Abstract
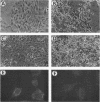
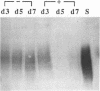
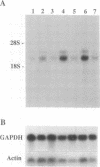
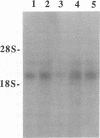
Cell-matrix interactions play an important role in the maintenance of cell shape, supposed to be mediated by the anchorage of cellular cytoskeleton to extracellular matrix via matrix receptors. In this work the expression of one of the known matrix receptors, syndecan, was studied during the hormone-induced change in the phenotype of Shionogi 115 (S115) mouse mammary tumor cells. In the presence of testosterone, when S115 cells express fibroblastic phenotype, they increased their growth rate and became gradually anchorage independent. These cells, however, revealed strong RGDS-dependent binding to fibronectin (FN) but not binding to the heparin-binding domain of FN. Instead, S115 cells growth without testosterone showed epithelial morphology and binding to the heparin-binding domain of FN, suggesting an alteration of syndecan expression in hormone-treated S115 cells. As quantitated by radioimmunoassay and by Western blot, the amounts of both matrix-binding ectodomain of syndecan and syndecan mRNA (2.6 kb) declined in hormone-treated S115 cells. The addition of antiandrogen cyproterone acetate to culture medium opposed the effect of testosterone on syndecan mRNA. We thus propose that the inactivation of syndecan gene and the consequent suppression of syndecan expression is related to the altered adhesion properties, the disappearance of epithelial phenotype, and, on the other hand, to the appearance of transformed-like phenotype in hormone-treated S115 cells.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger F. G., Watson G. Androgen-regulated gene expression. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:51–65. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck C. A., Horwitz A. F. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Skroch P., Weinmann J., Butkeraitis P., Ponta H. DNA sequences outside the receptor-binding sites differently modulate the responsiveness of the mouse mammary tumour virus promoter to various steroid hormones. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1403–1410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee B., Majumdar D., Ozbilen O., Murty C. V., Roy A. K. Molecular cloning and characterization of cDNA for androgen-repressible rat liver protein, SMP-2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):822–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. M., Chen W. T. Fibronectin-degrading proteases from the membranes of transformed cells. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90423-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Smith J. W., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. A novel vitronectin receptor integrin (alpha v beta x) is responsible for distinct adhesive properties of carcinoma cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couchman J. R., Yates J., King R. J., Badley R. A. Changes in microfilament and focal adhesion distribution with loss of androgen responsiveness in cultured mammary tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Jan;41(1):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darbre P. D., King R. J. Steroid hormone regulation of cultured breast cancer cells. Cancer Treat Res. 1988;40:307–341. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-1733-3_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darbre P., Page M., King R. J. Androgen regulation by the long terminal repeat of mouse mammary tumor virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2847–2854. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis N., Corcos D., Kruh J., Kitzis A. A rapid and accurate method for quantitating total RNA transferred during Northern blot analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2354–2354. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P., Vestweber D., Kemler R. Cell-matrix interactions and cell adhesion during development. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:27–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin W. M., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. A cell-surface molecule involved in organ-specific homing of lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):30–34. doi: 10.1038/304030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ham J., Thomson A., Needham M., Webb P., Parker M. Characterization of response elements for androgens, glucocorticoids and progestins in mouse mammary tumour virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5263–5276. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Hayashi M., Boutin E., Cunha G. R., Bernfield M., Trelstad R. L. Hormonal modification of epithelial differentiation and expression of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan in the mouse vaginal epithelium. An immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study. Lab Invest. 1988 Jan;58(1):68–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Hayashi M., Jalkanen M., Firestone J. H., Trelstad R. L., Bernfield M. Immunocytochemistry of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan in mouse tissues. A light and electron microscopic study. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Oct;35(10):1079–1088. doi: 10.1177/35.10.2957423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst R., Horwitz A., Buck C., Rohrschneider L. Phosphorylation of the fibronectin receptor complex in cells transformed by oncogenes that encode tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6470–6474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härkönen P. L., Laaksonen E. I., Valve E. M., Solic N., Darbre P. D. Temperature-sensitive mutants for steroid-sensitive growth of S115 mouse mammary tumor cells. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Feb;186(2):288–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90308-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen M., Nguyen H., Rapraeger A., Kurn N., Bernfield M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans from mouse mammary epithelial cells: localization on the cell surface with a monoclonal antibody. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):976–984. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen M., Rapraeger A., Saunders S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan of mouse mammary epithelial cells is shed by cleavage of its matrix-binding ectodomain from its membrane-associated domain. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):3087–3096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.3087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Cambray G. J., Robinson J. H. The role of receptors in the steroidal regulation of tumour cell proliferation. J Steroid Biochem. 1976 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):869–873. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(76)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koda J. E., Rapraeger A., Bernfield M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans from mouse mammary epithelial cells. Cell surface proteoglycan as a receptor for interstitial collagens. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8157–8162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBaron R. G., Esko J. D., Woods A., Johansson S., Hök M. Adhesion of glycosaminoglycan-deficient chinese hamster ovary cell mutants to fibronectin substrata. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):945–952. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A. Tumor invasion and metastases--role of the extracellular matrix: Rhoads Memorial Award lecture. Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;46(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léger J. G., Montpetit M. L., Tenniswood M. P. Characterization and cloning of androgen-repressed mRNAs from rat ventral prostate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):196–203. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mali M., Jaakkola P., Arvilommi A. M., Jalkanen M. Sequence of human syndecan indicates a novel gene family of integral membrane proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6884–6889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Caravatti M., Robert B., Cohen A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Gros F., Buckingham M. E. Mouse actin messenger RNAs. Construction and characterization of a recombinant plasmid molecule containing a complementary DNA transcript of mouse alpha-actin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. J., Parker M. G. Androgen-regulated expression of a cloned rat prostatic c3 gene transfected into mouse mammary tumor cells. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):495–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90469-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. J., Parker M. G. Effect of androgen on the transcription of rat prostatic binding protein genes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Aug;27(3):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plantefaber L. C., Hynes R. O. Changes in integrin receptors on oncogenically transformed cells. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90902-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poyet P., Labrie F. Comparison of the antiandrogenic/androgenic activities of flutamide, cyproterone acetate and megestrol acetate. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Oct;42(3):283–288. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan of mammary epithelial cells. Protease releases a heparan sulfate-rich ectodomain from a putative membrane-anchored domain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4103–4109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Jalkanen M., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan associates with the cytoskeleton at the basolateral cell surface of mouse mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2683–2696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Jalkanen M., Endo E., Koda J., Bernfield M. The cell surface proteoglycan from mouse mammary epithelial cells bears chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11046–11052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman A. G., Hiipakka R. A., Chang C., Liao S. Androgen repression of the production of a 29-kilodalton protein and its mRNA in the rat ventral prostate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):432–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan binds mouse mammary epithelial cells to fibronectin and behaves as a receptor for interstitial matrix. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):423–430. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S., Jalkanen M., O'Farrell S., Bernfield M. Molecular cloning of syndecan, an integral membrane proteoglycan. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1547–1556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stähli C., Miggiano V., Stocker J., Staehelin T., Häring P., Takács B. Distinction of epitopes by monoclonal antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:242–253. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., Mosher D. F., Rapraeger A. Heparan sulfate-mediated binding of epithelial cell surface proteoglycan to thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2885–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thesleff I., Jalkanen M., Vainio S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan expression correlates with epithelial-mesenchymal interaction during tooth morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1988 Oct;129(2):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90401-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Ruoslahti E. Fibroblast surface antigen produced but not retained by virus-transformed human cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):530–535. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Jalkanen M., Thesleff I. Syndecan and tenascin expression is induced by epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in embryonic tooth mesenchyme. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1945–1953. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Ivatt R., Destree A. T., Hynes R. O. Similarities and differences between the fibronectins of normal and transformed hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11708–11715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Couchman J. R., Johansson S., Hök M. Adhesion and cytoskeletal organisation of fibroblasts in response to fibronectin fragments. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):665–670. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Hök M., Kjellén L., Smith C. G., Rees D. A. Relationship of heparan sulfate proteoglycans to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix of cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1743–1753. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., King R. J. Correlation of growth properties and morphology with hormone responsiveness of mammary tumor cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1981 Jan;41(1):258–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]