant were older, more likely to be diabetic, or more likely to have atherosclerotic heart disease or heart failure. Patients who changed modality but received no transplant were similar in their characteristics, although they were somewhat younger and had lower percentages of diabetes, atherosclerosis, or heart failure. Patients who were transplanted, regardless of modality changes, were much younger and had less comorbidity.
Table 1.
Characteristics of 23,718 incident dialysis patients according to modality status at day 90, modality switches over the first 2 years, and transplant status (Trp) in DaVita dialysis clinics from July 1, 2001 to June 30, 2006
| Modality at Day 90 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incident HD Patients (n=22,360) | Incident PD Patients (n=1,358) | |||||||||
| Always HD | Switched HD to PD | P Value | Always PD | Switched PD to HD | P Value | |||||
| Not Trp | Trp | Not Trp | Trp | Not Trp | Trp | Not Trp | Trp | |||
| N | 19,884 | 1292 | 1091 | 93 | 419 | 167 | 695 | 77 | ||
| Age (yr) | 64±15 | 48±14 | 55±15 | 44±15 | <0.001 | 62±15 | 47±13 | 57±15 | 48±15 | <0.001 |
| Sex (women) | 46% | 38% | 43% | 40% | <0.001 | 48% | 47% | 47% | 43% | 0.87 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 64% | 43% | 52% | 39% | <0.001 | 59% | 36% | 57% | 48% | <0.001 |
| Race | ||||||||||
| Non-Hispanic white | 43% | 51% | 51% | 52% | <0.001 | 56% | 64% | 47% | 56% | 0.04 |
| Black | 30% | 19% | 25% | 20% | <0.001 | 16% | 16% | 23% | 22% | 0.03 |
| Hispanic | 18% | 18% | 13% | 14% | 0.003 | 13% | 8.4% | 18% | 17% | 0.009 |
| Asian | 3% | 5% | 5% | 11% | <0.001 | 7% | 6% | 5% | 5% | 0.68 |
| Employment status | ||||||||||
| Retired | 56% | 25% | 43% | 24% | <0.001 | 56% | 13% | 43% | 29% | <0.001 |
| Employed | 14% | 49% | 30% | 43% | <0.001 | 26% | 72% | 36% | 47% | <0.001 |
| Unemployed | 29% | 26% | 28% | 33% | 0.02 | 18% | 14% | 20% | 25% | 0.21 |
| Primary insurance | ||||||||||
| Medicare | 63% | 34% | 53% | 45% | <0.001 | 46% | 22% | 51% | 39% | <0.001 |
| Medicaid | 8% | 4% | 5% | 7% | <0.001 | 3% | 1% | 5% | 1% | 0.06 |
| Other | 30% | 62% | 42% | 49% | <0.001 | 52% | 77% | 44% | 61% | <0.001 |
| Marital status | ||||||||||
| Married | 47% | 60% | 53% | 59% | <0.001 | 66% | 72% | 61% | 59% | 0.16 |
| Divorced | 8% | 7% | 7% | 6% | 0.94 | 7% | 6% | 7% | 4% | 0.86 |
| Single | 27% | 30% | 28% | 29% | 0.21 | 15% | 20% | 22% | 27% | 0.09 |
| Widowed | 18% | 3% | 11% | 4% | <0.001 | 11% | 2% | 10% | 9% | 0.05 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||||||
| AIDS | 0.6% | 0.1% | 0.5% | 0.1% | 0.43 | 0.8% | 0.1% | 0.8% | 0.1% | 0.75 |
| Atherosclerotic heart | 24% | 9% | 21% | 16% | <0.001 | 23% | 4% | 17% | 5% | 0.40 |
| Cancer | 4% | 2% | 4.5% | 3% | <0.001 | 4% | 2% | 4% | 1% | 0.07 |
