Abstract
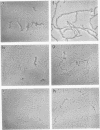
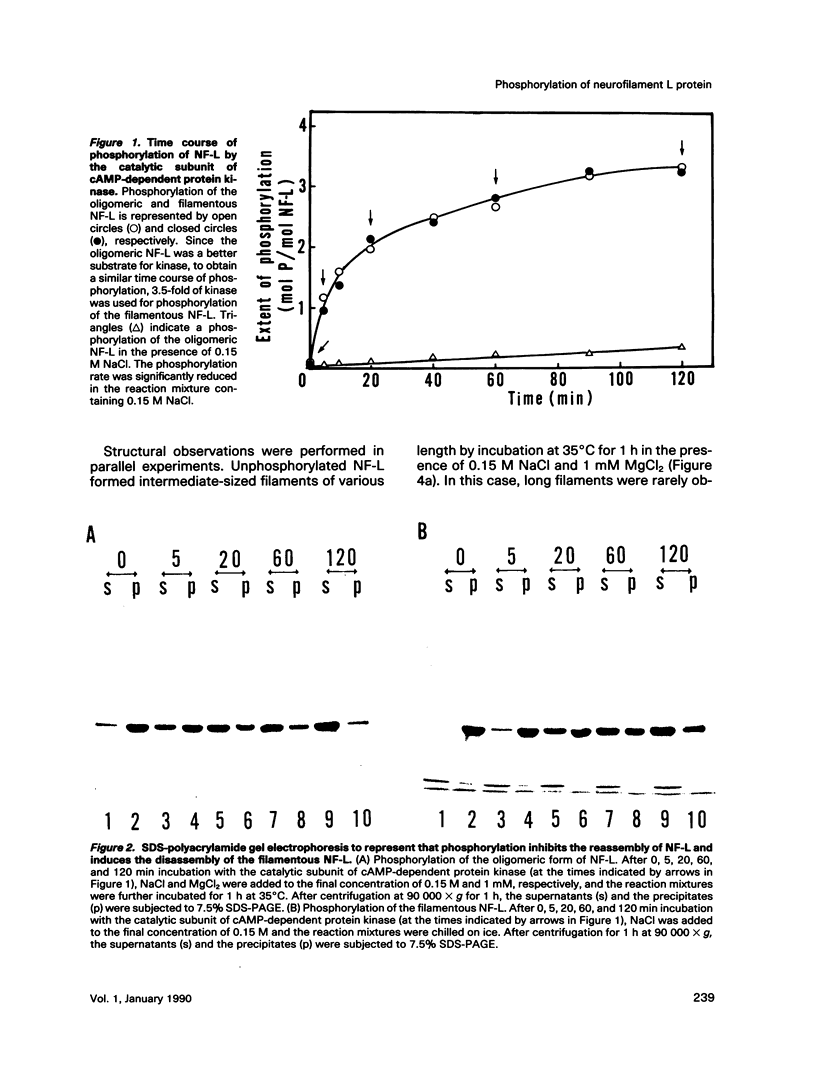
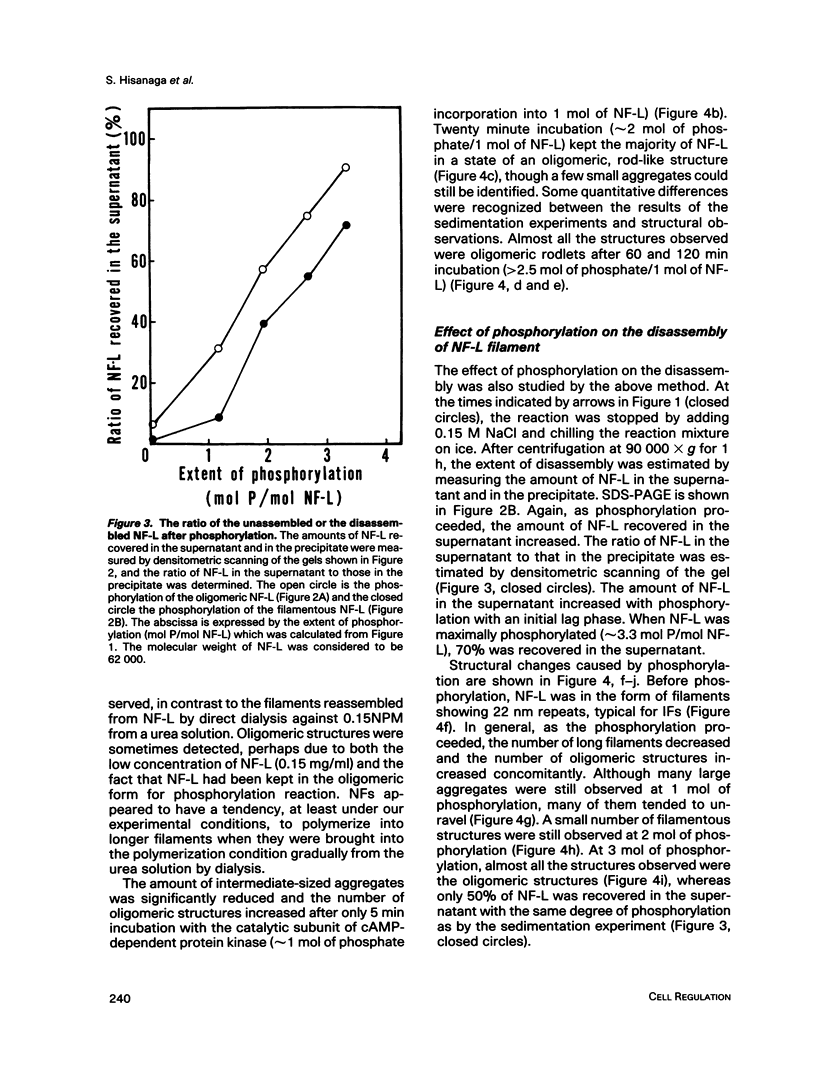
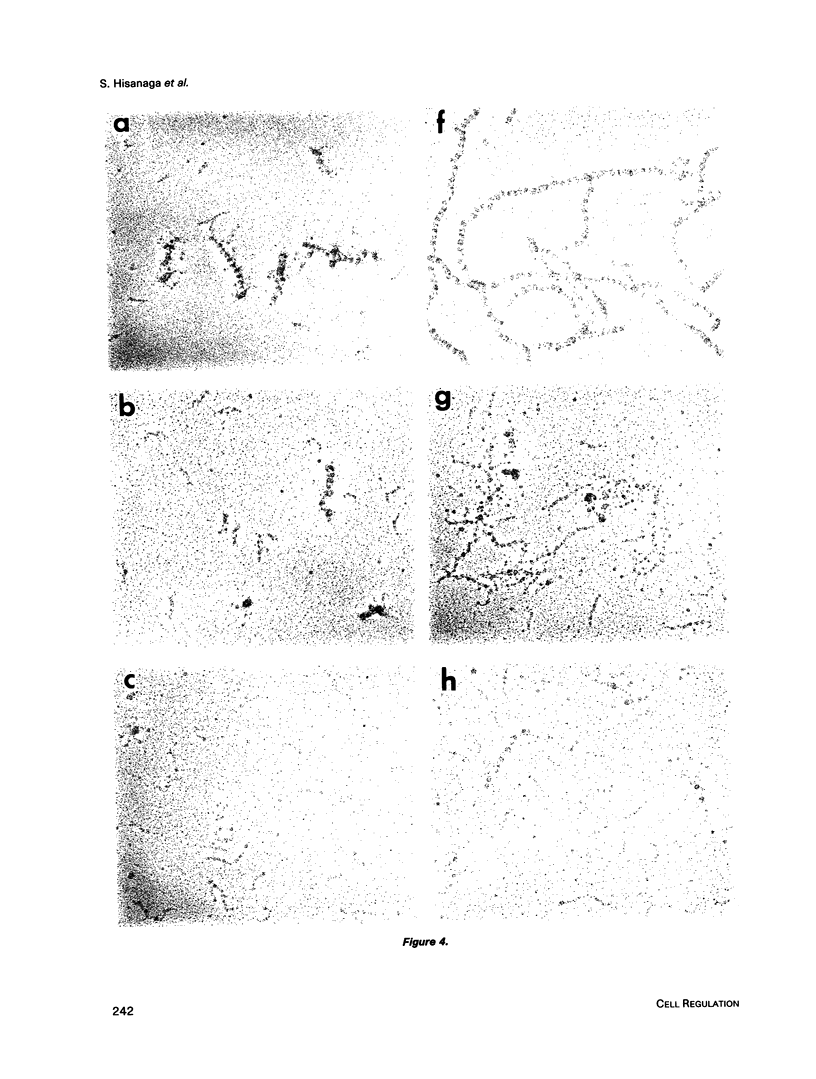
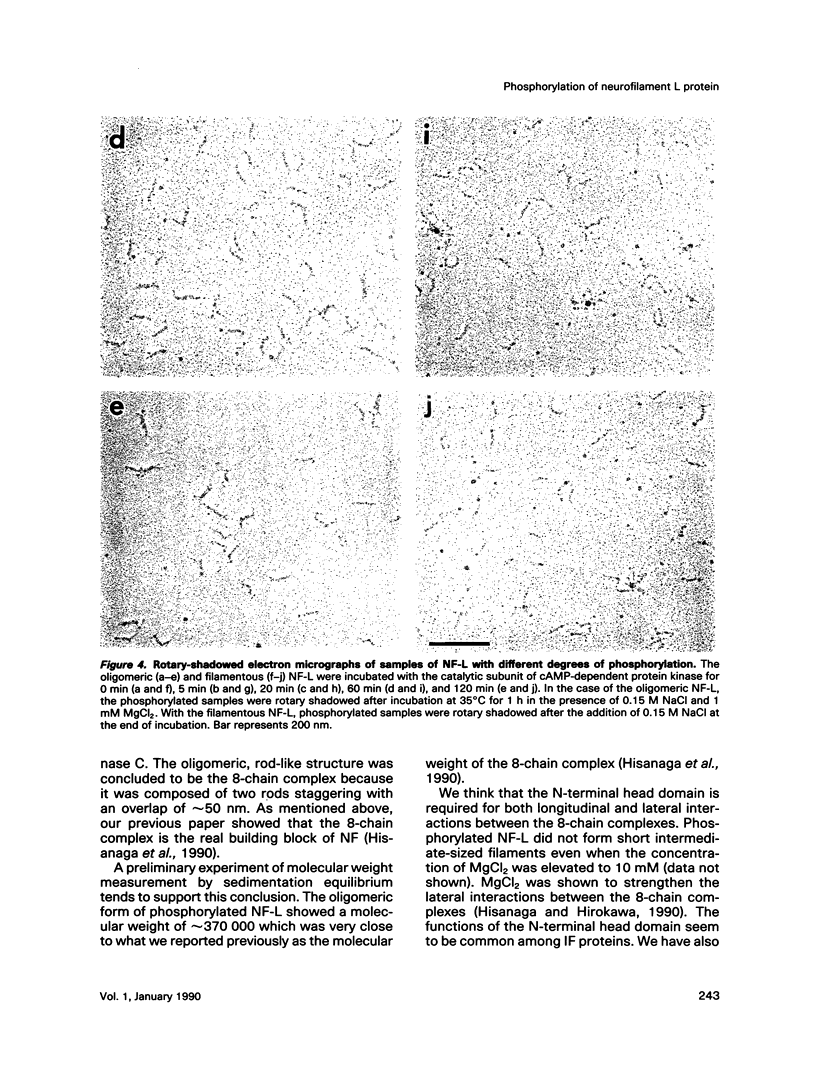
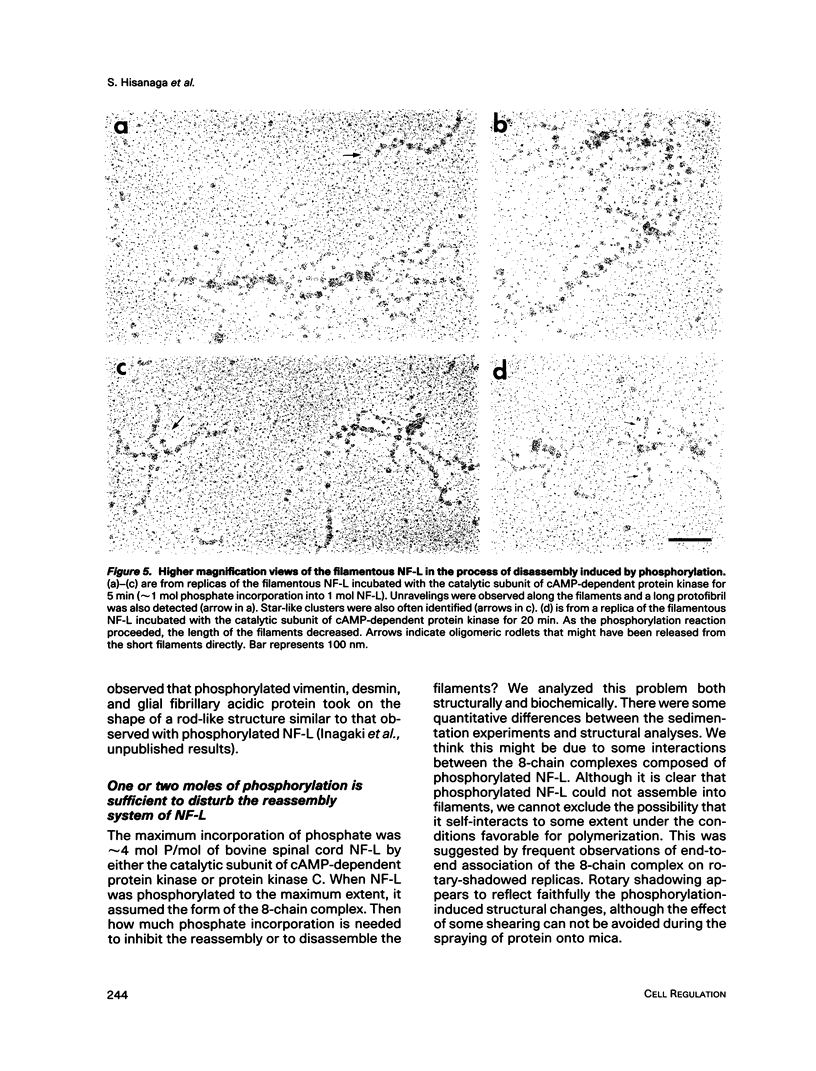
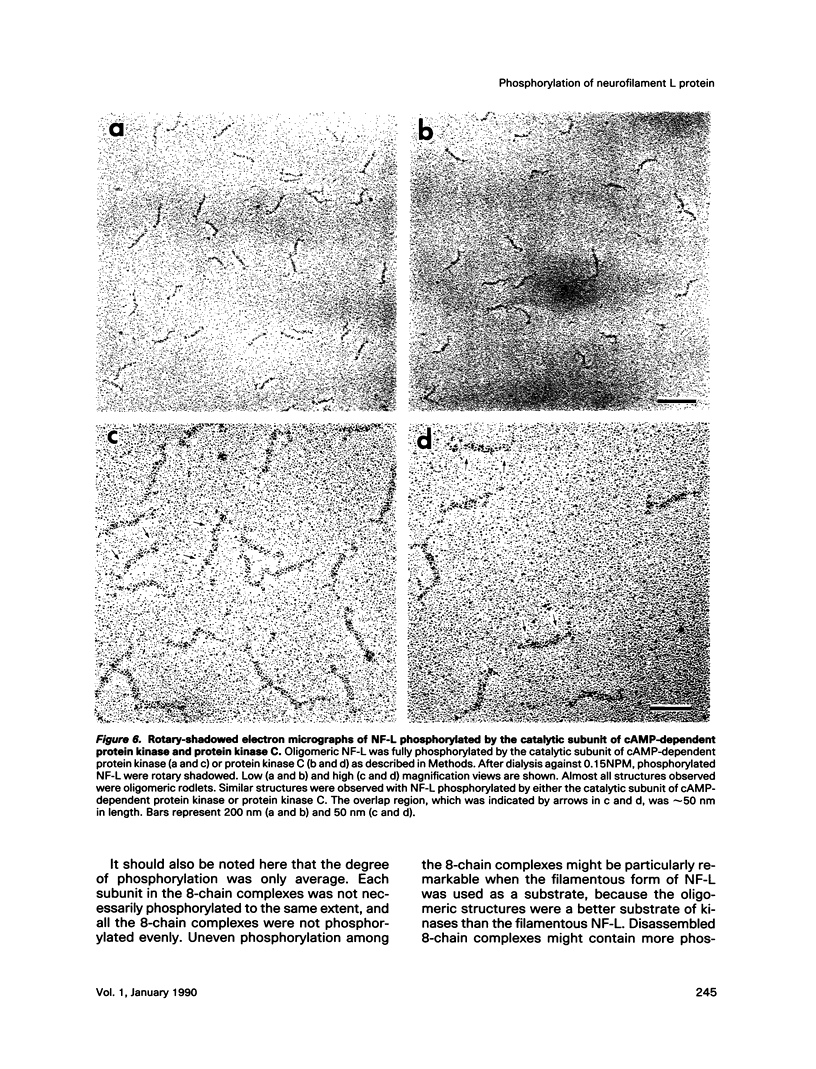
Effects of phosphorylation of the neurofilament L protein (NF-L) on the reassembly system were studied by both sedimentation experiments and low-angle rotary shadowing. Bovine spinal cord NF-L was phosphorylated with 3-4 mol/mol protein by either the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase or protein kinase C. Phosphorylated NF-L could not assemble into filaments. Phosphorylation by either cAMP-dependent protein kinase or protein kinase C inhibited the same step of the reassembly process. Phosphorylated NF-L remained as an 8-chain complex even in favorable conditions for reassembly. The extent of the effect of phosphorylation on the filamentous structure of NF-L was also investigated by using the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. The amount of unassembled NF-L increased linearly with increased phosphorylation in the sedimentation experiments. Structural observations indicated that 1 or 2 mol of phosphorylation is enough to inhibit reassembly and to induce disassembly, and the disassembly process was also observed. The filaments were shown to unravel with disassembly. Star-like clusters, which we reported as being the initial stage of reassembly, were also identified.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando S., Tanabe K., Gonda Y., Sato C., Inagaki M. Domain- and sequence-specific phosphorylation of vimentin induces disassembly of the filament structure. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2974–2979. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelides K. J., Smith K. E., Takeda M. Assembly and exchange of intermediate filament proteins of neurons: neurofilaments are dynamic structures. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1495–1506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Preparation of homogeneous cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase(s) and its subunits from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:299–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carden M. J., Schlaepfer W. W., Lee V. M. The structure, biochemical properties, and immunogenicity of neurofilament peripheral regions are determined by phosphorylation state. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9805–9817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Larsen P. M., Fey S. J., Celis A. Phosphorylation of keratin and vimentin polypeptides in normal and transformed mitotic human epithelial amnion cells: behavior of keratin and vimentin filaments during mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1429–1434. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. H., Rosevear E., Goldman R. D. Phosphorylation and disassembly of intermediate filaments in mitotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1885–1889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase-induced vimentin filament disassembly involves modification of the N-terminal domain of intermediate filament subunits. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 4;234(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Fink L. M. An alteration in the phosphorylation of vimentin-type intermediate filaments is associated with mitosis in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. Phosphorylation of vimentin in mitotically selected cells. In vitro cyclic AMP-independent kinase and calcium-stimulated phosphatase activities. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):67–78. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyer J., Leterrier J. F. Influence of the phosphorylation state of neurofilament proteins on the interactions between purified filaments in vitro. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):655–660. doi: 10.1042/bj2520655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Plessmann U., Weber K. The complete amino acid sequence of the major mammalian neurofilament protein (NF-L). FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 25;182(2):475–478. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80357-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Phosphorylation of desmin in vitro inhibits formation of intermediate filaments; identification of three kinase A sites in the aminoterminal head domain. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):15–20. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02778.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Self-assembly in Vitro of the 68,000 molecular weight component of the mammalian neurofilament triplet proteins into intermediate-sized filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D., Geisler N., Weber K. A periodic ultrastructure in intermediate filaments. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 25;155(2):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90444-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. 270K microtubule-associated protein cross-reacting with anti-MAP2 IgG in the crayfish peripheral nerve axon. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):33–39. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. Cross-linker system between neurofilaments, microtubules, and membranous organelles in frog axons revealed by the quick-freeze, deep-etching method. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):129–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Glicksman M. A., Willard M. B. Organization of mammalian neurofilament polypeptides within the neuronal cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1523–1536. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga S., Hirokawa N. Structure of the peripheral domains of neurofilaments revealed by low angle rotary shadowing. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga S., Hirokawa N. The effects of dephosphorylation on the structure of the projections of neurofilament. J Neurosci. 1989 Mar;9(3):959–966. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-03-00959.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbeck P. J. The transport and assembly of the axonal cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):223–227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Gonda Y., Matsuyama M., Nishizawa K., Nishi Y., Sato C. Intermediate filament reconstitution in vitro. The role of phosphorylation on the assembly-disassembly of desmin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5970–5978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Nishi Y., Nishizawa K., Matsuyama M., Sato C. Site-specific phosphorylation induces disassembly of vimentin filaments in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):649–652. doi: 10.1038/328649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Watanabe M., Hidaka H. N-(2-Aminoethyl)-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide, a newly synthesized protein kinase inhibitor, functions as a ligand in affinity chromatography. Purification of Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent and other protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2922–2925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. M., Williams R. C., Jr Phosphate content of mammalian neurofilaments. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):9902–9905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Mushynski W. E. Multiple phosphorylation sites in mammalian neurofilament polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10467–10470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann E., Weber K., Geisler N. Intermediate filament forming ability of desmin derivatives lacking either the amino-terminal 67 or the carboxy-terminal 27 residues. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 20;185(4):733–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura S., Ando S., Shibata M., Tanabe K., Sato C., Inagaki M. Protein kinase C phosphorylation of desmin at four serine residues within the non-alpha-helical head domain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5674–5678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milam L., Erickson H. P. Visualization of a 21-nm axial periodicity in shadowed keratin filaments and neurofilaments. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):592–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami Y., Sakai H. Dephosphorylation suppresses the activity of neurofilament to promote tubulin polymerization. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 17;185(2):239–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80914-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon R. A., Lewis S. E. Differential turnover of phosphate groups on neurofilament subunits in mammalian neurons in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16298–16301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon R. A., Logvinenko K. B. Multiple fates of newly synthesized neurofilament proteins: evidence for a stationary neurofilament network distributed nonuniformly along axons of retinal ganglion cell neurons. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):647–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sihag R. K., Nixon R. A. In vivo phosphorylation of distinct domains of the 70-kilodalton neurofilament subunit involves different protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):457–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Jones J. C., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 2):22s–27s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.22s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:593–625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro T., Komiya Y. Stable and dynamic forms of cytoskeletal proteins in slow axonal transport. J Neurosci. 1989 Mar;9(3):760–768. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-03-00760.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Vorgias C. E. Involvement of the N-terminal polypeptide of vimentin in the formation of intermediate filaments. J Cell Sci. 1983 Sep;63:43–67. doi: 10.1242/jcs.63.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Branton D. Rotary shadowing of extended molecules dried from glycerol. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 May;71(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(80)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Geisler N. Intermediate filaments: structural conservation and divergence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]