Abstract
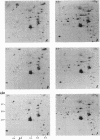
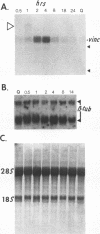
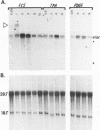
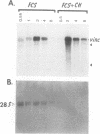
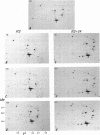
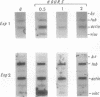
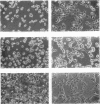
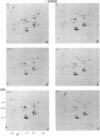
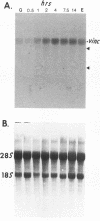
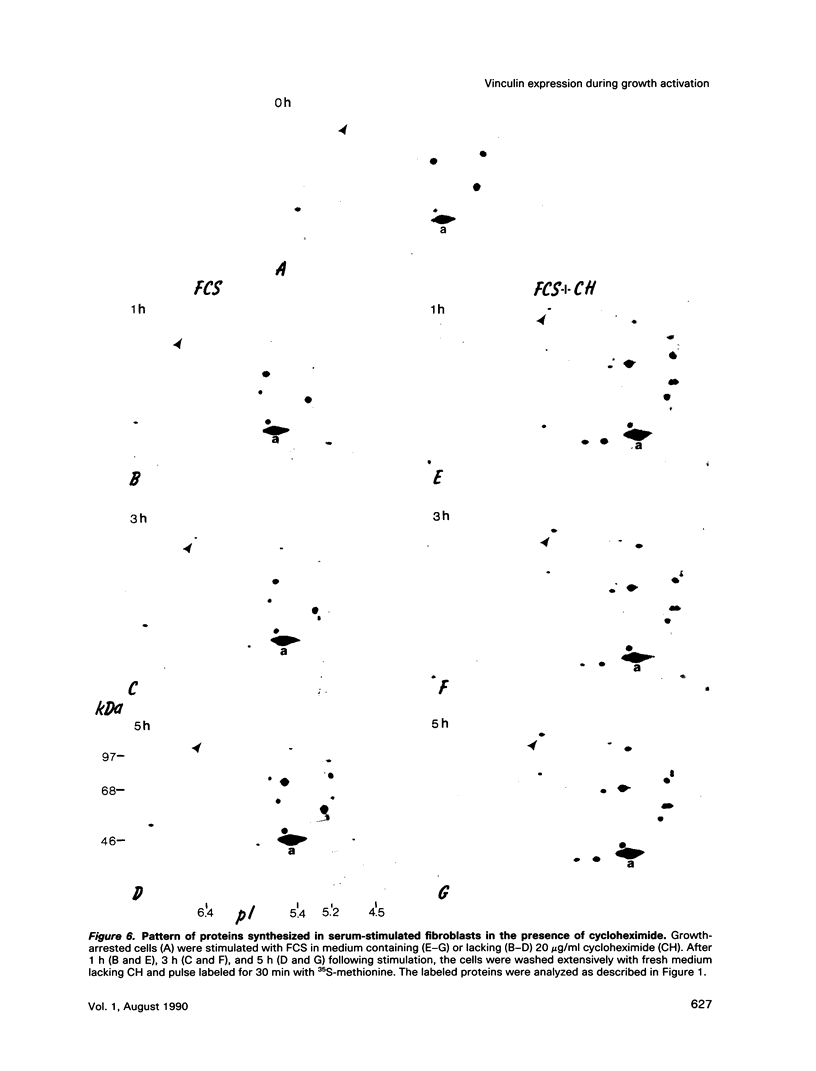
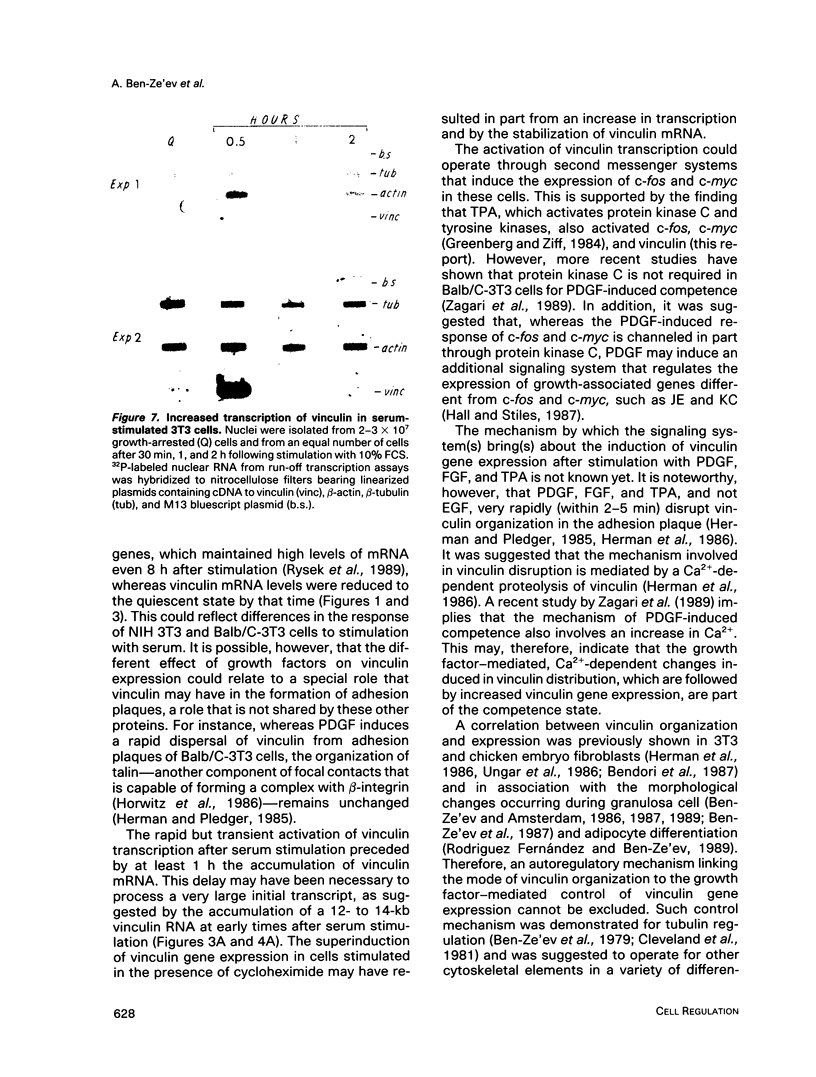
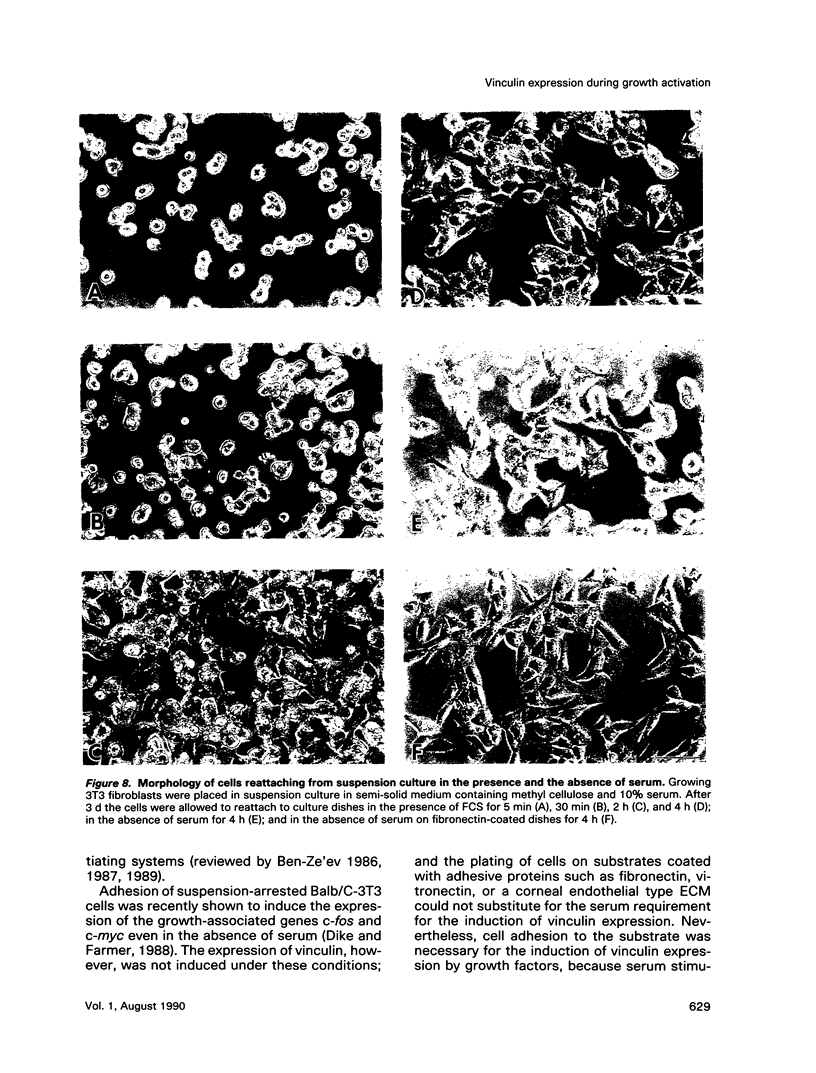
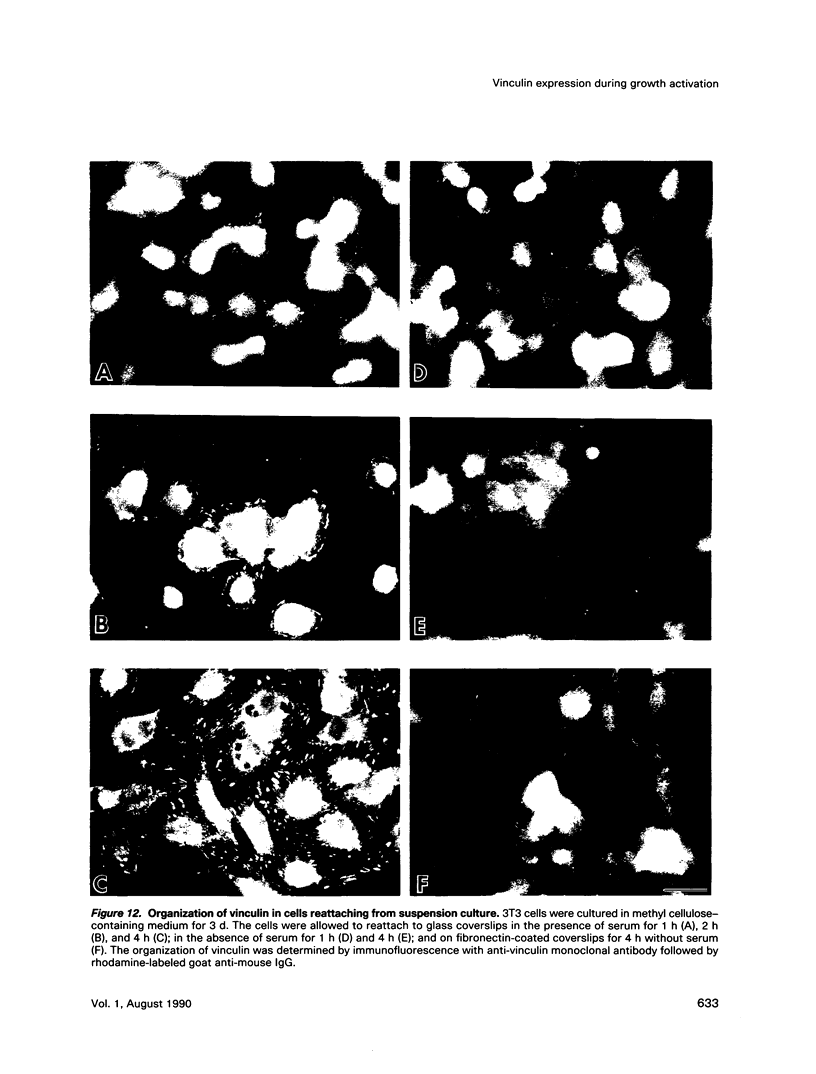
When stimulated with serum, quiescent Balb/C-3T3 fibroblasts were found to induce vinculin transcription transiently within 30 min, followed by accumulation of vinculin mRNA and protein synthesis between 2 and 4 h after stimulation and a decrease to the basal level by 6-8 h. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) each could elicit a similar response, albeit to a lesser extent, whereas epidermal growth factor (EGF) was inefficient in inducing vinculin expression. In cells stimulated with serum and cycloheximide, vinculin expression was superinduced and vinculin mRNA levels persisted longer than in cells stimulated with serum alone. Cells arrested in the presence of serum by anchorage denial in methyl cellulose suspension culture also induced vinculin expression and formed large vinculin positive plaques when reattaching and spreading on the substrate in the presence of serum. Cells replated from suspension culture in the absence of serum on either plastic or extracellular matrix (ECM) components were capable of extensive spreading, but failed to elevate vinculin expression and displayed diffuse vinculin staining. The results indicate that the changes in vinculin organization and expression in response to growth factor stimulation may reflect either a necessary step in the progression through the cell cycle or a response related to complex cellular processes such as wound repair and embryogenesis.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Amsterdam A. In vitro regulation of granulosa cell differentiation. Involvement of cytoskeletal protein expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5366–5376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Amsterdam A. Regulation of cytoskeletal protein organization and expression in human granulosa cells in response to gonadotropin treatment. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):1033–1041. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Amsterdam A. Regulation of cytoskeletal proteins involved in cell contact formation during differentiation of granulosa cells on extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2894–2898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A. Differential control of cytokeratins and vimentin synthesis by cell-cell contact and cell spreading in cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1424–1433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Farmer S. R., Penman S. Mechanisms of regulating tubulin synthesis in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Farmer S. R., Penman S. Protein synthesis requires cell-surface contact while nuclear events respond to cell shape in anchorage-dependent fibroblasts. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Kohen F., Amsterdam A. Gonadotropin-induced differentiation of granulosa cells is associated with the co-ordinated regulation of cytoskeletal proteins involved in cell-contact formation. Differentiation. 1987;34(3):222–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb00070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A. The role of changes in cell shape and contacts in the regulation of cytoskeleton expression during differentiation. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;8:293–312. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_8.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendori R., Salomon D., Geiger B. Contact-dependent regulation of vinculin expression in cultured fibroblasts: a study with vinculin-specific cDNA probes. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2897–2905. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benecke B. J., Ben-Ze'ev A., Penman S. The control of mRNA production, translation and turnover in suspended and reattached anchorage-dependent fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):931–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatti S. P., Foster D. N., Ranganathan G., Moses H. L., Getz M. J. Induction of fibronectin gene transcription and mRNA is a primary response to growth-factor stimulation of AKR-2B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1119–1123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockus B. J., Stiles C. D. Regulation of cytoskeletal architecture by platelet-derived growth factor, insulin and epidermal growth factor. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jul;153(1):186–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection and localization of a 130K protein in living fibroblasts: a relationship to actin and fibronectin. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):587–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., McKanna J. A., Cohen S. Rapid induction of morphological changes in human carcinoma cells A-431 by epidermal growth factors. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):260–265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dike L. E., Farmer S. R. Cell adhesion induces expression of growth-associated genes in suspension-arrested fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6792–6796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Surface modulation in cell recognition and cell growth. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):218–226. doi: 10.1126/science.769162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder P. K., Schmidt L. J., Ono T., Getz M. J. Specific stimulation of actin gene transcription by epidermal growth factor and cycloheximide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. R., Ben-Ze'av A., Benecke B. J., Penman S. Altered translatability of messenger RNA from suspended anchorage-dependent fibroblasts: reversal upon cell attachment to a surface. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. R., Wan K. M., Ben-Ze'ev A., Penman S. Regulation of actin mRNA levels and translation responds to changes in cell configuration. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):182–189. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath K. R., Edgell C. J., Burridge K. The distribution of distinct integrins in focal contacts is determined by the substratum composition. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jan;92(Pt 1):67–75. doi: 10.1242/jcs.92.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Moscona A. Role of cell shape in growth control. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):345–349. doi: 10.1038/273345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedkin M., Legg A., Rozengurt E. Antitubulin agents enhance the stimulation of DNA synthesis by polypeptide growth factors in 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3909–3912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. A 130K protein from chicken gizzard: its localization at the termini of microfilament bundles in cultured chicken cells. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. Cytoskeleton-associated cell contacts. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;1(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. J., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor-inducible genes respond differentially to at least two distinct intracellular second messengers. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15302–15308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman B., Harrington M. A., Olashaw N. E., Pledger W. J. Identification of the cellular mechanisms responsible for platelet-derived growth factor induced alterations in cytoplasmic vinculin distribution. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jan;126(1):115–125. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041260116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman B., Pledger W. J. Platelet-derived growth factor-induced alterations in vinculin and actin distribution in BALB/c-3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1031–1040. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A., Duggan K., Buck C., Beckerle M. C., Burridge K. Interaction of plasma membrane fibronectin receptor with talin--a transmembrane linkage. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):531–533. doi: 10.1038/320531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Madri J. A., Folkman J. Endothelial growth factors and extracellular matrix regulate DNA synthesis through modulation of cell and nuclear expansion. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 May;23(5):387–394. doi: 10.1007/BF02620997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness P. F., Walsh R. C., Jr Dihydrocytochalasin B disorganizes actin cytoarchitecture and inhibits initiation of DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mol J. A., Kwant M. M., Arnold I. C., Hazewinkel H. A. Elucidation of the sequence of canine (pro)-calcitonin. A molecular biological and protein chemical approach. Regul Pept. 1991 Sep 3;35(3):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(91)90082-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka H., Moskowitz M. Arrest of 3T3 cells in G1 phase in suspension culture. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Dec;87(2):213–219. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040870209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price G. J., Jones P., Davison M. D., Patel B., Bendori R., Geiger B., Critchley D. R. Primary sequence and domain structure of chicken vinculin. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj2590453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D. Recent developments in the cell biology of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez Fernández J. L., Ben-Ze'ev A. Regulation of fibronectin, integrin and cytoskeleton expression in differentiating adipocytes: inhibition by extracellular matrix and polylysine. Differentiation. 1989 Dec;42(2):65–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins B. J., Stiles C. D. Serum-inducible genes. Adv Cancer Res. 1989;53:1–32. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., MacDonald-Bravo H., Zerial M., Bravo R. Coordinate induction of fibronectin, fibronectin receptor, tropomyosin, and actin genes in serum-stimulated fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Feb;180(2):537–545. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90080-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Geiger B. Epidermal growth factor induces redistribution of actin and alpha-actinin in human epidermal carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Aug;134(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppä H., Grotendorst G., Seppä S., Schiffmann E., Martin G. R. Platelet-derived growth factor in chemotactic for fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):584–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker M., O'Neill C., Berryman S., Waxman V. Anchorage and growth regulation in normal and virus-transformed cells. Int J Cancer. 1968 Sep 15;3(5):683–693. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar F., Geiger B., Ben-Ze'ev A. Cell contact- and shape-dependent regulation of vinculin synthesis in cultured fibroblasts. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):787–791. doi: 10.1038/319787a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Lui G. M., Gospodarowicz D. Morphological appearance, growth behavior and migratory activity of human tumor cells maintained on extracellular matrix versus plastic. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):607–616. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittelsberger S. C., Kleene K., Penman S. Progressive loss of shape-responsive metabolic controls in cells with increasingly transformed phenotype. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):859–866. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagari M., Stephens M., Earp H. S., Herman B. Relationship of cytosolic ion fluxes and protein kinase C activation to platelet-derived growth factor induced competence and growth in BALB/c-3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Apr;139(1):167–174. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]