| Heart failure | 31% | 11.6% | 23% | 7.5% | <0.001 | 21% | 4.8% | 17% | 12% | <0.001 |
| COPD | 7% | 2% | 5% | 1% | <0.001 | 4% | 0.6% | 4% | 1% | 0.12 |
| Cerebral-vascular disease | 8% | 2% | 5% | 2% | <0.001 | 7% | 3% | 6% | 7% | 0.34 |
| HIV | 0.9% | 0.1% | 1.8% | 0.1% | 0.01 | 2% | 0.1% | 0.3% | 0.1% | 0.12 |
| Hypertension | 79% | 79% | 79% | 76% | 0.62 | 80% | 75% | 84% | 79% | 0.06 |
| Nonambulatory | 4% | 0.4% | 2% | 0.1% | <0.001 | 2% | 0.1% | 0.4% | 1% | 0.08 |
| Other heart diseases | 5% | 2% | 4% | 0.1% | <0.001 | 6% | 2% | 3% | 1% | 0.06 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 13% | 4.5% | 9.3% | 3% | <0.001 | 12% | 4% | 10.% | 3% | 0.006 |
| Smoker | 5% | 4% | 5% | 2% | 0.24 | 4% | 3% | 6% | 7% | 0.31 |
| BMI (kg/m2)a | 25.4 (22.0–29.9) | 25.4 (22.5–29.5) | 26.3 (22.7–30.9) | 25.1 (21.5–28.3) | 0.01 | 25.5 (23.3–27.8) | 27.8 (21.7–28.3) | 26.0 (22.3–30.2) | 26.1 (21.4–34.1) | 0.87 |
| Laboratory data | ||||||||||
| nPCR (g/kg per day) | 0.93±0.25 | 0.98±0.2 | 0.91±0.3 | 0.93±0.2 | <0.001 | 0.80±0.3 | 0.88±0.2 | 0.91±0.3 | 0.74±0.3 | 0.14 |
| Albumin (g/dl) | 3.6±0.5 | 3.8±0.4 | 3.7±0.5 | 3.9±0.4 | <0.001 | 3.4±0.5 | 3.8±0.4 | 3.5±0.6 | 3.7±0.5 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 6.8±2.7 | 9.1±3.0 | 7.4±3.2 | 9.1±3.7 | <0.001 | 6.5±2.6 | 7.7±2.7 | 7.1±3.0 | 8.0±2.9 | <0.001 |
| Ferritin (ng/ml)a | 246 (126–458) | 195 (93–354) | 230 (114–453) | 196 (86–374) | <0.001 | 229 (132–381) | 249 (141–464) | 291 (157–473) | 278 (126–436) | 0.008 |
| TIBC (mg/dl) | 213±46 | 227±43 | 224±48 | 236±40 | <0.001 | 243±52 | 257±47 | 247±49 | 250±49 | 0.02 |
| Calcium (mg/dl) | 9.1±0.7 | 9.3±0.7 | 9.2±0.7 | 9.3±0.6 | <0.001 | 9.1±0.7 | 9.3±0.7 | 9.1±0.7 | 9.5±0.8 | <0.001 |
| Phosphorous (mg/dl) | 5.4±1.4 | 5.9±1.3 | 5.5±1.5 | 5.6±1.2 | <0.001 | 4.9±1.2 | 5.1±1.2 | 5.0±1.3 | 5.3±1.2 | 0.04 |
| Intact PTH (pg/ml)a | 224 (128–377) | 238 (134–405) | 231 (121–399) | 280 (119–445) | 0.02 | 182 (86–414) | 128 (45–278) | 257 (75–386) | 134 (62–255) | 0.01 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dl) | 12.1±1.4 | 12.4±1.4 | 12.2±1.5 | 12.3±1.2 | <0.001 | 12.3±1.5 | 12.6±1.4 | 12.3±1.4 | 12.6±1.4 | 0.04 |
| White blood count (×103/μl) | 7.7±2.5 | 7.3±2.1 | 7.7±2.5 | 7.1±2.0 | <0.001 | 7.9±3.5 | 7.2±2.1 | 7.4±2.3 | 7.6±2.3 | 0.03 |
| Lymphocytes (% white blood count) | 20±7.6 | 22±7.6 | 20±7.5 | 21±7.0 | <0.001 | 19±7.3 | 20±7.4 | 20±7.3 | 23±7.7 | 0.003 |
COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; BMI, body mass index; nPCR, normalized protein catabolic rate; TIBC, total iron-binding capacity; PTH, parathyroid hormone.
Median and 25th and 75th percentiles presented instead of mean, because the predictor was not normally distributed.
