Abstract
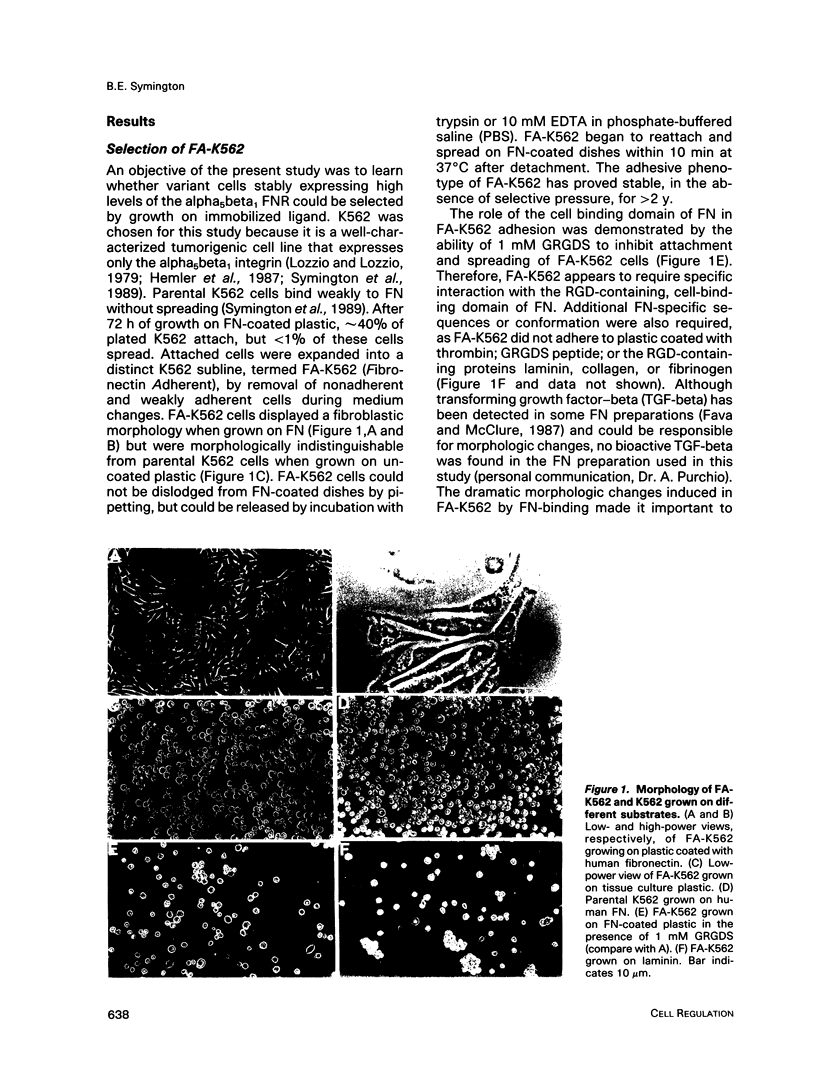
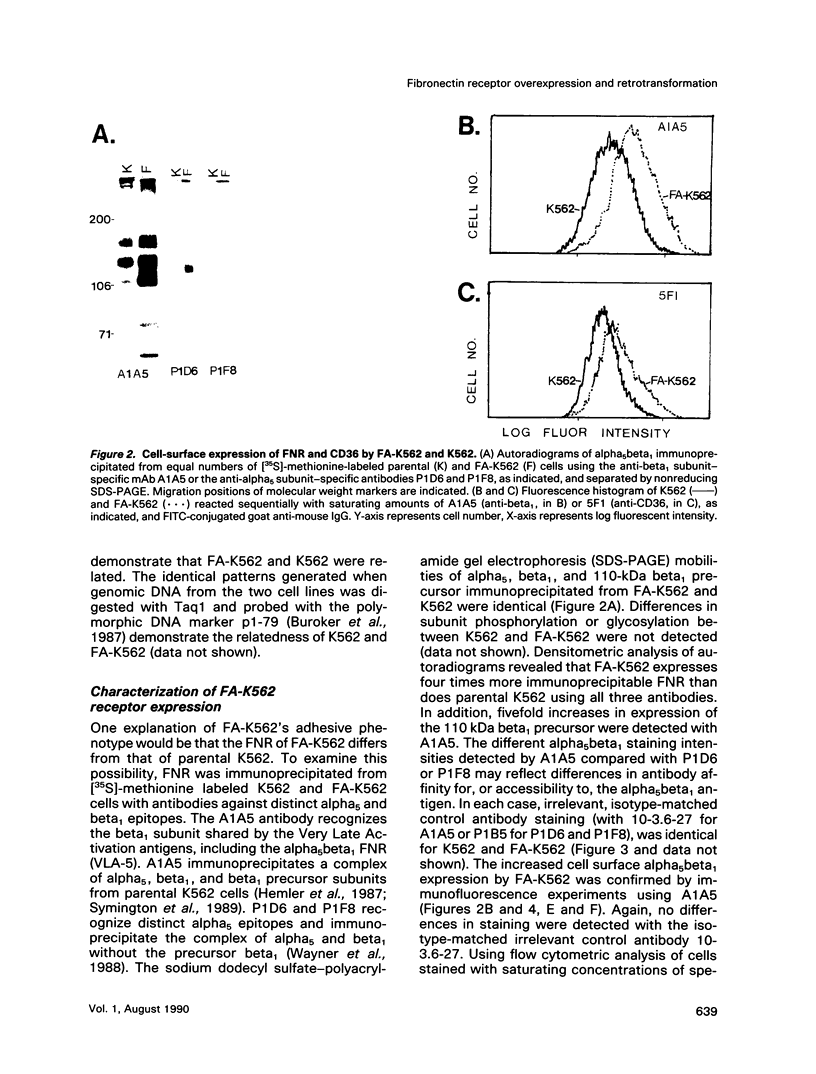
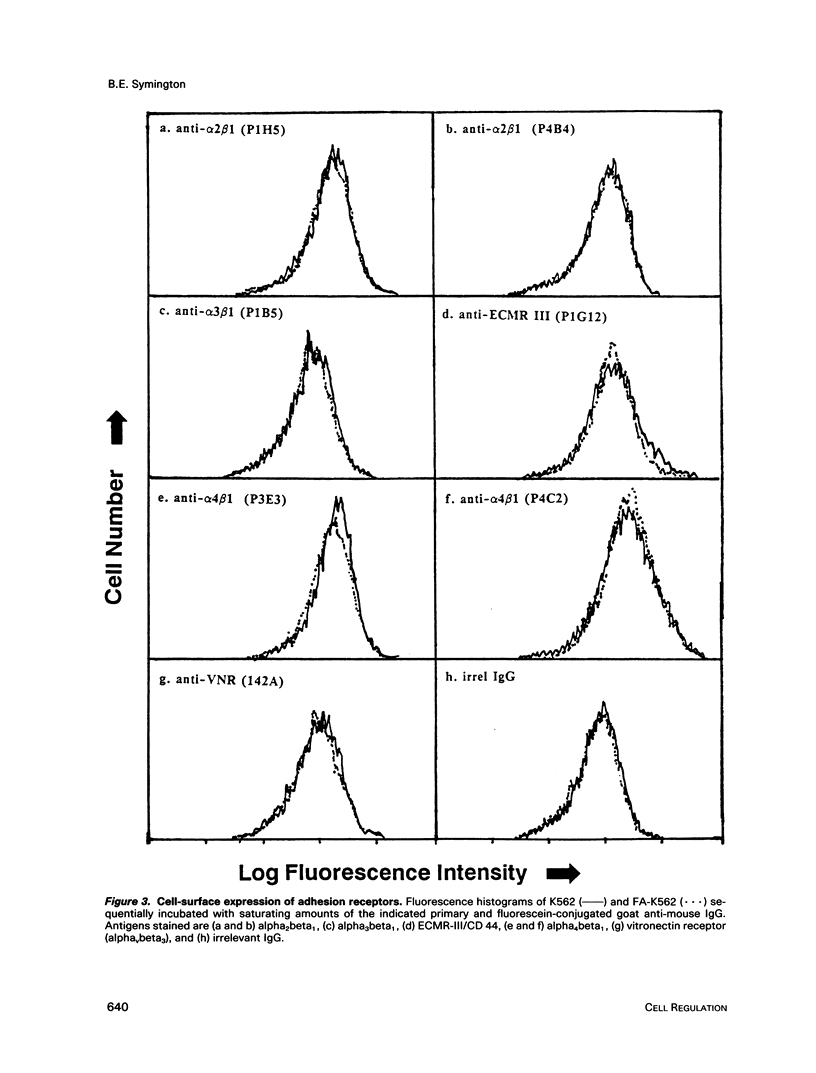
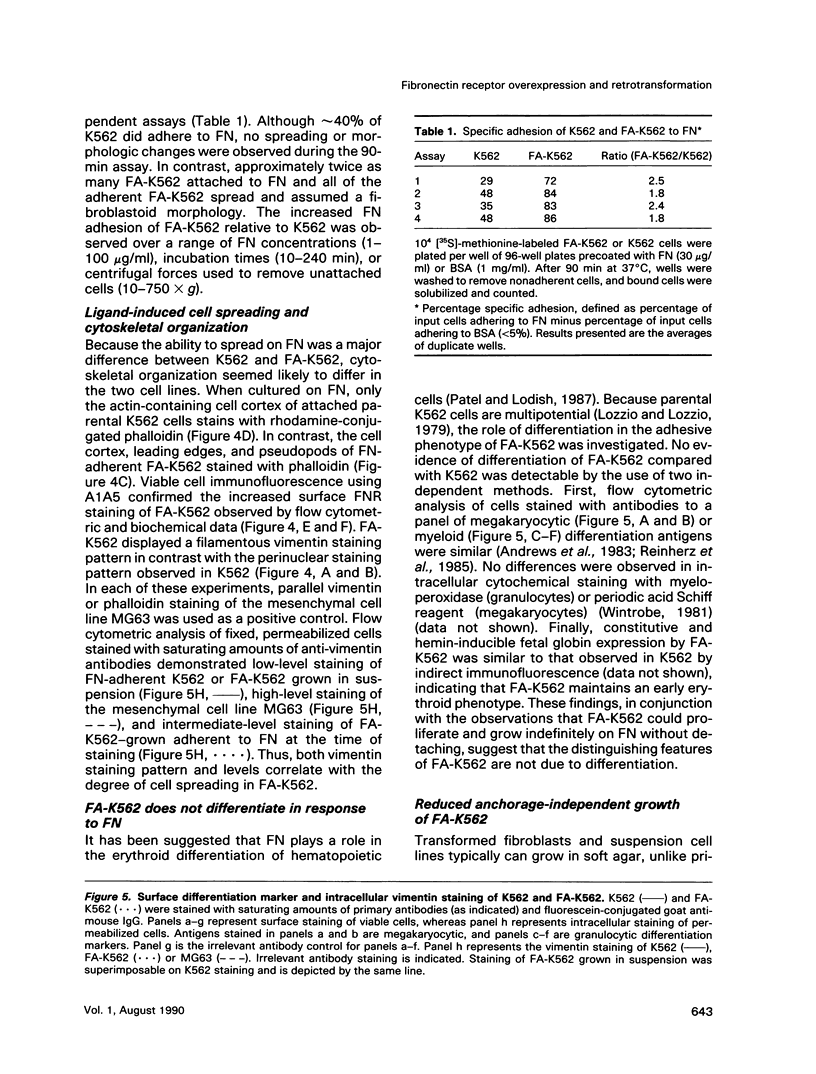
A variant of the K562 erythroleukemia cell line, FA-K562, was selected by cycles of adhesion to solid-phase plasma fibronectin (FN). FA-K562 expresses fourfold more cell-surface alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor (FNR) than parental K562. In addition to expected differences in adhesion to FN, other differences between FA-K562 and K562 implicate this FNR in the regulation of cell growth and morphology. FA-K562 proliferates slowly in liquid culture, its cloning efficiency in soft agar is only approximately 10% compared with approximately 85% for parental K562, and it is nontumorigenic in nude mice. The reduced soft agar growth potential of FA-K562 involves FNR function, because either glycine-arginine-glycine-aspartate-serine (GRGDS) or monoclonal anti-alpha 5 antibody in the agar medium increased cloning efficiency of FA-K562 about fivefold. Morphologically, FN-adherent FA-K562 become fibroblastoid in appearance, assemble filamentous actin, and differ from K562 in vimentin staining intensity and pattern. Soluble GRGDS peptide inhibits both FA-K562 adhesion to FN and the associated cytoskeletal changes. These findings link the alpha 5 beta 1 FNR to both the transformed phenotype and morphology of FA-K562.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. G., Torok-Storb B., Bernstein I. D. Myeloid-associated differentiation antigens on stem cells and their progeny identified by monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1983 Jul;62(1):124–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell M. J., Barcellos-Hoff M. H. The influence of extracellular matrix on gene expression: is structure the message? J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;8:327–343. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_8.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buroker N. E., Bufton L., Surti U., Leppert M., Kumlin E., Sheehy R., Magenis R. E., Litt M. A hypervariable region at the D19S11 locus. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):90–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00283056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedhar S., Argraves W. S., Suzuki S., Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Human osteosarcoma cells resistant to detachment by an Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptide overproduce the fibronectin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1175–1182. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duband J. L., Rocher S., Chen W. T., Yamada K. M., Thiery J. P. Cell adhesion and migration in the early vertebrate embryo: location and possible role of the putative fibronectin receptor complex. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):160–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., McClure D. B. Fibronectin-associated transforming growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1987 May;131(2):184–189. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Ruoslahti E. Elevated levels of the alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor suppress the transformed phenotype of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90098-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M. D., Ohgren Y., Ruoslahti E. Serum spreading factor (vitronectin) is present at the cell surface and in tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4003–4007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Huang C., Schwarz L. The VLA protein family. Characterization of five distinct cell surface heterodimers each with a common 130,000 molecular weight beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3300–3309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. VLA proteins in the integrin family: structures, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:365–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst R., Horwitz A., Buck C., Rohrschneider L. Phosphorylation of the fibronectin receptor complex in cells transformed by oncogenes that encode tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6470–6474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. Preparation from human serum of an alpha-one protein which induces the immediate growth of unadapted cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):297–308. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Olden K., Yamada K. M. A synthetic peptide from fibronectin inhibits experimental metastasis of murine melanoma cells. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.3726541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio B. B., Lozzio C. B. Properties and usefulness of the original K-562 human myelogenous leukemia cell line. Leuk Res. 1979;3(6):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(79)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., MONTAGNIER L. AGAR SUSPENSION CULTURE FOR THE SELECTIVE ASSAY OF CELLS TRANSFORMED BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Jun;23:291–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor J. L., Catimel B., Parmentier S., Clezardin P., Dechavanne M., Leung L. L. Rapid purification and partial characterization of human platelet glycoprotein IIIb. Interaction with thrombospondin and its role in platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):501–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menko A. S., Boettiger D. Occupation of the extracellular matrix receptor, integrin, is a control point for myogenic differentiation. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oquendo P., Hundt E., Lawler J., Seed B. CD36 directly mediates cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum parasitized erythrocytes. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90406-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plantefaber L. C., Hynes R. O. Changes in integrin receptors on oncogenically transformed cells. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90902-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan binds mouse mammary epithelial cells to fibronectin and behaves as a receptor for interstitial matrix. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):423–430. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savagner P., Imhof B. A., Yamada K. M., Thiery J. P. Homing of hemopoietic precursor cells to the embryonic thymus: characterization of an invasive mechanism induced by chemotactic peptides. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2715–2727. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington B. E., Symington F. W., Rohrschneider L. R. Phorbol ester induces increased expression, altered glycosylation, and reduced adhesion of K562 erythroleukemia cell fibronectin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13258–13266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Carter W. G. Identification of multiple cell adhesion receptors for collagen and fibronectin in human fibrosarcoma cells possessing unique alpha and common beta subunits. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1873–1884. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Carter W. G., Piotrowicz R. S., Kunicki T. J. The function of multiple extracellular matrix receptors in mediating cell adhesion to extracellular matrix: preparation of monoclonal antibodies to the fibronectin receptor that specifically inhibit cell adhesion to fibronectin and react with platelet glycoproteins Ic-IIa. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1881–1891. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Garcia-Pardo A., Humphries M. J., McDonald J. A., Carter W. G. Identification and characterization of the T lymphocyte adhesion receptor for an alternative cell attachment domain (CS-1) in plasma fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1321–1330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Tremble P. M., Behrendtsen O., Crowley E., Damsky C. H. Signal transduction through the fibronectin receptor induces collagenase and stromelysin gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):877–889. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







