Abstract
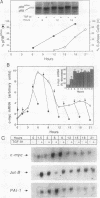
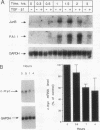
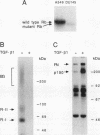
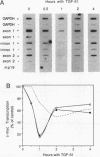
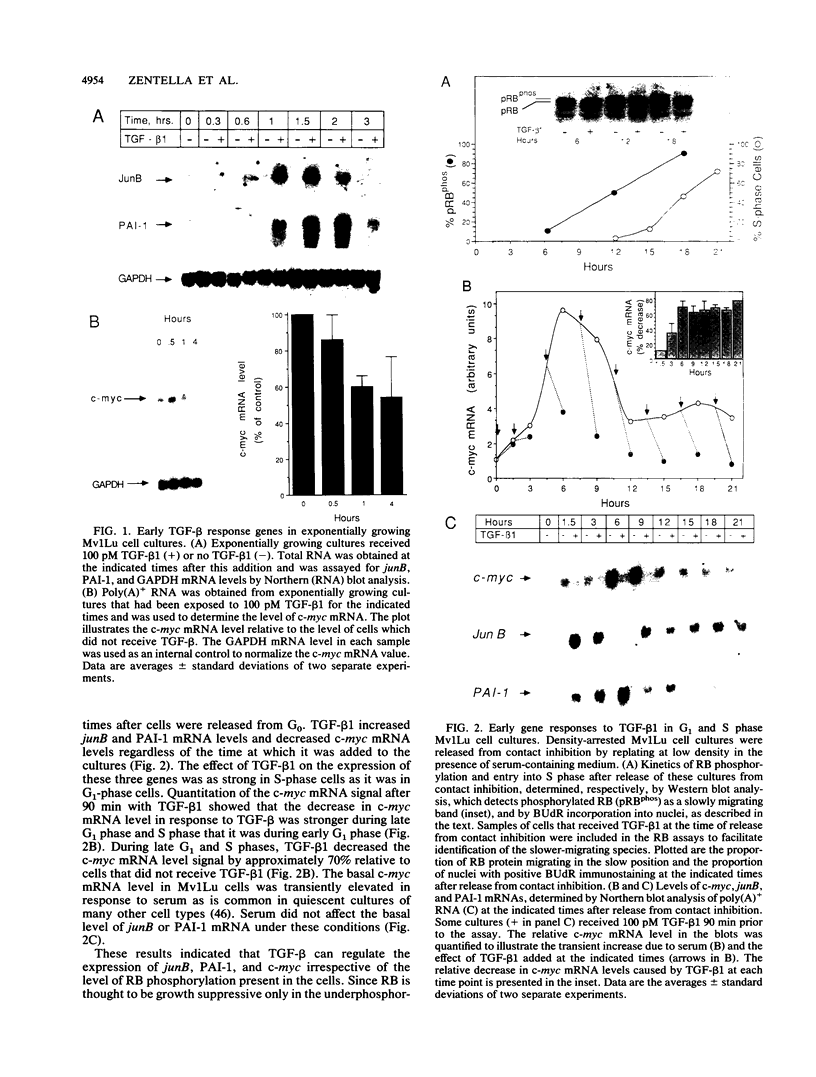
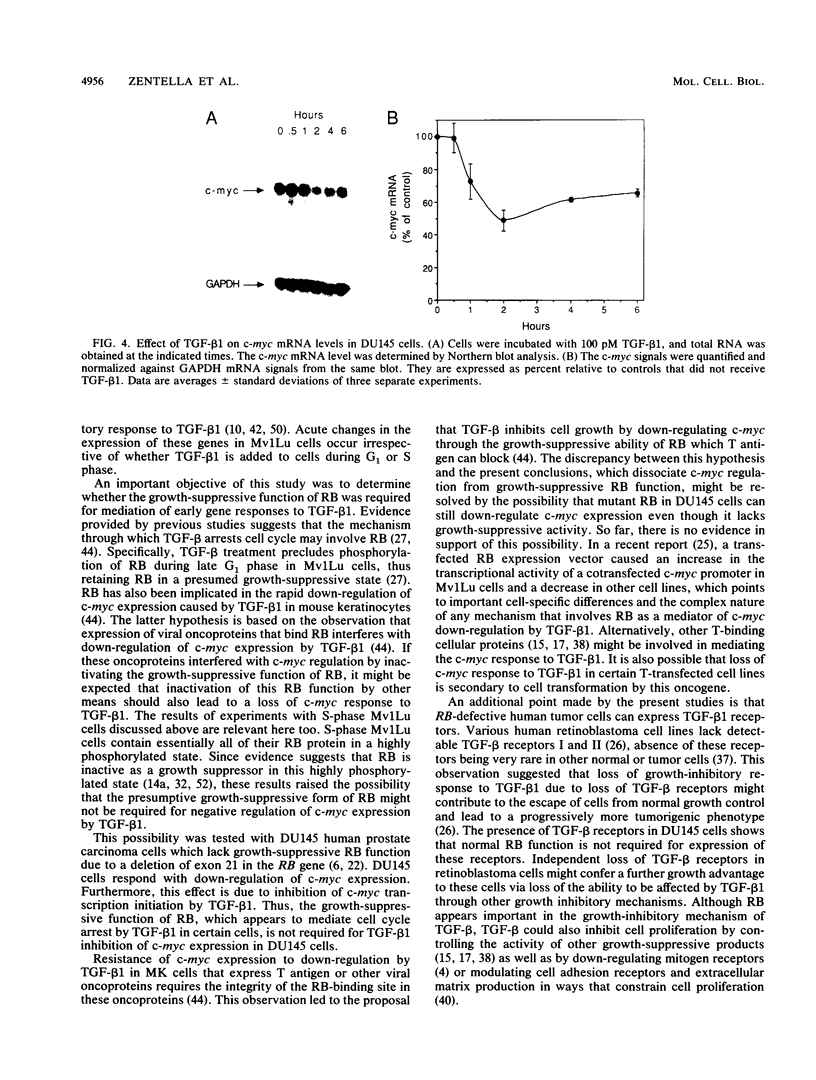
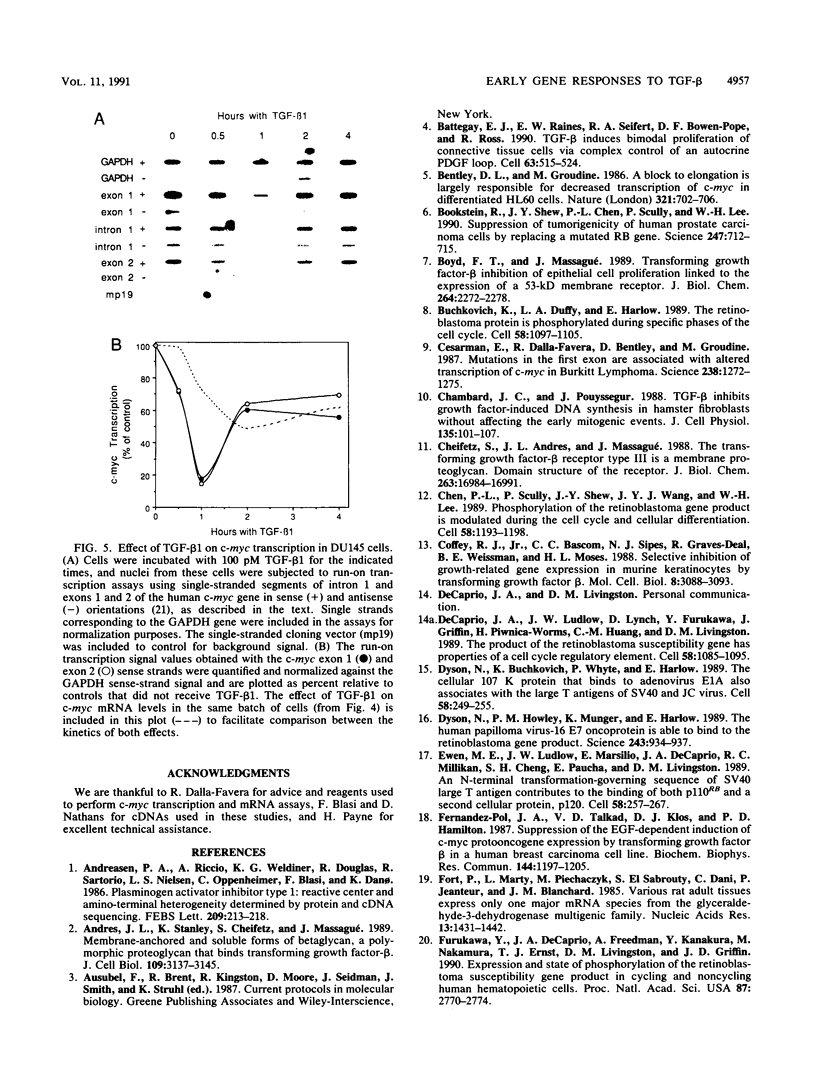
The growth-suppressive function of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product, RB, has been implicated in the mediation of growth inhibition and negative regulation of certain proliferation related genes by transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1). Early gene responses to TGF-beta 1 were examined in order to determine their dependence on the cell cycle and on the growth-suppressive function of RB. TGF-beta 1, which rapidly elevates the steady-state level of junB and PAI-1 mRNAs and decreases that of c-myc mRNA, induces these responses in S-phase populations of Mv1Lu lung epithelial cells containing RB in a phosphorylated state. Since in this state RB is presumed to lack growth-suppressive activity, the response to TGF-beta 1 was also examined in DU145 human prostate carcinoma cells whose mutant RB product lacks growth-suppressive function. In these cells, TGF-beta 1 also decreases c-myc expression at the transcription initiation level. These results suggests that the c-myc, junB, and PAI-1 responses to TGF-beta 1 are not restricted to the G1 phase of the cell cycle and that down-regulation of c-myc expression by TGF-beta 1 can occur through a mechanism independent from the growth-suppressive function of RB.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. A., Riccio A., Welinder K. G., Douglas R., Sartorio R., Nielsen L. S., Oppenheimer C., Blasi F., Danø K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1: reactive center and amino-terminal heterogeneity determined by protein and cDNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres J. L., Stanley K., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Membrane-anchored and soluble forms of betaglycan, a polymorphic proteoglycan that binds transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3137–3145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battegay E. J., Raines E. W., Seifert R. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. TGF-beta induces bimodal proliferation of connective tissue cells via complex control of an autocrine PDGF loop. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):515–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90448-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Scully P., Lee W. H. Suppression of tumorigenicity of human prostate carcinoma cells by replacing a mutated RB gene. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):712–715. doi: 10.1126/science.2300823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd F. T., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta inhibition of epithelial cell proliferation linked to the expression of a 53-kDa membrane receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2272–2278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchkovich K., Duffy L. A., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated during specific phases of the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesarman E., Dalla-Favera R., Bentley D., Groudine M. Mutations in the first exon are associated with altered transcription of c-myc in Burkitt lymphoma. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1272–1275. doi: 10.1126/science.3685977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambard J. C., Pouysségur J. TGF-beta inhibits growth factor-induced DNA synthesis in hamster fibroblasts without affecting the early mitogenic events. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Apr;135(1):101–107. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041350114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Andres J. L., Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta receptor type III is a membrane proteoglycan. Domain structure of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16984–16991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Scully P., Shew J. Y., Wang J. Y., Lee W. H. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product is modulated during the cell cycle and cellular differentiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Bascom C. C., Sipes N. J., Graves-Deal R., Weissman B. E., Moses H. L. Selective inhibition of growth-related gene expression in murine keratinocytes by transforming growth factor beta. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3088–3093. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Lynch D., Furukawa Y., Griffin J., Piwnica-Worms H., Huang C. M., Livingston D. M. The product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene has properties of a cell cycle regulatory element. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Buchkovich K., Whyte P., Harlow E. The cellular 107K protein that binds to adenovirus E1A also associates with the large T antigens of SV40 and JC virus. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90839-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Ludlow J. W., Marsilio E., DeCaprio J. A., Millikan R. C., Cheng S. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. An N-terminal transformation-governing sequence of SV40 large T antigen contributes to the binding of both p110Rb and a second cellular protein, p120. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90840-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Pol J. A., Talkad V. D., Klos D. J., Hamilton P. D. Suppression of the EGF-dependent induction of c-myc proto-oncogene expression by transforming growth factor beta in a human breast carcinoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 14;144(3):1197–1205. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91438-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa Y., DeCaprio J. A., Freedman A., Kanakura Y., Nakamura M., Ernst T. J., Livingston D. M., Griffin J. D. Expression and state of phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product in cycling and noncycling human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2770–2774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grignani F., Lombardi L., Inghirami G., Sternas L., Cechova K., Dalla-Favera R. Negative autoregulation of c-myc gene expression is inactivated in transformed cells. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3913–3922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe P. H., Draetta G., Leof E. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 inhibition of p34cdc2 phosphorylation and histone H1 kinase activity is associated with G1/S-phase growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1185–1194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. J., Yee J. K., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Bookstein R., Friedmann T., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. Suppression of the neoplastic phenotype by replacement of the RB gene in human cancer cells. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.3201247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Wang N. P., Tseng B. Y., Lee W. H., Lee E. H. Two distinct and frequently mutated regions of retinoblastoma protein are required for binding to SV40 T antigen. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1815–1822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Lee H. D., Robbins P. D., Busam K., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Regulation of transforming growth factor beta 1 gene expression by the product of the retinoblastoma-susceptibility gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3052–3056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Wang X. F., Weinberg R. A., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Absence of TGF-beta receptors and growth inhibitory responses in retinoblastoma cells. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):196–199. doi: 10.1126/science.2895499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Livingston D. M., Massagué J. Growth inhibition by TGF-beta linked to suppression of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Rönnstrand L., Heino J., Decaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Livingston D. M., Massagué J. Control of junB and extracellular matrix protein expression by transforming growth factor-beta 1 is independent of simian virus 40 T antigen-sensitive growth-sensitive growth-inhibitory events. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):972–978. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Weis F. M., Boyd F. T., Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Responsiveness to transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) restored by genetic complementation between cells defective in TGF-beta receptors I and II. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9108–9112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Weis M. B., Massagué J. Concomitant loss of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta receptor types I and II in TGF-beta-resistant cell mutants implicates both receptor types in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18518–18524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Hu J. S., Olson E. N. Different members of the jun proto-oncogene family exhibit distinct patterns of expression in response to type beta transforming growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1556–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., DeCaprio J. A., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large T antigen binds preferentially to an underphosphorylated member of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product family. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90983-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., Shon J., Pipas J. M., Livingston D. M., DeCaprio J. A. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product undergoes cell cycle-dependent dephosphorylation and binding to and release from SV40 large T. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90590-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. Tumor suppressor genes. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90641-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Cheifetz S., Boyd F. T., Andres J. L. TGF-beta receptors and TGF-beta binding proteoglycans: recent progress in identifying their functional properties. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;593:59–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Identification of receptors for type-beta transforming growth factor. Methods Enzymol. 