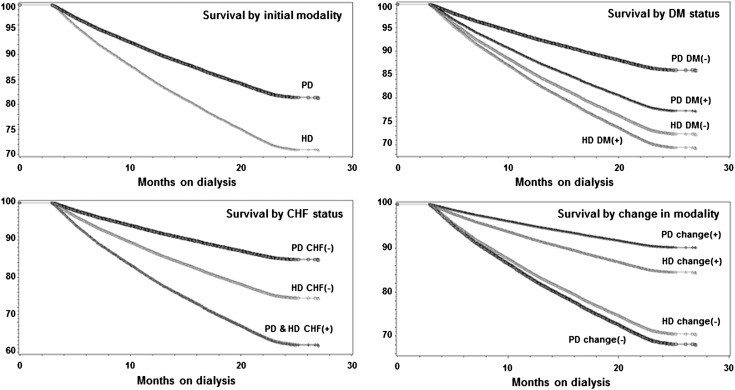
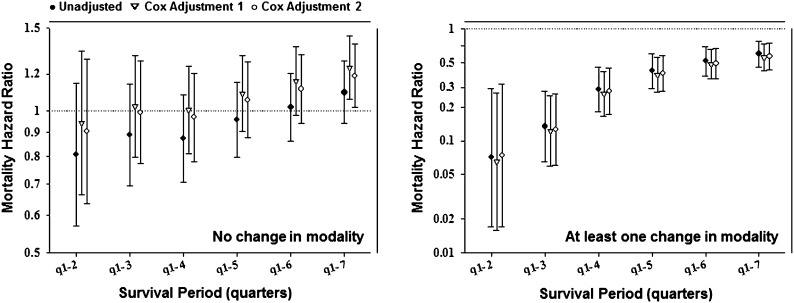
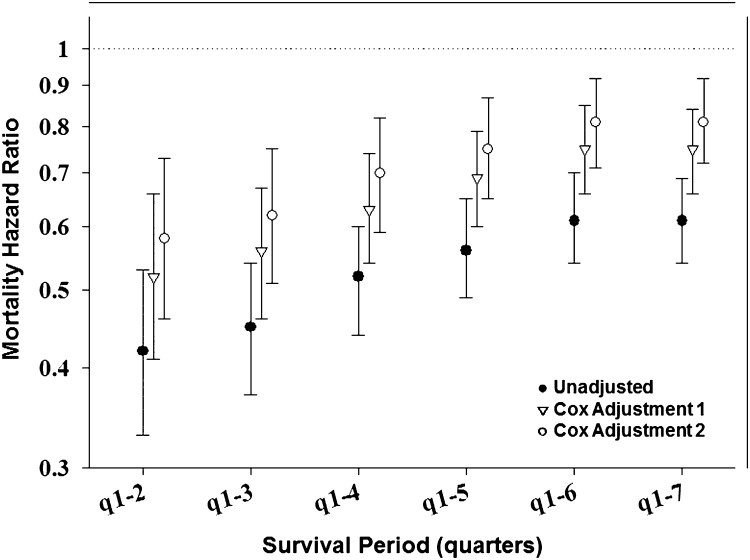
Case mix-adjusted Kaplan–Meier survival analyses are shown in Figure 1. PD patients had better survival than HD patients. Examining patients with and without modality changes, the former had better survival than the latter. Nevertheless, HD patients without a modality change had slightly better survival than their PD counterparts. Conventional (non-MSM) survival analyses to estimate death hazard ratios of PD versus HD modality are shown in Figures 2 and 3 and Supplemental Table 2. Non-MSM Cox proportional hazards models indicated that, despite lower death risk for PD patients during the first several months, this advantage seemed to mitigate over time, and therefore, among patients without any modality switches, no survival advantage was noticeable by the completion of the 2-year period.
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves adjusted for age, sex, race, and diabetes examining survival among peritoneal dialysis (PD) and hemodialysis (HD) patients (modality is defined on day 90) for incident dialysis patients initiating dialysis from July of 2001 to June of 2004 (n=23,718).
Figure 2.
