Abstract
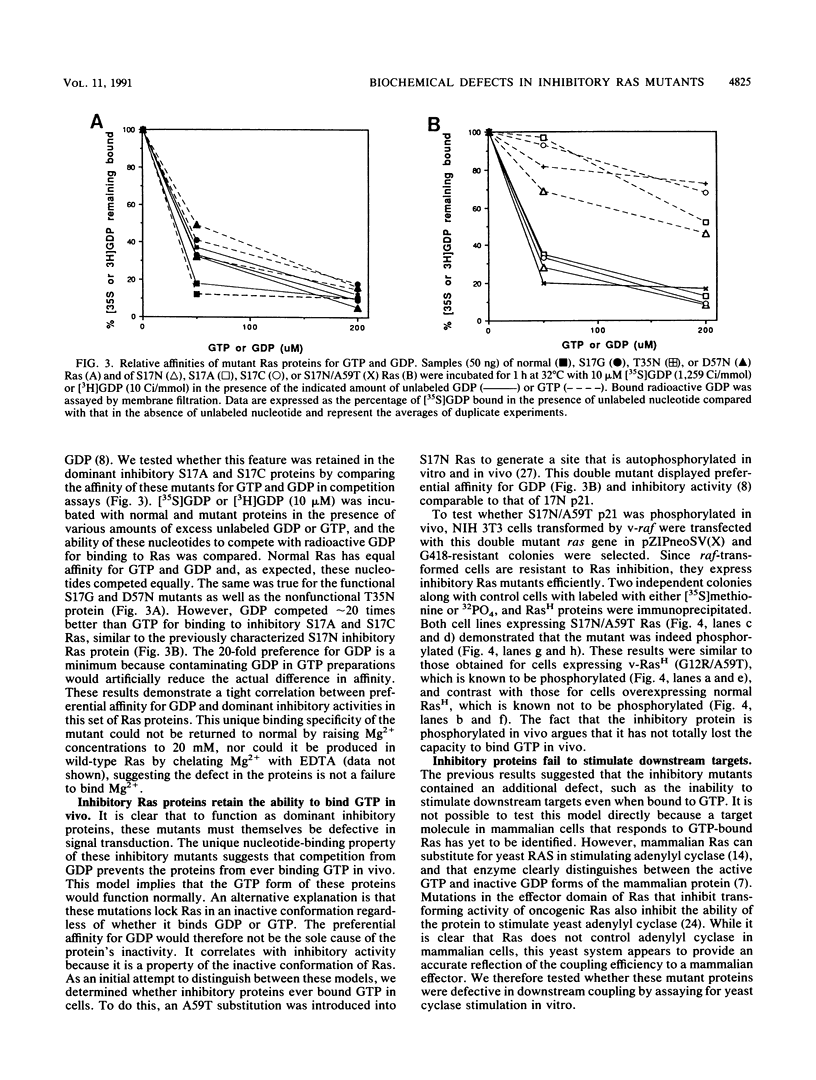
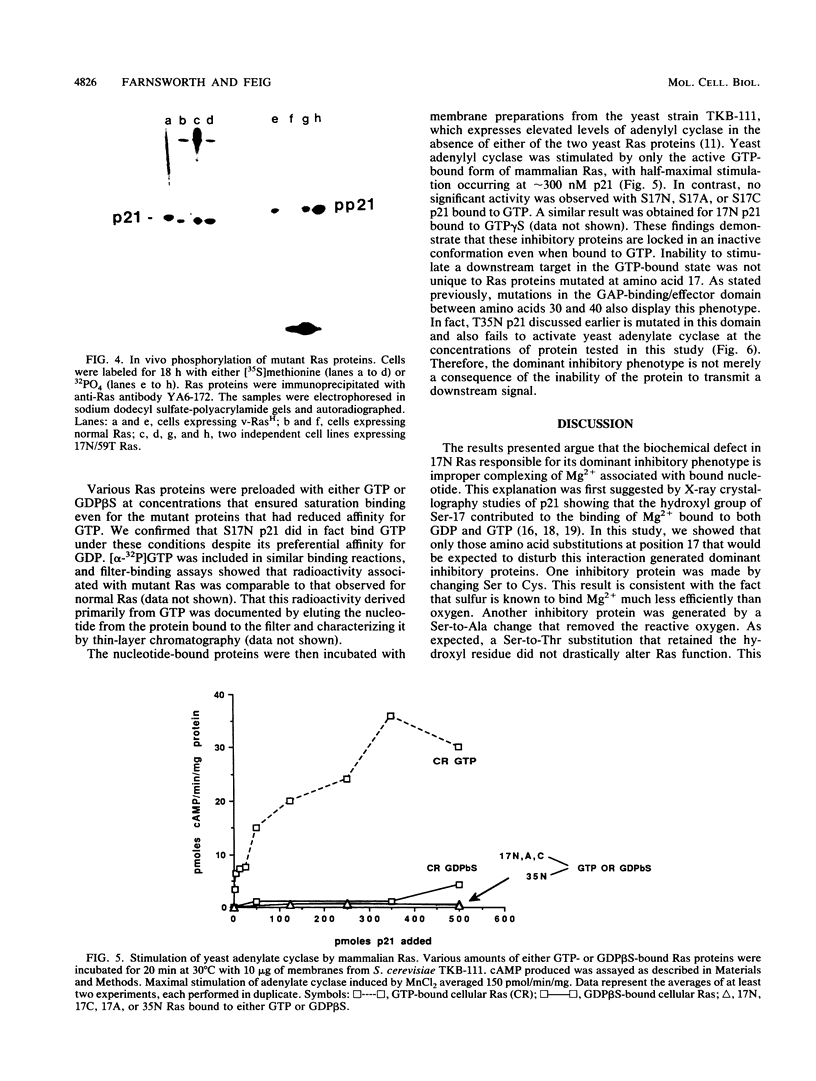
We have previously demonstrated that substitution of Asn for Ser at position 17 of RasH yields a dominant inhibitory protein whose expression in cells interferes with endogenous Ras function (L. A. Feig, and G. M. Cooper, Mol. Cell. Biol. 8:3235-3243, 1988). Subsequent structural studies have shown that the hydroxyl group of Ser-17 contributes to the binding of Mg2+ associated with bound nucleotide. In this report, we show that more subtle amino acid substitutions at this site that would be expected to interfere with complexing Mg2+, such as Cys or Ala, also generated dominant inhibitory mutants. In contrast, a Thr substitution that conserves a reactive hydroxyl group maintained normal Ras function. These results argue that the defect responsible for the inhibitory activity is improper coordination of Mg2+. Preferential affinity for GDP, observed in the original Asn-17 mutant, was found exclusively in inhibitory mutants. However, this binding specificity did not completely block the mutant proteins from binding GTP in vivo since introduction of the autophosphorylation site, Thr-59, in 17N Ras resulted in the phosphorylation of the double mutant in cells. Furthermore, inhibitory mutants failed to activate a model downstream target, yeast adenylate cyclase, even when bound to GTP. Thus, the consequence of improper complexing of Mg2+ was to lock the protein in a constitutively inactive state. A model is presented to explain how these properties could cause the mutant protein to inhibit the activation of endogenous Ras by competing for a guanine nucleotide-releasing factor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broek D., Toda T., Michaeli T., Levin L., Birchmeier C., Zoller M., Powers S., Wigler M. The S. cerevisiae CDC25 gene product regulates the RAS/adenylate cyclase pathway. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):789–799. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai H., Szeberényi J., Cooper G. M. Effect of a dominant inhibitory Ha-ras mutation on mitogenic signal transduction in NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5314–5323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clanton D. J., Hattori S., Shih T. Y. Mutations of the ras gene product p21 that abolish guanine nucleotide binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5076–5080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Créchet J. B., Poullet P., Mistou M. Y., Parmeggiani A., Camonis J., Boy-Marcotte E., Damak F., Jacquet M. Enhancement of the GDP-GTP exchange of RAS proteins by the carboxyl-terminal domain of SCD25. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):866–868. doi: 10.1126/science.2188363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. L., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Stacey D. W., Feig L. A. Preferential inhibition of the oncogenic form of RasH by mutations in the GAP binding/"effector" domain. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90246-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Cooper G. M. Inhibition of NIH 3T3 cell proliferation by a mutant ras protein with preferential affinity for GDP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3235–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Cooper G. M. Relationship among guanine nucleotide exchange, GTP hydrolysis, and transforming potential of mutated ras proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2472–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Pan B. T., Roberts T. M., Cooper G. M. Isolation of ras GTP-binding mutants using an in situ colony-binding assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4607–4611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Broek D., Kataoka T., Wigler M. Guanine nucleotide activation of, and competition between, RAS proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2128–2133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagag N., Halegoua S., Viola M. Inhibition of growth factor-induced differentiation of PC12 cells by microinjection of antibody to ras p21. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):680–682. doi: 10.1038/319680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. D., Day R., Farnsworth C. L., Feig L. A. A mutation in the putative Mg(2+)-binding site of Gs alpha prevents its activation by receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4830–4838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Powers S., Cameron S., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Broach J., Wigler M. Functional homology of mammalian and yeast RAS genes. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Tong L., deVos A. M., Brünger A., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Kim S. H. Molecular switch for signal transduction: structural differences between active and inactive forms of protooncogenic ras proteins. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):939–945. doi: 10.1126/science.2406906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Dhanasekaran N., Woon C. W., Johnson G. L. G alpha i-G alpha s chimeras define the function of alpha chain domains in control of G protein activation and beta gamma subunit complex interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):697–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Kabsch W., Krengel U., Holmes K. C., John J., Wittinghofer A. Structure of the guanine-nucleotide-binding domain of the Ha-ras oncogene product p21 in the triphosphate conformation. