Abstract
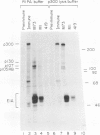
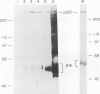
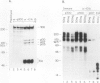
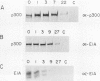
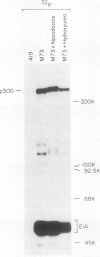
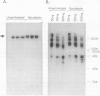
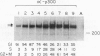
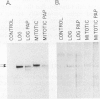
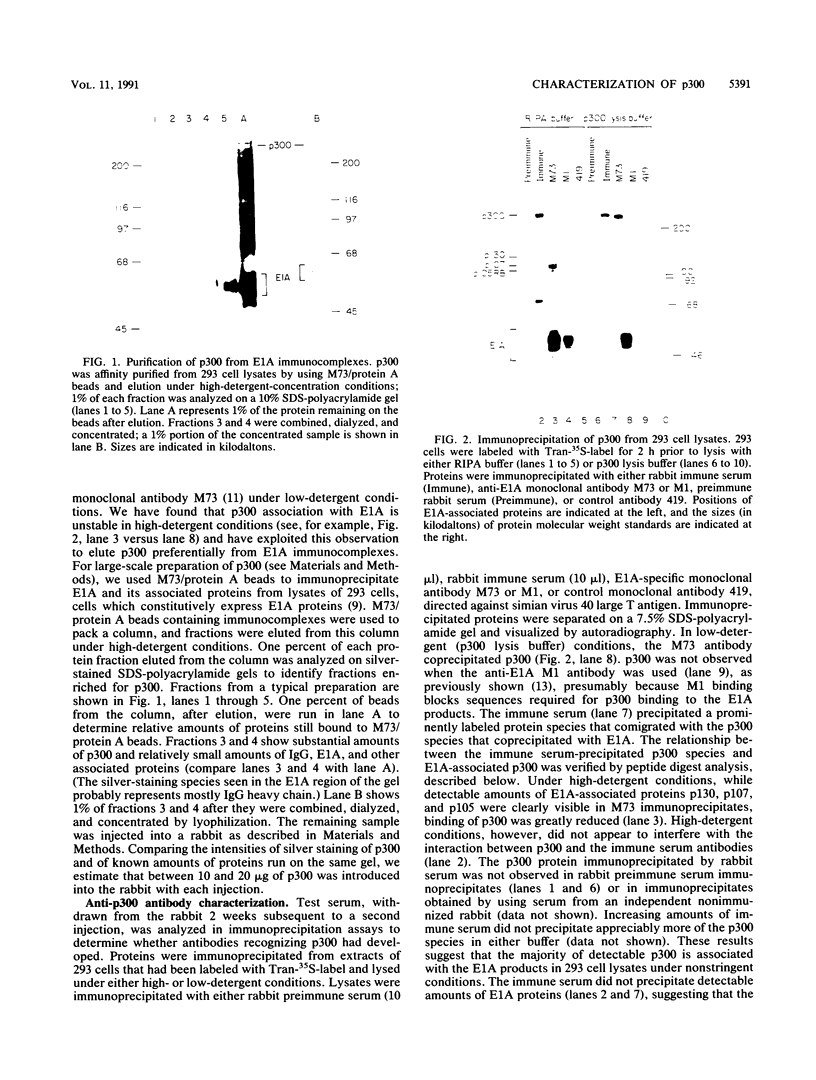
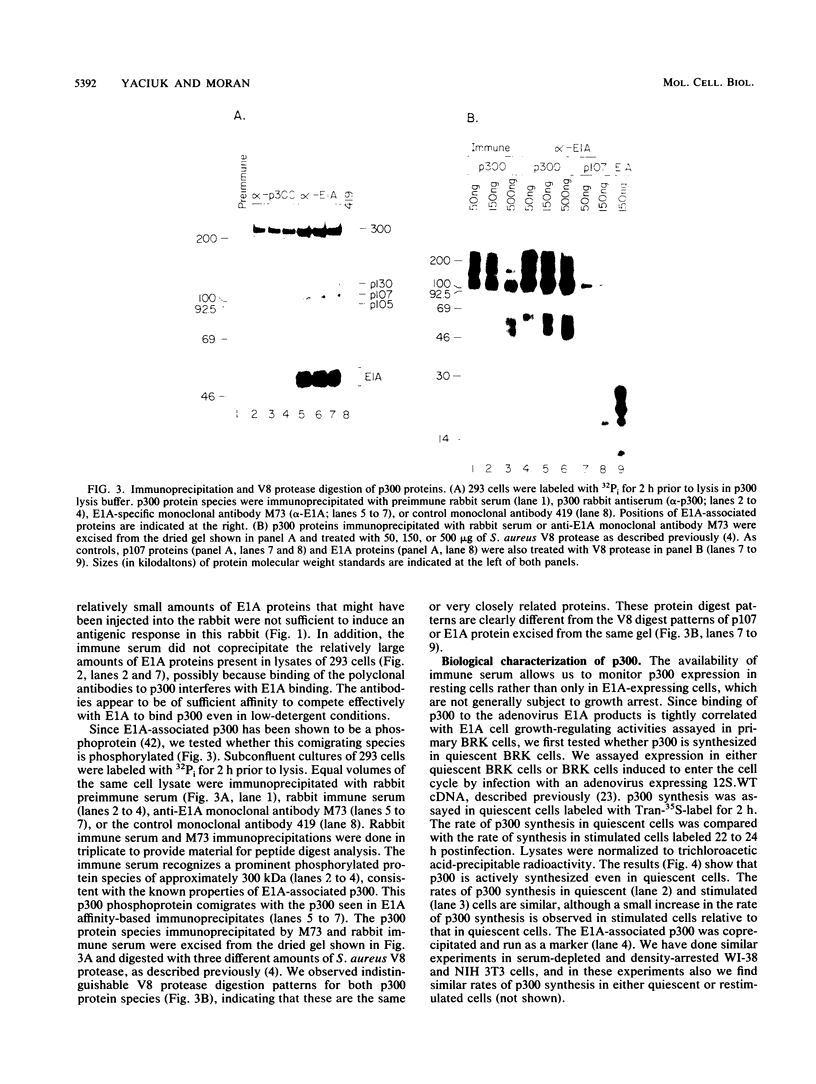
Binding of a 300-kDa host cell protein (p300) is tightly correlated with the ability of the adenovirus E1A products to induce quiescent baby rat kidney cells to proliferate. We have generated rabbit polyclonal antibodies against p300 to characterize this protein further. We have found p300 to be a nuclear phosphoprotein that is actively synthesized in both quiescent and proliferating baby rat kidney cells. In partially purified mitotic cell populations, we observe a form of p300 with decreased electrophoretic mobility in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels that shares a nearly identical partial proteolytic digest pattern with p300. The slower-migrating form of p300 is greatly reduced by treating immune complexes with potato acid phosphatase. The relative stability and presence of p300 even in resting cells suggests that p300 has a basal cell function, but the appearance of differentially modified forms during the cell cycle suggests the possibility that p300 function is modulated specifically in growing cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branton P. E., Rowe D. T. Stabilities and interrelations of multiple species of human adenovirus type 5 early region 1 proteins in infected and transformed cells. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):633–638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.633-638.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchkovich K., Duffy L. A., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated during specific phases of the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Scully P., Shew J. Y., Wang J. Y., Lee W. H. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product is modulated during the cell cycle and cellular differentiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Lynch D., Furukawa Y., Griffin J., Piwnica-Worms H., Huang C. M., Livingston D. M. The product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene has properties of a cell cycle regulatory element. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan C., Jelsma T. N., Howe J. A., Bayley S. T., Ferguson B., Branton P. E. Mapping of cellular protein-binding sites on the products of early-region 1A of human adenovirus type 5. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3955–3959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Localization of the adenovirus E1Aa protein, a positive-acting transcriptional factor, in infected cells infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):829–838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., McCall C., Whyte P., Franza B. R., Jr Human cyclin A and the retinoblastoma protein interact with similar but distinguishable sequences in the adenovirus E1A gene product. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):481–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for adenovirus early region 1A proteins: extensive heterogeneity in early region 1A products. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):533–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.533-546.