Associations between dialysis modality (PD versus HD) and mortality among incident dialysis patients who never changed modalities (n=21,762; left) and patients with at least one modality change over 2 years (n=1956; right). Cox adjustment 1, adjusted for inverse probability of treatment weight (IPTW) predictors only: age, sex, diabetes mellitus (DM), and race; Cox adjustment 2, fully adjusted model adjusted for IPTW predictors and additional confounders: marital status, employment, baseline comorbidities (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD], cancer, hypertension, ability to ambulate, heart failure, and atherosclerotic heart disease), and baseline serum levels of ferritin, calcium, phosphorus, and normalized protein catabolic rate (nPCR).
Figure 3.
Mortality hazard ratios (HRs) for dialysis modality (PD versus HD) in incident dialysis patients using Cox models (n=23,718) (Supplemental Table 2). Cox adjustment 1, adjusted for IPTW predictors only: age, sex, DM, and race; Cox adjustment 2, fully adjusted model adjusted for IPTW predictors and additional confounders: marital status, employment, baseline comorbidities (COPD, cancer, hypertension, ability to ambulate, heart failure, and atherosclerotic heart disease), and baseline serum levels of ferritin, calcium, phosphorus, and nPCR.
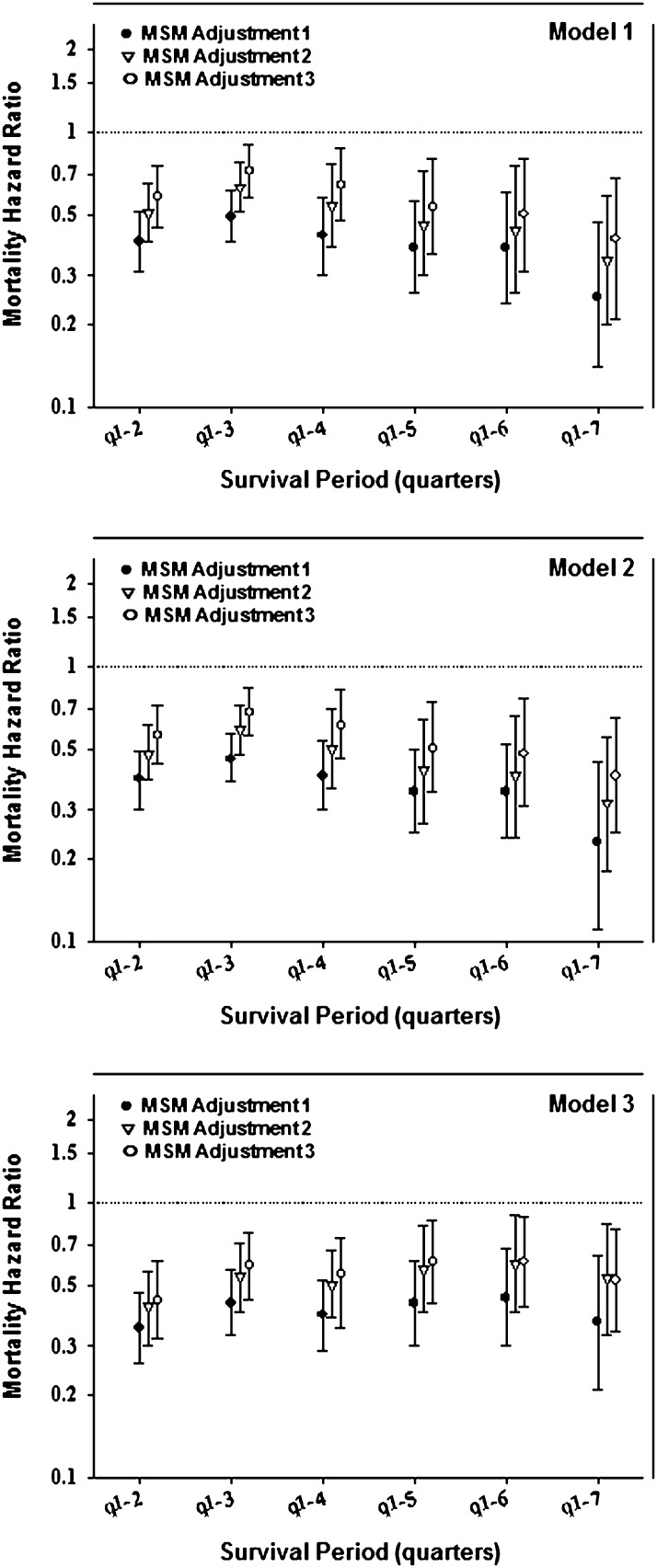
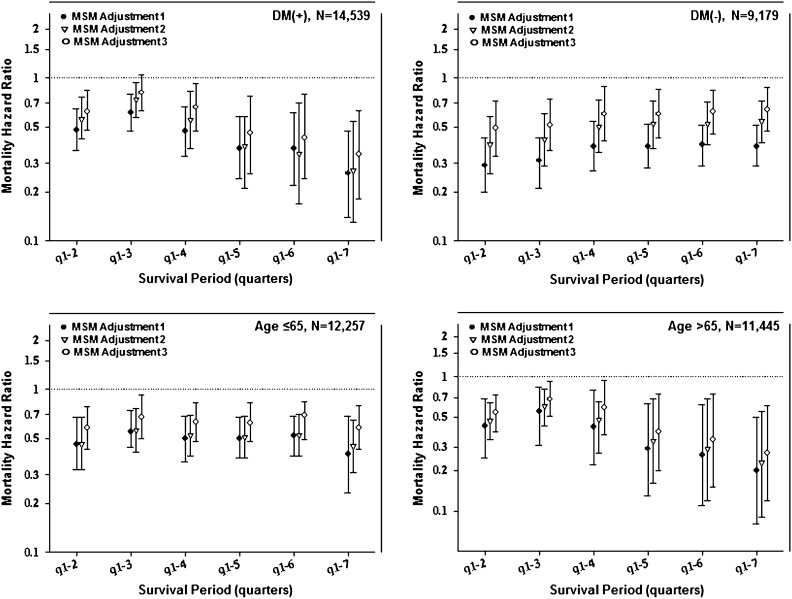
Figure 4 and Supplemental Table 3 show estimates of death hazard ratios for PD modality (with HD as reference) in the first 2 years of dialysis treatment using MSM and taking into account changes in modality over time as well as the differential censorship. In all models, PD patients showed a greater survival during the first 2 years. A difference between the conventional and MSM analyses was the persistence of the survival advantage of PD over the entire 2-year period, with no clear change in estimates over time. In models adjusted for time-varying laboratory measures, PD patients had 48% lower mortality (i.e., a death hazard ratio of 0.52 [95% confidence limit (CL)=0.34–0.80] in