Abstract
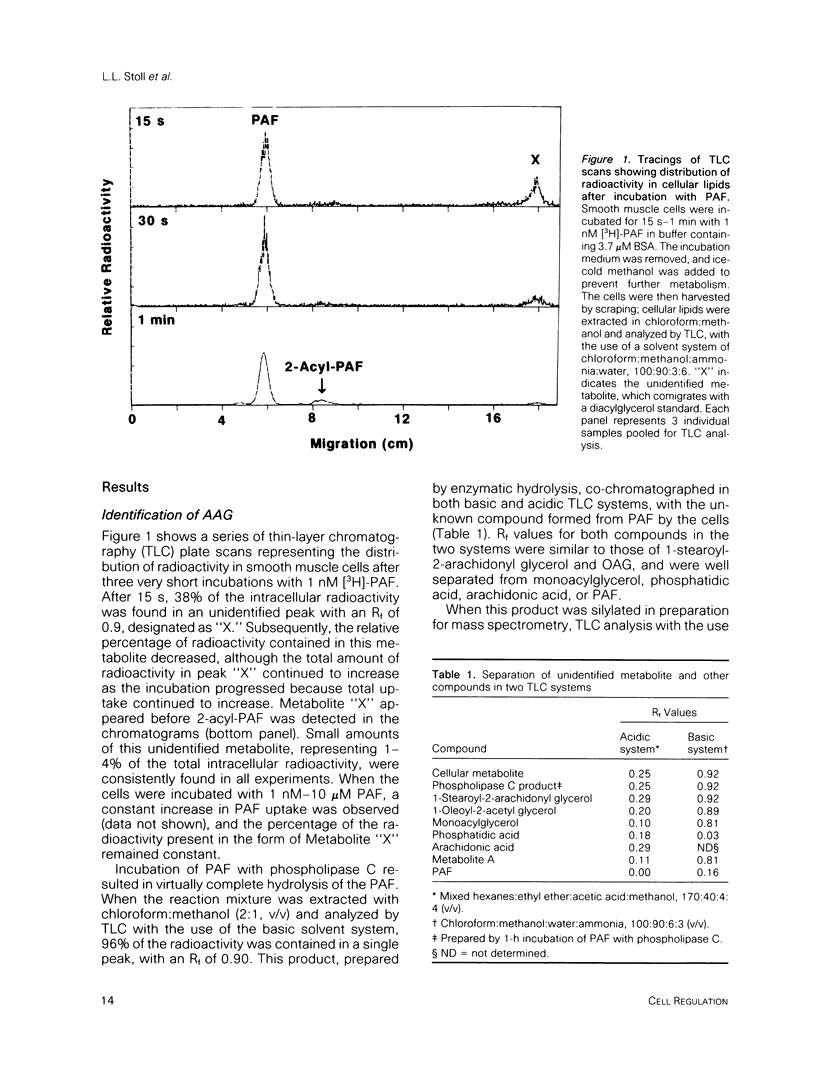
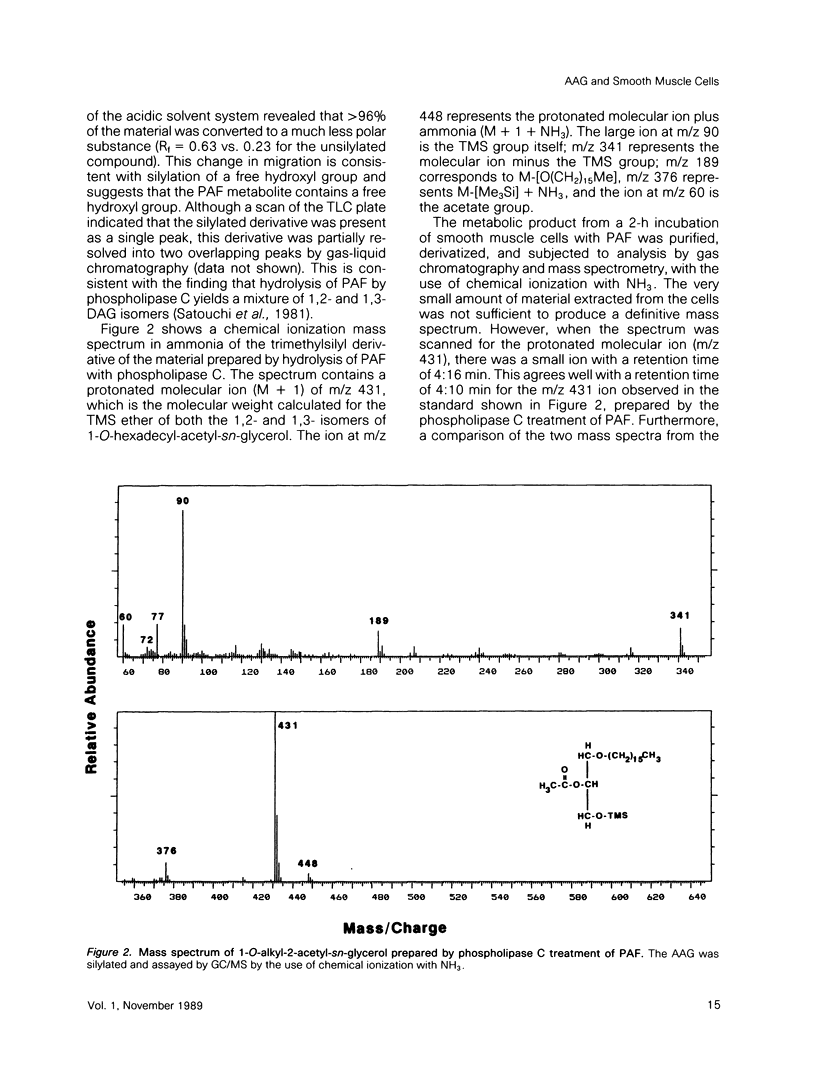
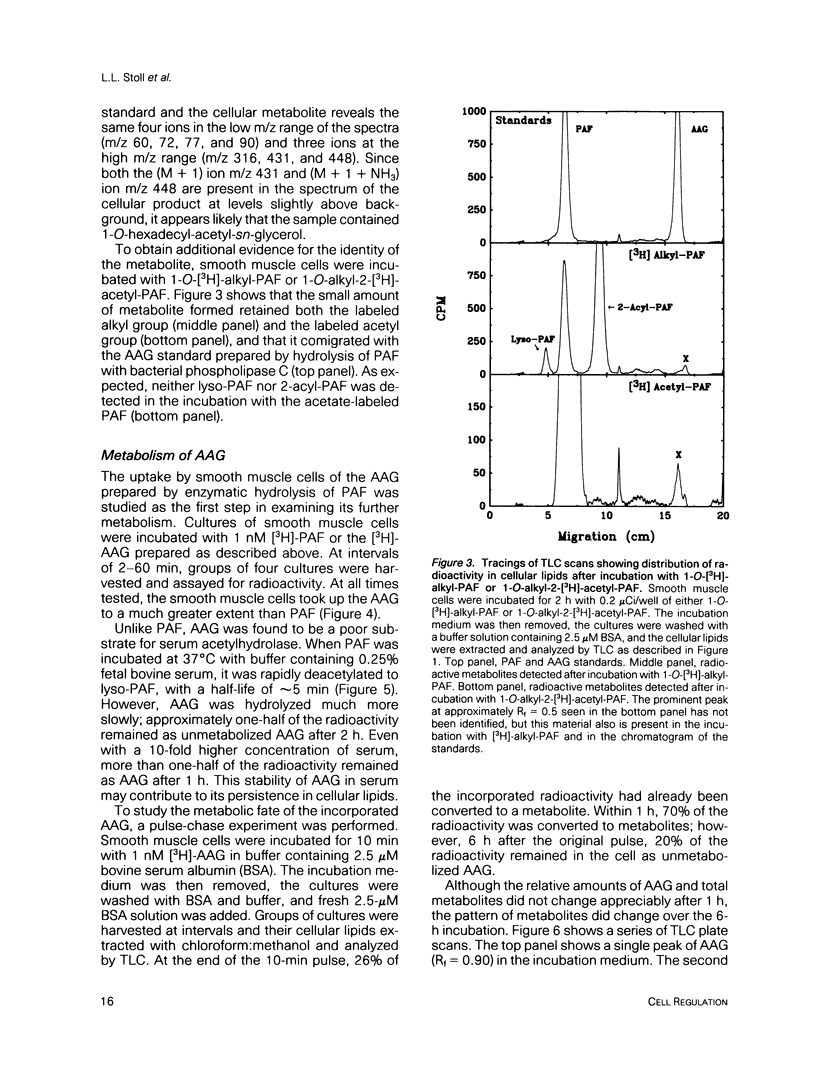
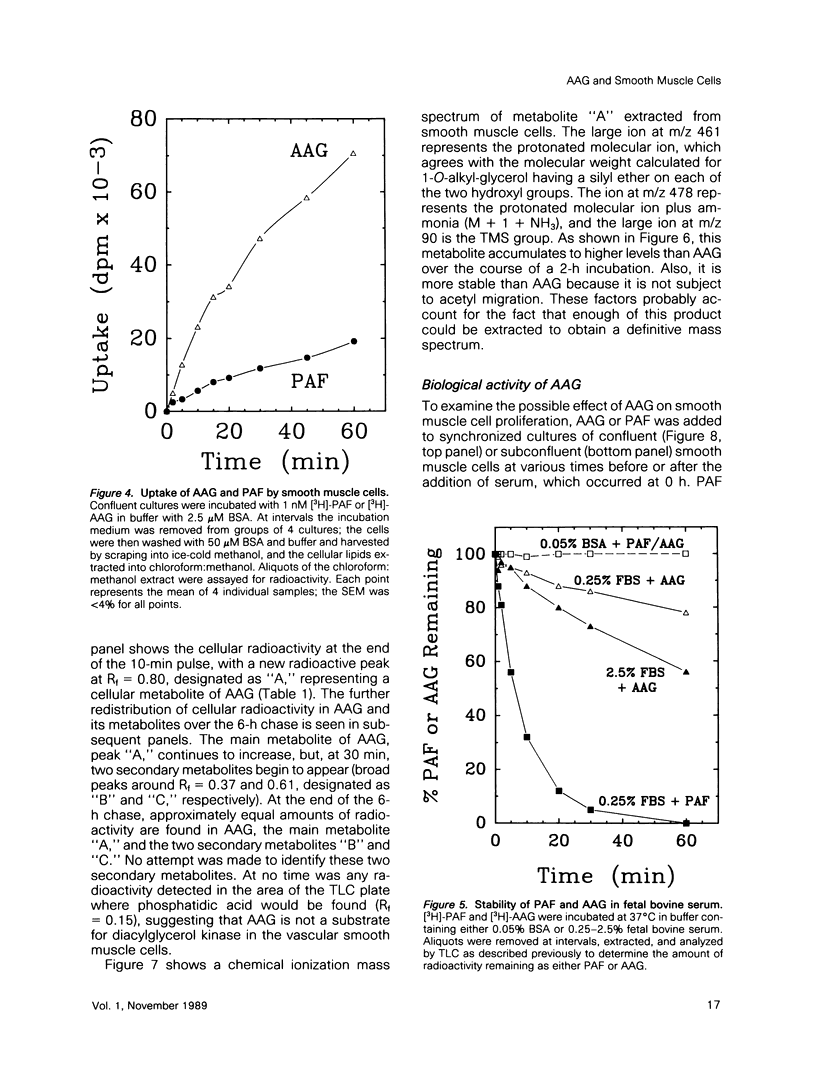
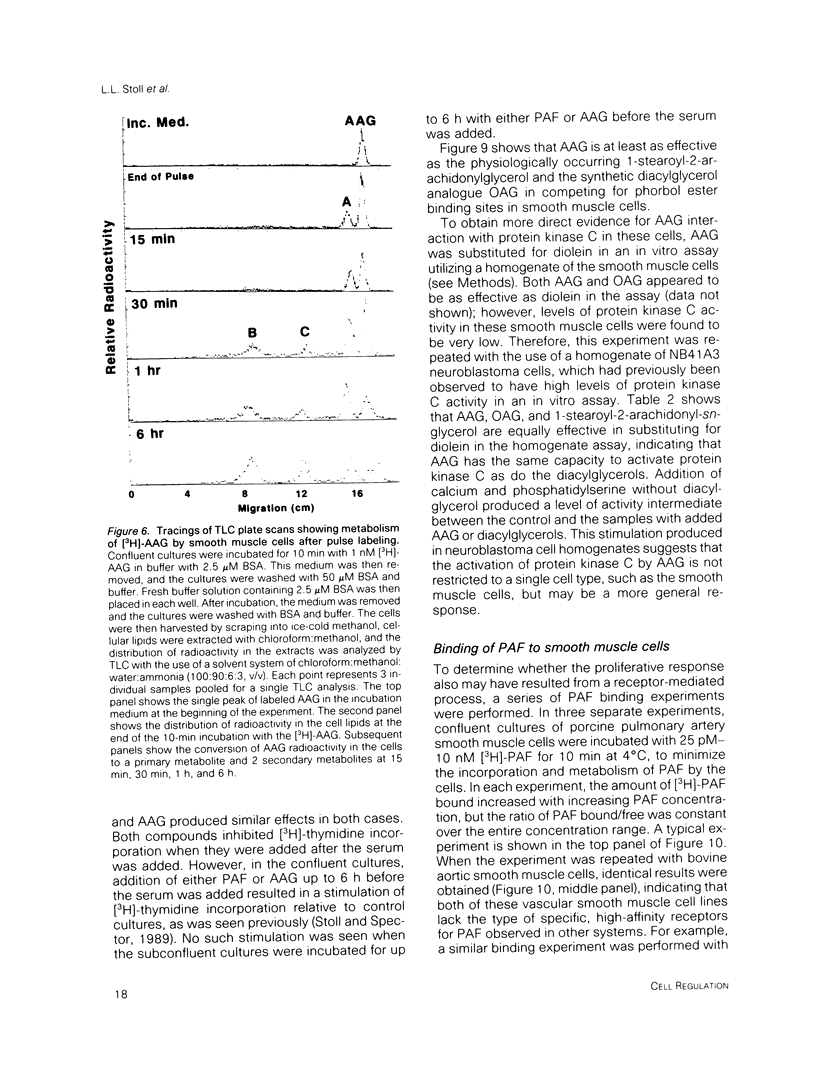
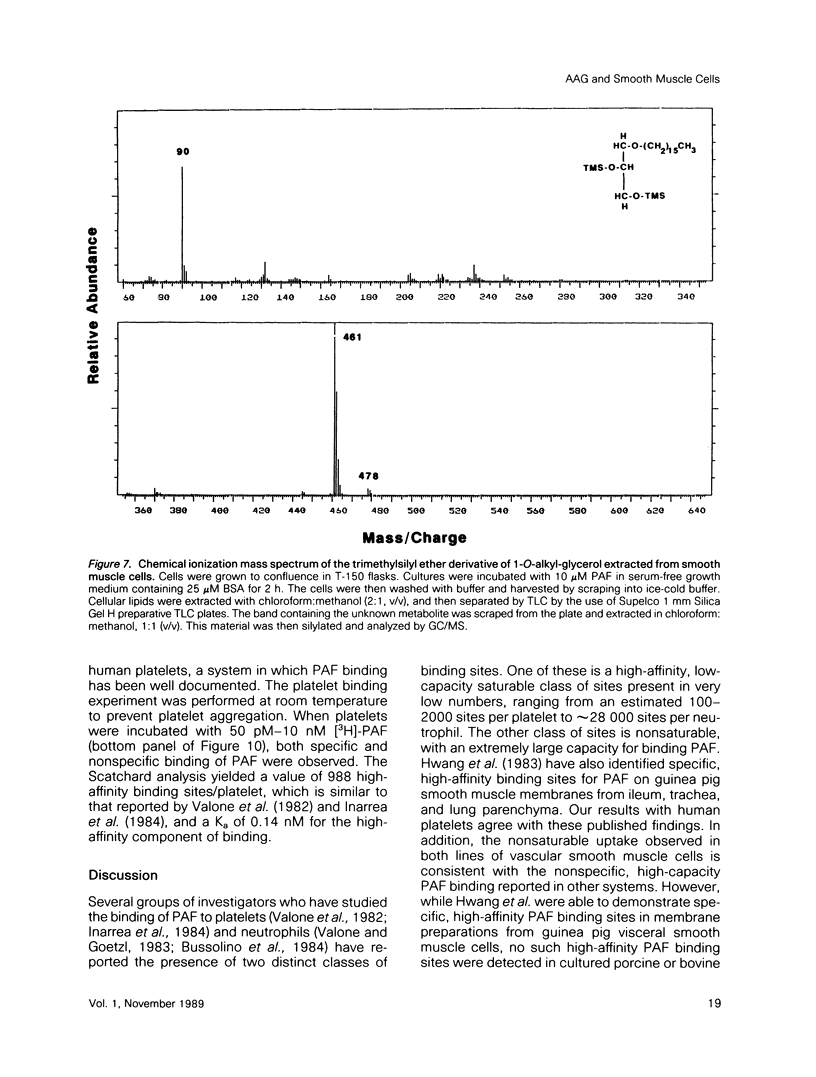
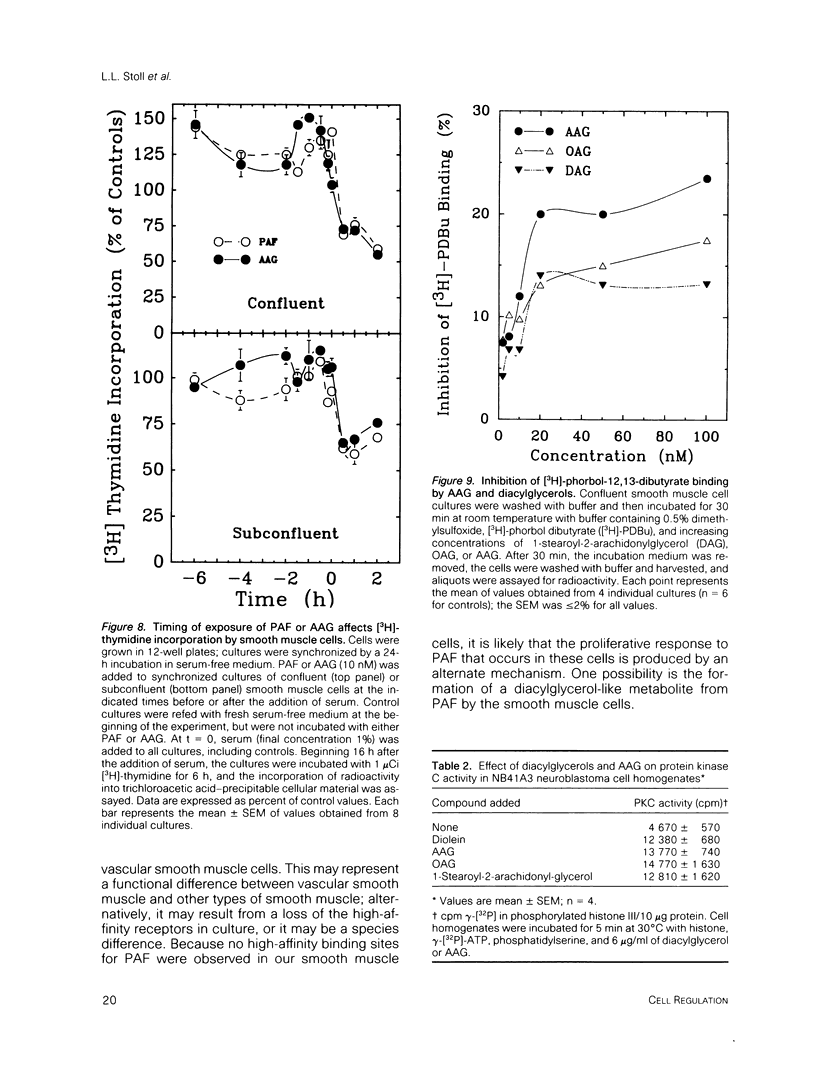
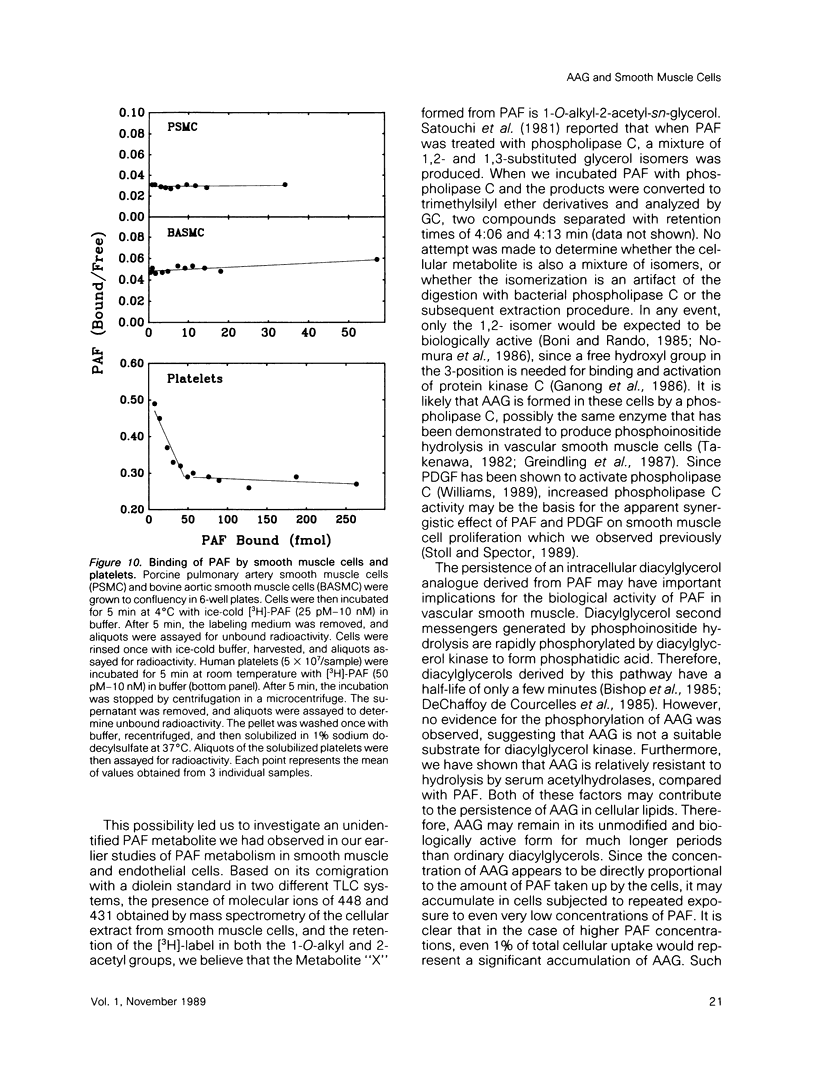
Platelet-activating factor (1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; PAF) is a potent vasoactive ether lipid produced by activated blood cells and endothelial cells. Vascular smooth muscle cells partially convert exogenous PAF to 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol (AAG), a biologically active diacylglycerol analogue. AAG is formed rapidly (less than 15 s) after exposure of the smooth muscle cells and does not appear to be a substrate for diacylglycerol kinase in these cells. Although most of the compound is metabolized to 1-O-alkyl-sn-glycerol, a small quantity remains as AAG for greater than or equal to 6 h. AAG inhibits phorbol ester binding, and it is as effective an activator of protein kinase C as diolein in an in vitro assay. Furthermore, AAG and PAF produce the same pattern of effects on smooth muscle cell proliferation. These observations suggest that at least some of the actions of PAF in vascular smooth muscle may be mediated through the formation of AAG, a stable, bioactive metabolite that appears to function as a diacylglycerol analogue.