Abstract
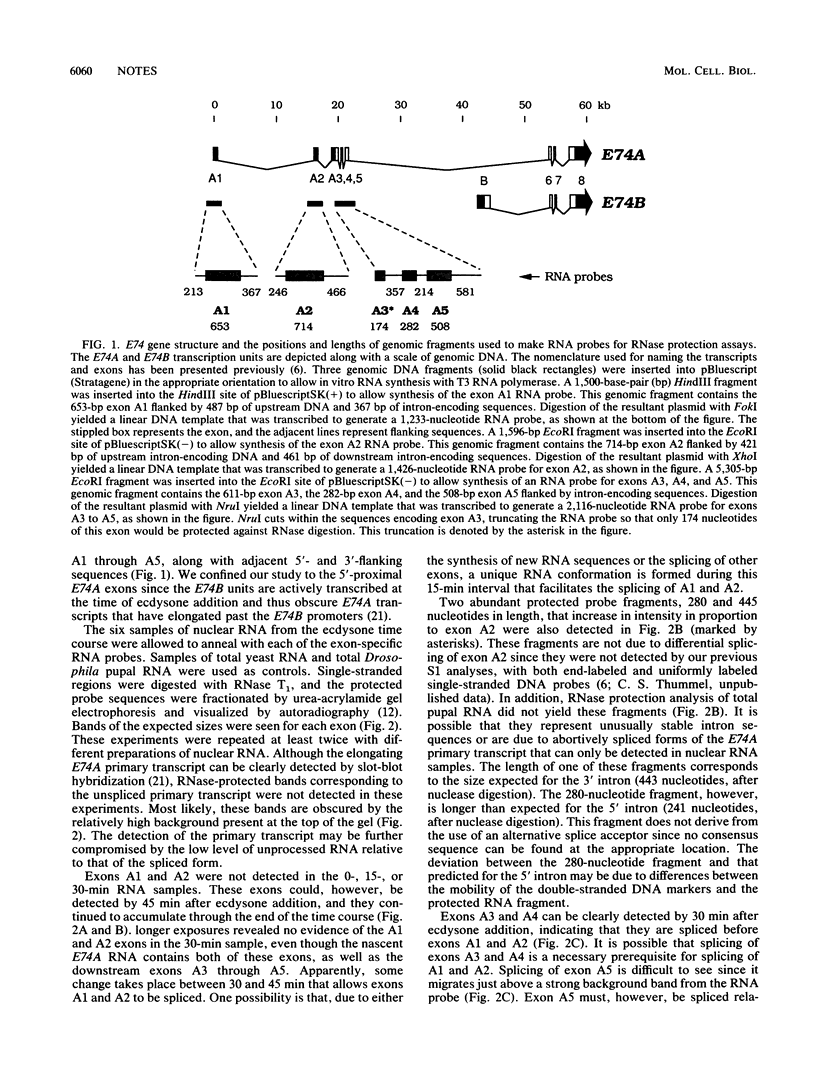
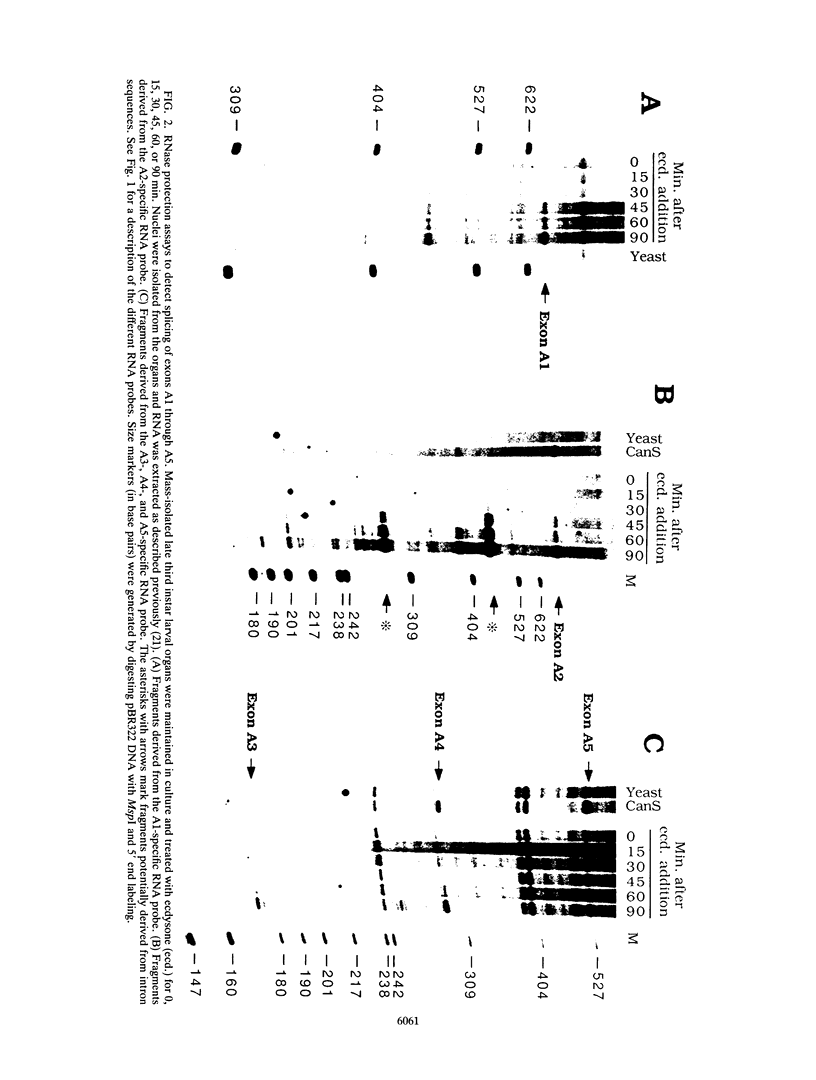
The E74 gene is one of a small set of early genes induced by the steroid hormone ecdysone at the onset of metamorphosis in the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster. This complex gene directs the synthesis of a 60-kilobase (kb) primary transcript that is spliced to form the 6-kb E74A mRNA. In a previous study, we found that ecdysone directly activates the E74A promoter and determined that RNA polymerase II transcribes this gene at a rate of approximately 1.1 kb/min. This elongation rate accounts for most of the 1-hour delay seen between the addition of ecdysone and the appearance of cytoplasmic E74A mRNA (C. S. Thummel, K. C. Burtis, and D. S. Hogness, Cell 61:101-111, 1990). We show here that nascent E74A transcripts are spliced, and we propose a model for the order of that splicing. This study provides, for the first time, direct biochemical evidence for splicing of a low-abundance cellular RNA before transcription termination and polyadenylation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adami G., Nevins J. R. Splice site selection dominates over poly(A) site choice in RNA production from complex adenovirus transcription units. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2107–2116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amara S. G., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide transcription unit: tissue-specific expression involves selective use of alternative polyadenylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2151–2160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M., Sharp P. A. Structure of late adenovirus 2 heterogeneous nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 25;129(4):547–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Osheim Y. N. Splice site selection, rate of splicing, and alternative splicing on nascent transcripts. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):754–765. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner D., Leder P. Role of an RNA cleavage/poly(A) addition site in the production of membrane-bound and secreted IgM mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8658–8662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeson R. B., Hedjran F., Yeakley J. M., Guise J. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Alternative production of calcitonin and CGRP mRNA is regulated at the calcitonin-specific splice acceptor. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):76–80. doi: 10.1038/341076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford J. P., Hsu M. T. Transcription pattern of in vivo-labeled late simian virus 40 RNA: equimolar transcription beyond the mRNA 3' terminus. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):795–801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.795-801.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Guise J., Tucker P. W., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site choice rather than splice site choice governs the regulated production of IgM heavy-chain RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2439–2443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohavong P., Gattoni R., LeMoullec J. M., Jacob M., Stévenin J. The orderly splicing of the first three leaders of the adenovirus-2 major late transcript. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1215–1229. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Splice commitment dictates neuron-specific alternative RNA processing in calcitonin/CGRP gene expression. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt N., Briggs D., Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. Definition of an efficient synthetic poly(A) site. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1019–1025. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariman E. C., van Beek-Reinders R. J., van Venrooij W. J. Alternative splicing pathways exist in the formation of adenoviral late messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 15;163(2):239–256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Steps in the processing of Ad2 mRNA: poly(A)+ nuclear sequences are conserved and poly(A) addition precedes splicing. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittler A., Gallinaro H., Jacob M. In vivo splicing of the premRNAs from early region 3 of adenovirus-2: the products of cleavage at the 5' splice site of the common intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1187–1207. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Burtis K. C., Hogness D. S. Spatial and temporal patterns of E74 transcription during Drosophila development. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Blanchard J. M., Ginsberg H., Darnell J. E., Jr Order of polyadenylic acid addition and splicing events in early adenovirus mRNA formation. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.286-291.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeevi M., Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Nuclear RNA is spliced in the absence of poly(A) addition. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]