model 3). Figure 5 and Supplemental Table 4 show MSM-estimated death hazard ratios in the cohort of incident dialysis patients stratified by diabetes status and age (<65 versus ≥65 years). The IPWs were calculated using the same baseline and time-dependent predictors used for model 2. As observed in the MSM analyses of the entire cohort, PD patients had lower risk of death observed consistently for up to 24 months after dialysis initiation. We also examined the differences between Cox and MSM with different weights. As shown in Supplemental Table 2, the models with the inverse probability of treatment weights differed the most from the conventional Cox models, whereas the results from the model that only adjusted for IPCW censoring were virtually identical to the conventional Cox models. This result indicates that adjusting for time-dependent confounding was the main driver of the differences between MSM and Cox models compared with adjustment for transplantation censoring.
Figure 4.
Mortality HRs for dialysis modality (PD versus HD) in 23,718 incident dialysis patients using a marginal structural model (MSM) taking into account changes in dialysis modality and transplant censorship in the first 2 years (Supplemental Table 3). Model 1, inverse probability weight (IPW): age, baseline modality, and time-dependent modality (TD; stabilized IPW mean=1.06); model 2, IPW: age, sex, race, DM, baseline modality, and TD (stabilized IPW mean=1.06); model 3, IPW: age, sex, race, DM, baseline modality (Alb and Hgb), and TD modality (Alb and Hgb; stabilized IPW mean=1.29); MSM adjustment 1, IPW-adjusted (IPWs were calculated using different sets of variables); MSM adjustment 2, IPW + adding the same variables used to calculate IPWs to control for residual confounding; MSM adjustment 3, same as MSM adjustment 2 + additional confounders: marital status, employment, baseline comorbidities (COPD, cancer, hypertension, ability to ambulate, heart failure, and atherosclerotic heart disease), and baseline serum levels of ferritin, calcium, phosphorus, and nPCR.