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):209–214. doi: 10.1038/341209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., O'Neill K., Wigler M. Dominant yeast and mammalian RAS mutants that interfere with the CDC25-dependent activation of wild-type RAS in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):390–395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Goldsborough M. D., Mark G. E., Bonner T. I., Groffen J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Structure and biological activity of v-raf, a unique oncogene transduced by a retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4218–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y. Adenylate cyclase assay. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:35–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Sibbald P. R., Wittinghofer A. The P-loop--a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):430–434. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90281-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaber M. D., Garsky V. M., Boylan D., Hill W. S., Scolnick E. M., Marshall M. S., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Ras interaction with the GTPase-activating protein (GAP). Proteins. 1989;6(3):306–315. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting I., Almo S. C., Rapp G., Wilson K., Petratos K., Lentfer A., Wittinghofer A., Kabsch W., Pai E. F., Petsko G. A. Time-resolved X-ray crystallographic study of the conformational change in Ha-Ras p21 protein on GTP hydrolysis. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):309–315. doi: 10.1038/345309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Zelenetz A. D., Cooper G. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of the chicken gene homologous to the transforming gene of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):531–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Papageorge A. G., Stokes P. E., Weeks M. O., Scolnick E. M. Guanine nucleotide-binding and autophosphorylating activities associated with the p21src protein of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):686–691. doi: 10.1038/287686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Feig L. A., Gibbs J. B. Dominant inhibitory Ras mutants selectively inhibit the activity of either cellular or oncogenic Ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4053–4064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeberényi J., Cai H., Cooper G. M. Effect of a dominant inhibitory Ha-ras mutation on neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M., Kung H. F., Kamata T. A novel membrane factor stimulates guanine nucleotide exchange reaction of ras proteins. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 1;259(2):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80019-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]