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Whyte P., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Association of adenovirus early-region 1A proteins with cellular polypeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1579–1589. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. A., Mymryk J. S., Egan C., Branton P. E., Bayley S. T. Retinoblastoma growth suppressor and a 300-kDa protein appear to regulate cellular DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5883–5887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsma T. N., Howe J. A., Evelegh C. M., Cunniff N. F., Skiadopoulos M. H., Floroff M. R., Denman J. E., Bayley S. T. Use of deletion and point mutants spanning the coding region of the adenovirus 5 E1A gene to define a domain that is essential for transcriptional activation. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):494–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsma T. N., Howe J. A., Mymryk J. S., Evelegh C. M., Cunniff N. F., Bayley S. T. Sequences in E1A proteins of human adenovirus 5 required for cell transformation, repression of a transcriptional enhancer, and induction of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):120–130. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90518-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Loewenstein P. M., Green M. R., Green M. Functional domains of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1091–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara K., Cao X. R., Yen A., Chandler S., Driscoll B., Murphree A. L., T'Ang A., Fung Y. K. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of phosphorylation of the human retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.2588006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran B., Zerler B. Interactions between cell growth-regulating domains in the products of the adenovirus E1A oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1756–1764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E. A region of SV40 large T antigen can substitute for a transforming domain of the adenovirus E1A products. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):168–170. doi: 10.1038/334168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Grodzicker T., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Zerler B. Lytic and transforming functions of individual products of the adenovirus E1A gene. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):765–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.765-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Mathews M. B. Multiple functional domains in the adenovirus E1A gene. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90418-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Zerler B., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. Identification of separate domains in the adenovirus E1A gene for immortalization activity and the activation of virus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3470–3480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offringa R., Gebel S., van Dam H., Timmers M., Smits A., Zwart R., Stein B., Bos J. L., van der Eb A., Herrlich P. A novel function of the transforming domain of E1a: repression of AP-1 activity. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochette-Egly C., Fromental C., Chambon P. General repression of enhanson activity by the adenovirus-2 E1A proteins. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):137–150. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. F., Fisher F., Goding C. R., Jones N. C. Mutational analysis of the adenovirus E1a gene: the role of transcriptional regulation in transformation. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2053–2060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02470.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Ziff E. B. The amino-terminal region of the adenovirus serotype 5 E1a protein performs two separate functions when expressed in primary baby rat kidney cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3882–3890. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Berk A. J. Rapid intracellular turnover of adenovirus 5 early region 1A proteins. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):706–710. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.706-710.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. W., Corrigan M., Yaciuk P., Whelan J., Moran E. Analysis of E1A-mediated growth regulation functions: binding of the 300-kilodalton cellular product correlates with E1A enhancer repression function and DNA synthesis-inducing activity. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4421–4427. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4421-4427.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian T., Kuppuswamy M., Nasr R. J., Chinnadurai G. An N-terminal region of adenovirus E1a essential for cell transformation and induction of an epithelial cell growth factor. Oncogene. 1988 Feb;2(2):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a ras cooperation activity is separate from its positive and negative transcription regulatory functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2177–2183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. G., Draetta G., Moran E. E1A induces phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein independently of direct physical association between the E1A and retinoblastoma products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4253–4265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Williamson N. M., Harlow E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaciuk P., Carter M. C., Pipas J. M., Moran E. Simian virus 40 large-T antigen expresses a biological activity complementary to the p300-associated transforming function of the adenovirus E1A gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2116–2124. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Branton P. E. Detection of cellular proteins associated with human adenovirus type 5 early region 1A polypeptides. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):142–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Moran E. Different functional domains of the adenovirus E1A gene are involved in regulation of host cell cycle products. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):821–829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Offringa R., Meijer I., Stein B., Smits A. M., Herrlich P., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J. Differential effects of the adenovirus E1A oncogene on members of the AP-1 transcription factor family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5857–5864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Offringa R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L., Jones N. C., van der Eb A. J. The repression of the growth factor-inducible genes JE, c-myc and stromelysin by adenovirus E1A is mediated by conserved region 1. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1207–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]