Figure 5.
Mortality HRs for dialysis modality (PD versus HD) in 23,718 incident dialysis patients using an MSM taking into account changes in dialysis modality and transplant censorship in the first 2 years stratifying on diabetes status (P value for the interaction=0.07) and age (P value for the interaction=0.26) (Supplemental Table 4). Model 2 IPTWs were used for all stratified models. MSM adjustment 1, IPW-adjusted (IPWs were calculated using different sets of variables); MSM adjustment 2, IPW + adding the same variables used to calculate IPWs to control for residual confounding; MSM adjustment 3, same as MSM adjustment 2 + additional confounders: marital status, employment, baseline comorbidities (COPD, cancer, hypertension, ability to ambulate heart failure, and atherosclerotic heart disease), and baseline serum levels of ferritin, calcium, phosphorus, and nPCR.
Discussion
Examining a cohort of incident dialysis patients, including 22,360 HD and 1358 PD patients, on day 90 of dialysis treatment, we found that incident PD patients were nine times more likely to switch dialysis modality and three times more likely to receive a kidney transplant. Comparing two modalities over the first 2 years of dialysis treatment, we found that, in MSM, PD patients had a persistently lower death risk after adjustment for known confounders, including dialysis modality switch or transplant censorship. Hence, a 48% lower mortality was observed by the end of second year. These findings may have important clinical and policy implications given the high mortality of HD during the first 2 years and lower costs of PD.
Our study is one of a few using MSMs. The reason for using these models was to try to validly handle time-varying confounding and selection bias from longitudinal censoring (15). MSM uses IPWs to control for time-dependent confounders rather than including them in the model directly (10,16). Inverse probability weighting rebalances the compared populations to create similar distributions of the covariates in the treatment model at each time point and thus, reduces or eliminates time-varying confounding by these covariates (17). The study by Mehrotra et al. (18) used MSM techniques, but laboratory measurements over time were not available, because the data were solely based on the USRDS dataset; however, our current study used detailed laboratory data from the DaVita cohort. Hence, we accounted for time-varying laboratory measures at several levels in model 3. Because MSMs can produce causal estimates, the results of MSM analyses can be comparable with randomized trials (10). Although the Netherlands trial was stopped because of insufficient enrolment (7), the results obtained from 38 patients indicated that PD patients had better overall 5-year survival. Death hazard ratio for HD versus PD patients was 3.60 (95% CL=0.80–15.40) (7). Although the study did not have enough power to reach meaningful conclusions, the results were consistent with our findings based on MSM.
Our findings indicate that PD patients had significantly and persistently lower mortality risk during the entire first 2 years after dialysis initiation, despite differential censorship of transplantation and higher likelihood of modality switch among PD patients. A study by Quinn et al. (19) suggested that the lower death risk seen in PD patients was potentially a result of sicker patients without prior nephrologist care being more likely to initiate HD, which then could account for the higher mortality among HD patients during early dialysis. Although we did not have reliable data on predialysis nephrology care, our results of MSM did not show a significantly distinct pattern of early survival advantage in the first 6–12 months.
Our findings are partially similar and partially in contrast to a study by van der Wal et al. (14), which also used MSM to investigate dialysis modality differentials in Europe but did not account for modality changes over time. The study (14) found that, although PD patients did better during the first 3 months of dialysis treatment, their survival advantage decreased thereafter, and HD patients had better survival during the entire second year. We found that PD patients tend to change dialysis modality more often in the United States. The absolute number of patients undergoing PD and HD who changed dialysis modalities in our cohort is remarkably similar. However, because the total number of patients undergoing PD at any point in time is much smaller, this number represents a substantially larger proportion of PD than HD patients. Hence, censoring patients at the time of first modality change could potentially result in a much greater effect on PD outcomes compared with HD outcomes. Similar concerns are valid for the much higher rate of transplantation among PD patients, which potentially depletes the PD cohort of its healthiest patients who would have otherwise survived much longer than the remainder of the cohort. Because patients who changed modalities or underwent transplantation had significantly better survival compared with those patients who did not, then naturally no advantage of PD could be detected if patients were censored at the time of switch or transplantation. Indeed, we found that, in non-MSM survival analyses, PD survival was significantly less or even reversed by the end of 2 years (Figures 1–3), whereas in MSM analyses, which account for time-varying confounders, a persistent PD survival was evident (Figures 4 and 5). Comparing the results from MSMs with the conventional Cox models, we observed that, although the CLs largely overlapped, the survival differential of PD increased slightly with vintage in MSMs but was not evident in conventional analysis. This finding is not surprising given the ability of MSM to handle time-varying confounding and censoring. An article by Suarez et al. (17) examined the publications in which MSM and conventional analyses were used and found that, in 40% of the analyses, the estimates differed by at least 40%; in 11% of the analyses, the opposite results were reported when MSM versus conventional models were compared.
