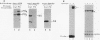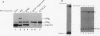Abstract
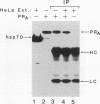
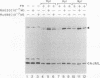
Steroid receptors regulate transcription of target genes in vivo and in vitro in a steroid hormone-dependent manner. Unoccupied progesterone receptor exists in the low-salt homogenates of target cells as a functionally inactive 8 to 10S complex with several nonreceptor components such as two molecules of 90-kDa heat shock protein (hsp90), a 70-kDa heat shock protein (hsp70), and a 56-kDa heat shock protein (hsp56). Ligand-induced dissociation of receptor-associated proteins such as hsp90 has been proposed as the mechanism of receptor activation. Nevertheless, it has not been established whether, beyond release of heat shock proteins, the steroidal ligand plays a role in modulating receptor activity. To examine whether the release of these nonreceptor proteins from receptor complex results in a constitutively active receptor, we isolated an unliganded receptor form essentially free of hsp90, hsp70, and hsp56. Using a recently developed steroid hormone-responsive cell-free transcription system, we demonstrate for the first time that the dissociation of heat shock proteins is not sufficient to generate a functionally active receptor. This purified receptor still requires hormone for high-affinity binding to a progesterone response element and for efficient transcriptional activation of a target gene. When an antiprogestin, Ru486, is bound to the receptor, it fails to promote efficient transcription. We propose that in the cell, in addition to the release of receptor-associated inhibitory proteins, a distinct hormone-mediated activation event must precede efficient gene activation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi M. K., Elliston J. F., Tsai S. Y., Edwards D. P., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Steroid hormone-dependent interaction of human progesterone receptor with its target enhancer element. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1221–1229. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi M. K., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Identification of a functional intermediate in receptor activation in progesterone-dependent cell-free transcription. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):547–550. doi: 10.1038/345547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi M. K., Tsai S. Y., Weigel N. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Regulation of in vitro transcription by progesterone receptor. Characterization and kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5129–5134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly A., Le Page C., Rauch M., Milgrom E. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the progesterone receptor to the uteroglobin gene: effects of hormone, antihormone and receptor phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3235–3241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baulieu E. E. Contragestion and other clinical applications of RU 486, an antiprogesterone at the receptor. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1351–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.2781282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baulieu E. E. Steroid hormone antagonists at the receptor level: a role for the heat-shock protein MW 90,000 (hsp 90). J Cell Biochem. 1987 Oct;35(2):161–174. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240350209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann R. P., Mizzen L. E., Welch W. J. Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):850–854. doi: 10.1126/science.2188360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Arnemann J., Slater E., Brüller H. J., Gross B., Beato M. Differential gene activation by glucocorticoids and progestins through the hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):371–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Poellinger L., Wikstöm A. C., Gustafsson J. A. Requirement of hormone for thermal conversion of the glucocorticoid receptor to a DNA-binding state. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):686–688. doi: 10.1038/333686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A. The molybdate-stabilized nonactivated glucocorticoid receptor contains a dimer of Mr 90,000 non-hormone-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11803–11806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes P. A., Suba E. J., Lawler-Heavner J., Elashry-Stowers D., Wei L. L., Toft D. O., Sullivan W. P., Horwitz K. B., Edwards D. P. Immunologic analysis of human breast cancer progesterone receptors. 1. Immunoaffinity purification of transformed receptors and production of monoclonal antibodies. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6250–6262. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groyer A., Schweizer-Groyer G., Cadepond F., Mariller M., Baulieu E. E. Antiglucocorticosteroid effects suggest why steroid hormone is required for receptors to bind DNA in vivo but not in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):624–626. doi: 10.1038/328624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard K. J., Holley S. J., Yamamoto K. R., Distelhorst C. W. Mapping the HSP90 binding region of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11928–11935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joab I., Radanyi C., Renoir M., Buchou T., Catelli M. G., Binart N., Mester J., Baulieu E. E. Common non-hormone binding component in non-transformed chick oviduct receptors of four steroid hormones. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):850–853. doi: 10.1038/308850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalff M., Gross B., Beato M. Progesterone receptor stimulates transcription of mouse mammary tumour virus in a cell-free system. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):360–362. doi: 10.1038/344360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Tsai S. Y., Weigel N. L., Allan G. F., Riley D., Rodriguez R., Schrader W. T., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. The progesterone receptor stimulates cell-free transcription by enhancing the formation of a stable preinitiation complex. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90740-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kost S. L., Smith D. F., Sullivan W. P., Welch W. J., Toft D. O. Binding of heat shock proteins to the avian progesterone receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3829–3838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Bodwell J. E., Gametchu B., Harrison R. W., Munck A. Molybdate-stabilized nonactivated glucocorticoid-receptor complexes contain a 90-kDa non-steroid-binding phosphoprotein that is lost on activation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3758–3763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. Heat-shock proteins. Coming in from the cold. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):776–777. doi: 10.1038/332776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Khursheed B., Garabedian M. J., Fortin M. G., Lindquist S., Yamamoto K. R. Reduced levels of hsp90 compromise steroid receptor action in vivo. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):166–168. doi: 10.1038/348166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Salser S. J., Yamamoto K. R. A movable and regulable inactivation function within the steroid binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B., Jolly D. J., Pratt D. V., Hollenberg S. M., Giguere V., Cadepond F. M., Schweizer-Groyer G., Catelli M. G., Evans R. M., Baulieu E. E. A region in the steroid binding domain determines formation of the non-DNA-binding, 9 S glucocorticoid receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B. Transformation of glucocorticoid and progesterone receptors to the DNA-binding state. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Sep;35(1):51–68. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240350105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riehl R. M., Sullivan W. P., Vroman B. T., Bauer V. J., Pearson G. R., Toft D. O. Immunological evidence that the nonhormone binding component of avian steroid receptors exists in a wide range of tissues and species. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 5;24(23):6586–6591. doi: 10.1021/bi00344a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Faber L. E., Henzel W. J., Pratt W. B. The 56-59-kilodalton protein identified in untransformed steroid receptor complexes is a unique protein that exists in cytosol in a complex with both the 70- and 90-kilodalton heat shock proteins. Biochemistry. 1990 May 29;29(21):5145–5152. doi: 10.1021/bi00473a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R. Hsp56: a novel heat shock protein associated with untransformed steroid receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22067–22070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Meshinchi S., Tienrungroj W., Schlesinger M. J., Toft D. O., Pratt W. B. Relationship of the 90-kDa murine heat shock protein to the untransformed and transformed states of the L cell glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6986–6991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Toft D. O., Schlesinger M. J., Pratt W. B. Evidence that the 90-kDa phosphoprotein associated with the untransformed L-cell glucocorticoid receptor is a murine heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12398–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Schowalter D. B., Kost S. L., Toft D. O. Reconstitution of progesterone receptor with heat shock proteins. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1704–1711. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strähle U., Klock G., Schütz G. A DNA sequence of 15 base pairs is sufficient to mediate both glucocorticoid and progesterone induction of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7871–7875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. K., Maeda Y., Nakao K., Wakim N. G., Duhring J. L., Faber L. E. A 59-kilodalton protein associated with progestin, estrogen, androgen, and glucocorticoid receptors. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5269–5275. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Carlstedt-Duke J., Weigel N. L., Dahlman K., Gustafsson J. A., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular interactions of steroid hormone receptor with its enhancer element: evidence for receptor dimer formation. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Cooperative binding of steroid hormone receptors contributes to transcriptional synergism at target enhancer elements. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90919-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Rapid purification of mammalian 70,000-dalton stress proteins: affinity of the proteins for nucleotides. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1229–1237. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willmann T., Beato M. Steroid-free glucocorticoid receptor binds specifically to mouse mammary tumour virus DNA. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):688–691. doi: 10.1038/324688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Ashry D., Oñate S. A., Nordeen S. K., Edwards D. P. Human progesterone receptor complexed with the antagonist RU 486 binds to hormone response elements in a structurally altered form. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1545–1558. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]