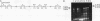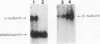Abstract
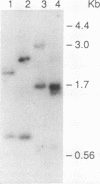
Several nonphotoautotrophic mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii were generated by transforming strain nit1-305 (cw 15) with exogenous DNA. An enrichment for potential photophosphorylation mutants was performed on medium containing arsenate, and acetate-requiring auxotrophs were then identified by replica plating. Strains containing a potential mutation in the nuclear DNA encoding the chloroplast coupling factor 1 (CF1) gamma-subunit (the atpC gene) were first identified serologically with a monospecific antiserum directed against the CF1 gamma-subunit polypeptide. Of several mutants isolated, one, designated T1-54, was characterized at the protein, DNA, and RNA levels. Mutant strain T1-54 lacks anti-CF1 gamma-subunit cross-reacting material, exhibits polymorphism at the atpC locus compared with the parental strain, and lacks the mRNA transcript for the CF1 gamma-subunit. The data are consistent with there being an insertion of exogenous DNA, a deletion of DNA, or both at the 5' end of the gene encoding the CF1 gamma-subunit.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amzel L. M., Pedersen P. L. Proton atpases: structure and mechanism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:801–824. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers A. D., Ellmore G. S., Klein U., Bogorad L. Transcriptional analysis of endogenous and foreign genes in chloroplast transformants of Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell. 1990 Nov;2(11):1059–1070. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.11.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W., Harris E. H., Hosler J. P., Johnson A. M., Jones A. R., Randolph-Anderson B. L., Robertson D., Klein T. M., Shark K. B. Chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas with high velocity microprojectiles. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1534–1538. doi: 10.1126/science.2897716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day A., Schirmer-Rahire M., Kuchka M. R., Mayfield S. P., Rochaix J. D. A transposon with an unusual arrangement of long terminal repeats in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):1917–1927. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman D. S., Levine R. P. Cytochrome f and plastocyanin: their sequence in the photosynthetic electron transport chain of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1665–1669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudock M. O., Togasaki R. K., Lien S., Hosek M., San Pietro A. A uniparentally inherited mutation affecting photophosphorylation in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 15;87(1):66–71. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91647-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketcham S. R., Davenport J. W., Warncke K., McCarty R. E. Role of the gamma subunit of chloroplast coupling factor 1 in the light-dependent activation of photophosphorylation and ATPase activity by dithiothreitol. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7286–7293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L. High-frequency nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1228–1232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L., Richards K. L., Stern D. B. Engineering the chloroplast genome: techniques and capabilities for chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1721–1725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L., Schnell R. A., Fernández E., Lefebvre P. A. Stable nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas using the Chlamydomonas gene for nitrate reductase. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2589–2601. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire C., Wollman F. A. The chloroplast ATP synthase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. II. Biochemical studies on its biogenesis using mutants defective in photophosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10235–10242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield S. P., Kindle K. L. Stable nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using a C. reinhardtii gene as the selectable marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2087–2091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchant S., Bogorad L. Regulation by copper of the expression of plastocyanin and cytochrome c552 in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):462–469. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin C. M., McCarty R. E. Role of a disulfide bond in the gamma subunit in activation of the ATPase of chloroplast coupling factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7275–7280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccioni R. G., Bennoun P., Chua N. H. A nuclear mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii defective in photosynthetic photophosphorylation. Characterization of the algal coupling factor ATPase. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):93–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przibilla E., Heiss S., Johanningmeier U., Trebst A. Site-specific mutagenesis of the D1 subunit of photosystem II in wild-type Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell. 1991 Feb;3(2):169–174. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Cotranscription of the wild-type chloroplast atpE gene encoding the CF1/CF0 epsilon subunit with the 3' half of the rps7 gene in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and characterization of frameshift mutations in atpE. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Apr;221(2):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00261715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D., Woessner J. P., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Molecular characterization of two point mutants in the chloroplast atpB gene of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii defective in assembly of the ATP synthase complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2331–2337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGER R., GRANICK S. Nutritional control of sexuality in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Jul 20;37(6):729–742. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.6.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd H. S., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Mutations in nine chloroplast loci of Chlamydomonas affecting different photosynthetic functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1353–1357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spreitzer R. J., Mets L. An assessment of arsenate selection as a method for obtaining nonphotosynthetic mutants of chlamydomonas. Genetics. 1982 Mar;100(3):417–425. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spreitzer R. J., Ogren W. L. Rapid recovery of chloroplast mutations affecting ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6293–6297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. M., Merchant S., Theg S. M., Selman B. R. Isolation of a cDNA clone for the gamma subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: import and cleavage of the precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1369–1373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. M., Selman B. R. cDNA sequence and predicted primary structure of the gamma subunit from the ATP synthase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19342–19345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]