Our findings also indicate that changes in modality during the first 2 years of dialysis may affect the survival patterns over time. The reasons for better survival of patients who switch modalities, which was also shown in the work by Van Biesen et al. (20) earlier, are not clearly evident. Thus, there is a need to further elucidate the causes determining the outcome of patients who switch dialysis therapies. These causes may be biologic or a result of unmeasured and/or unaccounted bias. Often, a switch from PD to HD relates to the technique failure, whereas problems with vascular access, higher risk of cardiovascular disease, or personal preference are commonly cited when HD patients switch to PD (21,22). In our study, patients with the same transplantation status had similar characteristics regardless of whether they changed an initial modality (Table 1). Therefore, any differences in survival between the two modalities can mostly be attributed to the changes in modality over time. This result may indicate that change of modality may be considered as a practical option if a patient does not show improvement or becomes sicker. It is also consistent with the previous findings that patents who initiate dialysis with PD tend to do better in the first 24 months (23). Our data suggest that it may make sense to recommend that patients receive more information and education about choice of modality before dialysis initiation. As was shown previously, when patients get educated about dialysis modalities, the number of patients who decide to initiate PD increases, and the level of satisfaction also increases with the choice of modality (24,25).
Our study should be qualified by its nonrandomized nature, which is threatened by uncontrolled confounding (especially confounding by indication), measurement errors, and selection bias. We did not examine survival beyond 24 months after dialysis initiation. The strengths of our study include the large cohort of dialysis patients from the entire United States, inclusion of detailed laboratory measures that were processed in a single laboratory center, adjusting time-varying modality changes and transplant censorship using MSM, and detailed comparisons between the conventional models and MSM techniques.
Comparing survival of PD and HD among 23,718 incident dialysis patients during their first 2 years of dialysis treatment in a nationally representative cohort using statistical techniques that account for time-varying confounding and differential censorships, we found that incident PD patients had 48% greater survival. These findings, if further confirmed, may have important implications for the choice of dialysis modality and resource allocations in renal replacement therapy programs. Additional research is needed to examine the effect of modality and its changes on the survival of dialysis patients over a longer time period.
Disclosures
R.M. has received grant support and/or honoraria from DaVita Inc. and Baxter Healthcare. A.R.N. is Chief Medical Officer of DaVita Inc. K.K-Z. was the medical director of DaVita Harbor—University of California at Los Angeles/Medical Foundation, Inc. in Long Beach, CA. Other authors have not declared any conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank DaVita Clinical Research for providing the clinical data, analysis, and review for this research project and advancing the knowledge and practice of kidney care.
This manuscript serves as a main component of the doctoral thesis of L.R.L. for a degree in Epidemiology at University of California at Los Angeles Fielding School of Public Health. Other authors are the members of the thesis committee.
This work was sponsored by National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease Grant R21-DK078012. O.A.A. is supported by a career grant (Veni 916.96.059) awarded by The Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO).
Footnotes
Published online ahead of print. Publication date available at www.cjasn.org.
This article contains supplemental material online at http://cjasn.asnjournals.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.2215/CJN.04810512/-/DCSupplemental.
See related editorial, “Assessments of Causal Effects—Theoretically Sound, Practically Unattainable, and Clinically Not So Relevant,” on pages 520–522.