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnoux B., Duval D., Benveniste J. Release of platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) from alveolar macrophages by the calcium ionophore A23187 and phagocytosis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;10(6):437–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb02082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop W. R., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M. Attenuation of sn-1,2-diacylglycerol second messengers by diacylglycerol kinase. Inhibition by diacylglycerol analogs in vitro and in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6993–7000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M. L., Spector A. A., Kaduce T. L., Lee T. C., Snyder F. Metabolism of platelet activating factor (1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) and 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol by human endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 21;876(3):373–378. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boni L. T., Rando R. R. The nature of protein kinase C activation by physically defined phospholipid vesicles and diacylglycerols. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10819–10825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Aglietta M., Coda R., Bussolino F., Piacibello W., Tetta C. Release of platelet-activating factor (PAF) and histamine. II. The cellular origin of human PAF: monocytes, polymorphonuclear neutrophils and basophils. Immunology. 1981 Feb;42(2):191–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Aglietta M., Malavasi F., Tetta C., Piacibello W., Sanavio F., Bussolino F. The release of platelet-activating factor from human endothelial cells in culture. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2397–2403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czervionke R. L., Hoak J. C., Fry G. L. Effect of aspirin on thrombin-induced adherence of platelets to cultured cells from the blood vessel wall. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):847–856. doi: 10.1172/JCI109197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCorleto P. E., Bowen-Pope D. F. Cultured endothelial cells produce a platelet-derived growth factor-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1919–1923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. B., Sprecher H. Unidimensional thin-layer chromatography of phospholipids on boric acid-impregnated plates. J Lipid Res. 1982 May;23(4):660–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong B. R., Loomis C. R., Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Specificity and mechanism of protein kinase C activation by sn-1,2-diacylglycerols. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B., Lee C. S., Cheah M. J., Shen T. Y. Specific receptor sites for 1-O-alkyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet activating factor) on rabbit platelet and guinea pig smooth muscle membranes. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4756–4763. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iñarrea P., Gomez-Cambronero J., Nieto M., Crespo M. S. Characteristics of the binding of platelet-activating factor to platelets of different animal species. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 15;105(3-4):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90623-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Minakuchi R., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C) from rat brain. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:288–298. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Reep B., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M. Exogenous sn-1,2-diacylglycerols containing saturated fatty acids function as bioregulators of protein kinase C in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1358–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig J. C., McManus L. M., Clark P. O., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Modulation of platelet-activating factor (PAF) synthesis and release from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN): role of extracellular Ca2+. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jul;232(1):102–110. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90525-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas R. L., Turk J., Oates J. A., Brash A. R. Formation of a novel dihydroxy acid from arachidonic acid by lipoxygenase-catalyzed double oxygenation in rat mononuclear cells and human leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7056–7067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara M. J., Schmitt J. D., Wykle R. L., Daniel L. W. 1-0-Hexadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol stimulates differentiation of HL-60 human promyelocytic leukemia cells to macrophage-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):824–830. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura H., Ase K., Sekiguchi K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y., Nakano Y., Satoh T. Stereospecificity of diacylglycerol for stimulus-response coupling in platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 14;140(3):1143–1151. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90754-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R. Regulation of protein kinase C activity by lipids. FASEB J. 1988 May;2(8):2348–2355. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.8.3282960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubin R., Benveniste J. Formation of prostaglandins, leukotrienes and paf-acether by macrophages. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985;8(2):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(85)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satouchi K., Oda M., Saito K., Hanahan D. J. Metabolism of 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol by washed rabbit platelets: formation of platelet activating factor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Oct;234(1):318–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90355-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satouchi K., Pinckard R. N., McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J. Modification of the polar head group of acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine and subsequent effects upon platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4425–4432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll L. L., Spector A. A. Interaction of platelet-activating factor with endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells in coculture. J Cell Physiol. 1989 May;139(2):253–261. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll L. L., Spector A. A. Lipid transfer between endothelial and smooth muscle cells in coculture. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Oct;133(1):103–110. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenawa T. Inositol phospholipids in stimulated smooth muscles. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Coles E., Reinhold V. R., Goetzl E. J. Specific binding of phospholipid platelet-activating factor by human platelets. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1637–1641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Goetzl E. J. Specific binding by human polymorphonuclear leucocytes of the immunological mediator 1-O-hexadecyl/octadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine. Immunology. 1983 Jan;48(1):141–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2538922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Chaffoy de Courcelles D. C., Roevens P., Van Belle H. R 59 022, a diacylglycerol kinase inhibitor. Its effect on diacylglycerol and thrombin-induced C kinase activation in the intact platelet. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15762–15770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


