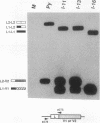
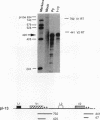
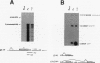
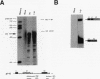
Abstract
The relationship between polyadenylation and splicing was investigated in a model system consisting of two tandem but nonidentical polyomavirus late transcription units. This model system exploits the polyomavirus late transcription termination and polyadenylation signals, which are sufficiently weak to allow the production of many multigenome-length primary transcripts with repeating introns, exons, and poly(A) sites. This double-genome construct contains exons of two types, those bordered by 3' and 5' splice sites (L1 and L2) and those bordered by a 3' splice site and a poly(A) site (V1 and V2). The L1 and L2 exons are distinguishable from one another but retain identical flanking RNA processing signals, as is the case for the V1 and V2 exons. Analysis of cytoplasmic RNAs obtained from mouse cells transfected with this construct and its derivatives revealed the following. (i) V1 and V2 exons are often skipped during pre-mRNA processing, while L1 and L2 exons are not skipped. (ii) No messages contain internal, unused polyadenylation signals. (iii) Poly(A) site choice is not required for the selection of an upstream 3' splice site. (iv) When two tandem poly(A) sites are placed downstream of a 3' splice site, the first poly(A) site is chosen almost exclusively, even though transcription can proceed past both sites. (v) Placing a 3' splice site between these two tandem poly(A) sites allows the more distal site to be chosen. These and other available data are most consistent with a model in which terminal exons are produced by the coordinate selection and use of a 3' splice site with the nearest available downstream poly(A) site.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H. Kinetics and efficiency of polyadenylation of late polyomavirus nuclear RNA: generation of oligomeric polyadenylated RNAs and their processing into mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):722–729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson N. H. Polyoma virus giant RNAs contain tandem repeats of the nucleotide sequence of the entire viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4754–4758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson N. H. Transcription during productive infection with polyoma virus and Simian virus 40. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G. R., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus late leader region serves an essential spacer function necessary for viability and late gene expression. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):417–425. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.417-425.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G. R., Carmichael G. G. The length but not the sequence of the polyoma virus late leader exon is important for both late RNA splicing and stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2593–2610. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G. R., Marlor C. W., Barrett N. L., Carmichael G. G. Leader-to-leader splicing is required for efficient production and accumulation of polyomavirus late mRNAs. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):85–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.85-93.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G., Nevins J. R. Splice site selection dominates over poly(A) site choice in RNA production from complex adenovirus transcription units. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2107–2116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akusjärvi G., Persson H. Controls of RNA splicing and termination in the major late adenovirus transcription unit. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):420–426. doi: 10.1038/292420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Bothwell A. L., Knapp M., Siden E., Mather E., Koshland M., Baltimore D. Synthesis of secreted and membrane-bound immunoglobulin mu heavy chains is directed by mRNAs that differ at their 3' ends. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amara S. G., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide transcription unit: tissue-specific expression involves selective use of alternative polyadenylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2151–2160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M., Moore C., Sharp P. A. Spliced segments at the 5' terminus of adenovirus 2 late mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3171–3175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindereif A., Green M. R. An ordered pathway of snRNP binding during mammalian pre-mRNA splicing complex assembly. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2415–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill K. B., Carmichael G. G. Deletion analysis of the polyomavirus late promoter: evidence for both positive and negative elements in the absence of early proteins. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3634–3642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3634-3642.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Steitz J. A. Multiple interactions between the splicing substrate and small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in spliceosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):281–293. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Spliceosome assembly in yeast. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):1014–1027. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Gelinas R. E., Broker T. R., Roberts R. J. An amazing sequence arrangement at the 5' ends of adenovirus 2 messenger RNA. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deninger P. L., Esty A., LaPorte P., Hsu H., Friedmann T. The nucleotide sequence and restriction enzyme sites of the polyoma genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 25;8(4):855–860. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeson R. B., Hedjran F., Yeakley J. M., Guise J. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Alternative production of calcitonin and CGRP mRNA is regulated at the calcitonin-specific splice acceptor. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):76–80. doi: 10.1038/341076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck-Pedersen E., Logan J. Regulation of poly(A) site selection in adenovirus. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):532–541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.532-541.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N., Ziff E. RNA structures near poly(A) of adenovirus-2 late messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Krämer A., Keller W. Different small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles are involved in different steps of splicing complex formation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:287–298. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R., Mandel G., Carmichael G. G., Barncastle J. P., Dawe C. J., Benjamin T. L. Polyomavirus tumor induction in mice: influences of viral coding and noncoding sequences on tumor profiles. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2232–2239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2232-2239.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Guise J. W., McDevitt M. A., Tucker P. W., Nevins J. R. Relative position and strengths of poly(A) sites as well as transcription termination are critical to membrane versus secreted mu-chain expression during B-cell development. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):471–481. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Seiler S. R., Sharp P. A. A multicomponent complex is involved in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A. Affinity chromatography of splicing complexes: U2, U5, and U4 + U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in the spliceosome. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1294–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.3638792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde-DeRuyscher R. P., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus late pre-mRNA processing: DNA replication-associated changes in leader exon multiplicity suggest a role for leader-to-leader splicing in the early-late switch. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5823–5832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5823-5832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Favaloro J., Parker J. Topography of the three late mRNA's of polyoma virus which encode the virion proteins. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):637–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.637-651.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Morahan G., Cowman A. F., Harris A. W. Production of RNA for secreted immunoglobulin mu chains does not require transcriptional termination 5' to the microM exons. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):84–86. doi: 10.1038/301084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of complexes involved in the splicing of precursors to mRNAs. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):845–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in formation of spliceosomes. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90614-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanoix J., Tseng R. W., Acheson N. H. Duplication of functional polyadenylation signals in polyomavirus DNA does not alter efficiency of polyadenylation or transcription termination. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):733–742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.733-742.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Splice commitment dictates neuron-specific alternative RNA processing in calcitonin/CGRP gene expression. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1091–1117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Flavell A. J., Cowie A., Kamen R. Amplification in the leader sequence of late polyoma virus mRNAs. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):373–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Mode of regulation of immunoglobulin mu- and delta-chain expression varies during B-lymphocyte maturation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Wilson M. C. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):113–118. doi: 10.1038/290113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa M., Rose S. D., Berget S. M. In vitro polyadenylation is stimulated by the presence of an upstream intron. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1552–1559. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Perry R. P. Regulated production of mu m and mu s mRNA requires linkage of the poly(A) addition sites and is dependent on the length of the mu s-mu m intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8883–8887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Perry R. P. The regulated production of mu m and mu s mRNA is dependent on the relative efficiencies of mu s poly(A) site usage and the c mu 4-to-M1 splice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):726–738. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Rymond B. C., Rosbash M. Electrophoresis of ribonucleoproteins reveals an ordered assembly pathway of yeast splicing complexes. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):341–345. doi: 10.1038/324341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson B. L., Cote G. J., Berget S. M. Exon definition may facilitate splice site selection in RNAs with multiple exons. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):84–94. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Fasel N., Wall R. A novel RNA in which the 5' end is generated by cleavage at the poly(A) site of immunoglobulin heavy-chain secreted mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4749–4752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. Specific and stable intron-factor interactions are established early during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):131–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. R., Ziff E. B. Transcripts from the adenovirus-2 major late promoter yield a single early family of 3' coterminal mRNAs and five late families. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:527–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Porro E. B., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Scanning from an independently specified branch point defines the 3' splice site of mammalian introns. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):243–247. doi: 10.1038/342243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Characterisation of polyoma late mRNA leader sequences by molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):4867–4888. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.4867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Kamen R. Structure of polyoma virus late nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):273–301. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90539-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng R. W., Acheson N. H. Use of a novel S1 nuclease RNA-mapping technique to measure efficiency of transcription termination on polyomavirus DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1624–1632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall C., La Mantia G., Thacker C. M., Favaloro J., Kamen R. A region of the polyoma virus genome between the replication origin and late protein coding sequences is required in cis for both early gene expression and viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6231–6250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]