References
- 1.US Renal Data System : USRDS 2009 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States National Institute of Health Volume 1, Bethesda, MD, National Institute of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease, 2009 [Google Scholar]
- 2.US Renal Data System : USRDS 2009 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States National Institute of Health Volume 2, Bethesda, MD, National Institute of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease, 2009 [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nesrallah G, Mendelssohn DC: Modality options for renal replacement therapy: The integrated care concept revisited. Hemodial Int 10: 143–151, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.US Renal Data System : USRDS 2011 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States, Bethesda, MD, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2011 [Google Scholar]
- 5.Burkart J: The future of peritoneal dialysis in the United States: Optimizing its use. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4[Suppl 1]: S125–S131, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jiwakanon S, Chiu YW, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Mehrotra R: Peritoneal dialysis: An underutilized modality. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 19: 573–577, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Korevaar JC, Feith GW, Dekker FW, van Manen JG, Boeschoten EW, Bossuyt PM, Krediet RT, NECOSAD Study Group : Effect of starting with hemodialysis compared with peritoneal dialysis in patients new on dialysis treatment: A randomized controlled trial. Kidney Int 64: 2222–2228, 2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chiu YW, Jiwakanon S, Lukowsky L, Duong U, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Mehrotra R: An update on the comparisons of mortality outcomes of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients. Semin Nephrol 31: 152–158, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mehrotra R: Choice of dialysis modality. Kidney Int 80: 909–911, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Robins JM, Hernán MA, Brumback B: Marginal structural models and causal inference in epidemiology. Epidemiology 11: 550–560, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cole SR, Hernán MA: Constructing inverse probability weights for marginal structural models. Am J Epidemiol 168: 656–664, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hernán MA, Brumback B, Robins JM: Marginal structural models to estimate the causal effect of zidovudine on the survival of HIV-positive men. Epidemiology 11: 561–570, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Brunelli SM, Joffe MM, Israni RK, Yang W, Fishbane S, Berns JS, Feldman HI: History-adjusted marginal structural analysis of the association between hemoglobin variability and mortality among chronic hemodialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3: 777–782, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.van der Wal WM, Noordzij M, Dekker FW, Boeschoten EW, Krediet RT, Korevaar JC, Geskus RB: Comparing mortality in renal patients on hemodialysis versus peritoneal dialysis using a marginal structural model. Int J Biostat 6: Article 2, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Greenland S, Robins JM: Identifiability, exchangeability and confounding revisited. Epidemiol Perspect Innov 6: 4, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.VanderWeele TJ: Marginal structural models for the estimation of direct and indirect effects. Epidemiology 20: 18–26, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Suarez D, Borràs R, Basagaña X: Differences between marginal structural models and conventional models in their exposure effect estimates: A systematic review. Epidemiology 22: 586–588, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mehrotra R, Chiu YW, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Bargman J, Vonesh E: Similar outcomes with hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in patients with end-stage renal disease. Arch Intern Med 171: 110–118, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Quinn RR, Hux JE, Oliver MJ, Austin PC, Tonelli M, Laupacis A: Selection bias explains apparent differential mortality between dialysis modalities. J Am Soc Nephrol 22: 1534–1542, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Van Biesen W, Vanholder R, Lameire N: The role of peritoneal dialysis as the first-line renal replacement modality. Perit Dial Int 20: 375–383, 2000 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liberek T, Renke M, Skonieczny B, Kotewicz K, Kowalewska J, Chmielewski M, Kot J, Lichodziejewska-Niemierko M, Rutkowski B: Therapy outcome in peritoneal dialysis patients transferred from haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24: 2889–2894, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Covic A, Bammens B, Lobbedez T, Segall L, Heimbürger O, van Biesen W, Fouque D, Vanholder R: Educating end-stage renal disease patients on dialysis modality selection: Clinical advice from the European Renal Best Practice (ERBP) Advisory Board. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25: 1757–1759, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sinnakirouchenan R, Holley JL: Peritoneal dialysis versus hemodialysis: Risks, benefits, and access issues. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 18: 428–432, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lameire N, Van Biesen W: Epidemiology of peritoneal dialysis: A story of believers and nonbelievers. Nat Rev Nephrol 6: 75–82, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.van Biesen W, Veys N, Lameire N, Vanholder R: Why less success of the peritoneal dialysis programmes in Europe? Nephrol Dial Transplant 23: 1478–1481, 2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]