1987;146:174–195. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)46020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:597–641. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missero C., Filvaroff E., Dotto G. P. Induction of transforming growth factor beta 1 resistance by the E1A oncogene requires binding to a specific set of cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3489–3493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent M. A., Newman M. J. Inhibition of normal rat kidney cell growth by transforming growth factor-beta is mediated by collagen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18060–18067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttinen R. P., Kobayashi S., Bornstein P. Transforming growth factor beta increases mRNA for matrix proteins both in the presence and in the absence of changes in mRNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1105–1108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertovaara L., Sistonen L., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Keski-Oja J., Alitalo K. Enhanced jun gene expression is an early genomic response to transforming growth factor beta stimulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1255–1262. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Holt J. T., Stein R. W., Moses H. L. Transforming growth factor beta 1 suppression of c-myc gene transcription: role in inhibition of keratinocyte proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3758–3762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Stein R. W., Moran E., Yaciuk P., Schlegel R., Lyons R. M., Pittelkow M. R., Münger K., Howley P. M., Moses H. L. TGF-beta 1 inhibition of c-myc transcription and growth in keratinocytes is abrogated by viral transforming proteins with pRB binding domains. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90188-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins B. J., Stiles C. D. Serum-inducible genes. Adv Cancer Res. 1989;53:1–32. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segarini P. R., Seyedin S. M. The high molecular weight receptor to transforming growth factor-beta contains glycosaminoglycan chains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8366–8370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino V., Bandyopadhyay S. TGF beta inhibits Go/S-phase transition in primary fibroblasts. Loss of response to the antigrowth effect of TGF beta is observed after immortalization. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):569–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takehara K., LeRoy E. C., Grotendorst G. R. TGF-beta inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation: alteration of EGF binding and EGF-induced growth-regulatory (competence) gene expression. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90294-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton D. J., Park S. H., Lanier L., Weinberg R. A. Nonfunctional mutants of the retinoblastoma protein are characterized by defects in phosphorylation, viral oncoprotein association, and nuclear tethering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3033–3037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilding G., Zugmeier G., Knabbe C., Flanders K., Gelmann E. Differential effects of transforming growth factor beta on human prostate cancer cells in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Mar;62(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]