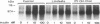Abstract
We have shown previously that experimental modifications of the cellular lipid composition of an insulin-sensitive rat hepatoma cell line (Zajdela Hepatoma Culture, ZHC) affect both binding and biological actions of insulin. Discrepancies between insulin binding and actions implied a postbinding defect, responsible for the observed insulin resistance in lipid-treated cells. To elucidate the mechanism for this defect, we have studied insulin binding and insulin receptor kinase activity in partially purified receptor preparations from ZHC cells grown either in normal medium or in medium supplemented with linoleic acid or 25-hydroxycholesterol. Insulin binding to the lectin-purified insulin receptor showed only a small alteration in receptor affinity for the preparations from lipid-treated cells. Insulin-stimulated autophosphorylation of the beta-subunit of the insulin receptor, as well as insulin-induced phosphorylation of the artificial substrate poly(Glu,Tyr)4:1, was significantly decreased in the preparations from lipid-modified cells. Although differences in basal levels were observed, the magnitude of the insulin-stimulated kinase activity was significantly decreased in receptor preparations from lipid-treated cells. These findings indicate that experimental modification of the lipids of cultured hepatoma cells can produce in insulin receptor kinase activity changes that are proportional to the reduced insulin action observed in these cells.
Full text
PDF
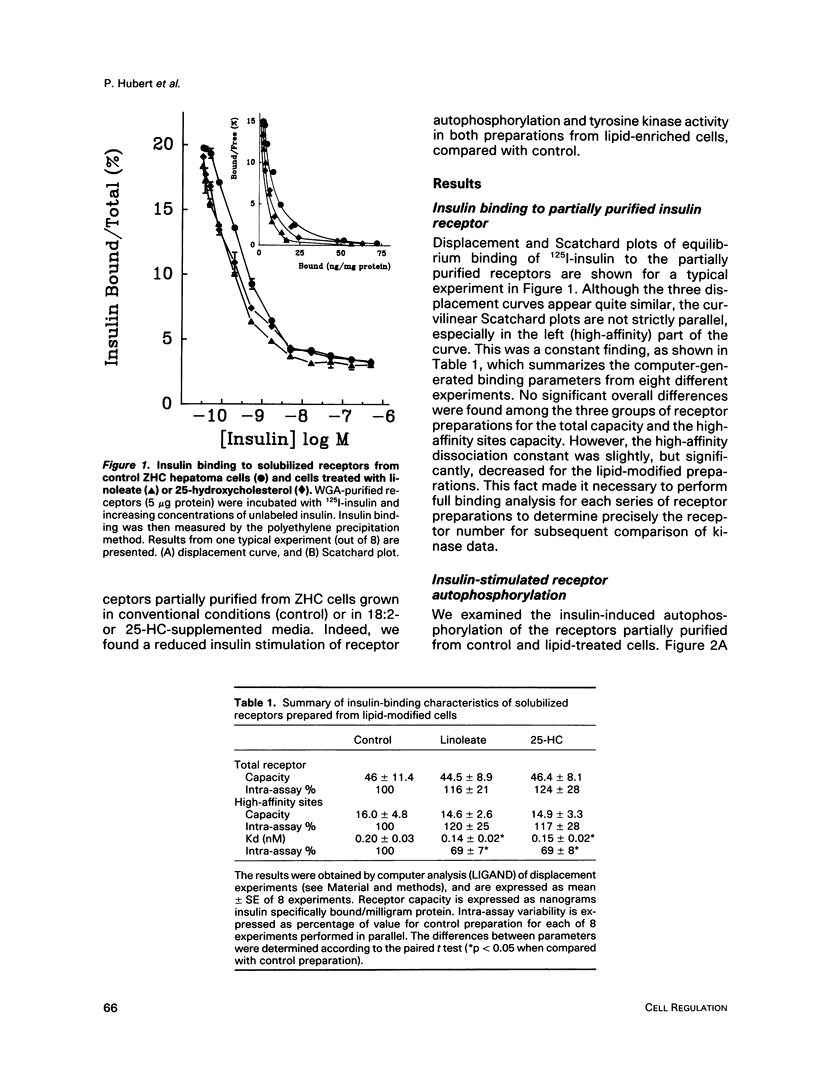
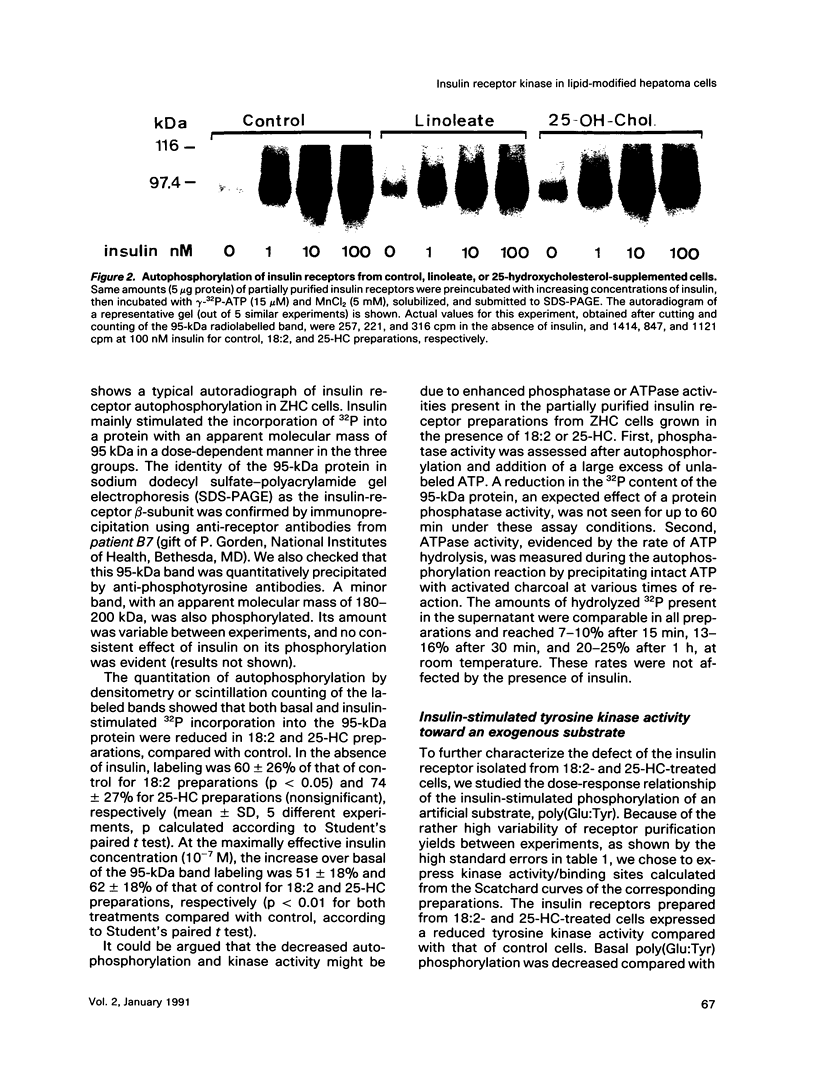
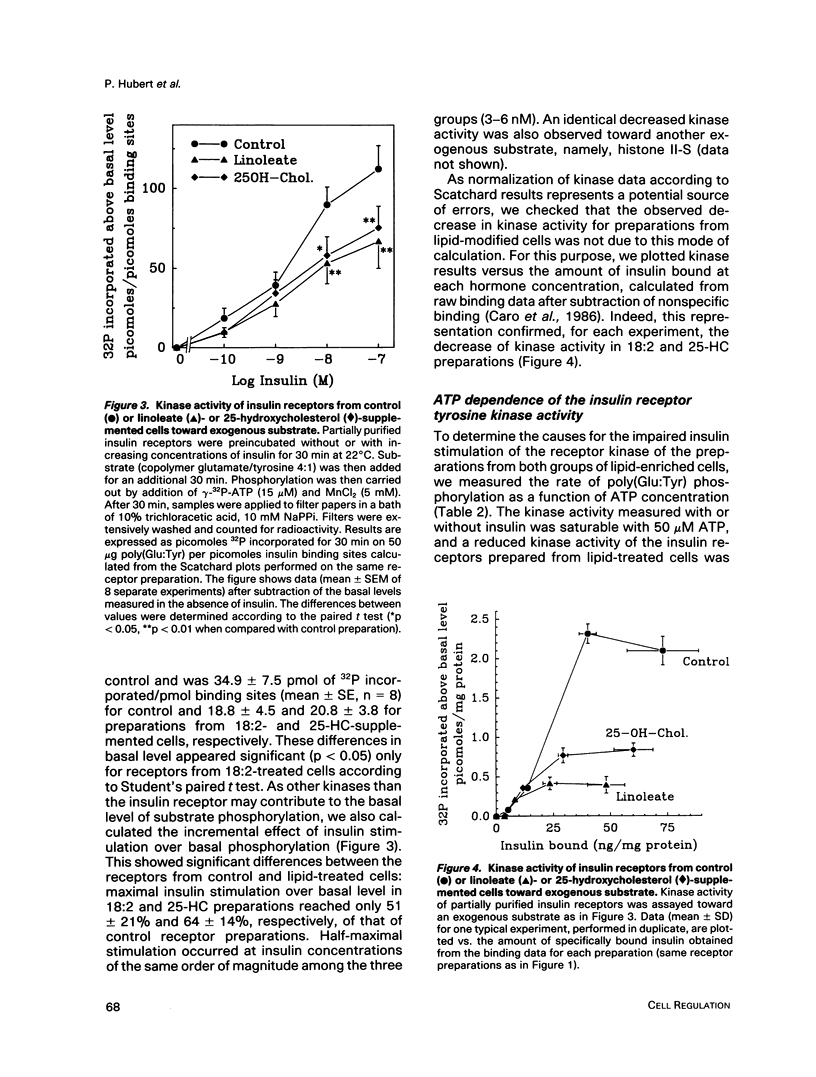




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamo M., LeRoith D., Simon J., Roth J. Effect of altered nutritional states on insulin receptors. Annu Rev Nutr. 1988;8:149–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.08.070188.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amatruda J. M., Finch E. D. Modulation of hexose uptake and insulin action by cell membrane fluidity. The effects of temperature on membrane fluidity, insulin action, and insulin binding. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2619–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballotti R., Lammers R., Scimeca J. C., Dull T., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A., Van Obberghen E. Intermolecular transphosphorylation between insulin receptors and EGF-insulin receptor chimerae. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3303–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner J. A., Frank H. J., Karasic D., Capdeville M. Lipoprotein-induced insulin resistance in aortic endothelium. Diabetes. 1984 Nov;33(11):1039–1044. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.11.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremer E. G., Schlessinger J., Hakomori S. Ganglioside-mediated modulation of cell growth. Specific effects of GM3 on tyrosine phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2434–2440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruneau C., Staedel-Flaig C., Crémel G., Leray C., Beck J. P., Hubert P. Influence of lipid environment on insulin binding in cultured hepatoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 May 18;928(3):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Ittoop O., Pories W. J., Meelheim D., Flickinger E. G., Thomas F., Jenquin M., Silverman J. F., Khazanie P. G., Sinha M. K. Studies on the mechanism of insulin resistance in the liver from humans with noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Insulin action and binding in isolated hepatocytes, insulin receptor structure, and kinase activity. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):249–258. doi: 10.1172/JCI112558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S., Larkins R. G., De Luise M., Melick R. A. The effects of trypsin and phospholipase C on insulin binding and action in the isolated adipocyte. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):535–540. doi: 10.1042/bj1860535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras I., Caro J. The collisional hypothesis of insulin action, receptor internalization and diabetes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Oct;14(10):399–399. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debant A., Ponzio G., Clauser E., Contreres J. O., Rossi B. Receptor cross-linking restores an insulin metabolic effect altered by mutation on tyrosine 1162 and tyrosine 1163. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):14–17. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. J., Ginsberg B. H., Spector A. A. Lipid effects on the binding properties of a reconstituted insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunfeld C., Baird K. L., Kahn C. R. Maintenance of 3T3-L1 cells in culture media containing saturated fatty acids decreases insulin binding and insulin action. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 16;103(1):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedo J. A., Collier E., Watkinson A. Myristyl and palmityl acylation of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):954–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häring H., Obermaier-Kusser B. Insulin receptor kinase defects in insulin-resistant tissues and their role in the pathogenesis of NIDDM. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1989 Aug;5(5):431–441. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610050502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., White M. F. The insulin receptor and the molecular mechanism of insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1151–1156. doi: 10.1172/JCI113711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski A., Gazzano H., Fehlmann M., Van Obberghen E. Dephosphorylation of the hepatic insulin receptor: absence of intrinsic phosphatase activity in purified receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91679-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Grémeaux T., Ballotti R., Van Obberghen E. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase is defective in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant obese mice. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):676–679. doi: 10.1038/315676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. E., Czech M. P. Phospholipid environment alters hormone-sensitivity of the purified insulin receptor kinase. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):829–836. doi: 10.1042/bj2480829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer J., Ota A., Adamo M., LeRoith D. Insulin-sensitive tyrosine kinase is increased in livers of adult obese Zucker rats: correction with prolonged fasting. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):140–148. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Dudley D. T., Pessin J. E., Spector A. A. Phospholipid activation of the insulin receptor kinase: regulation by phosphatidylinositol. FASEB J. 1987 Jul;1(1):55–59. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.1.3038645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watarai T., Kobayashi M., Takata Y., Sasaoka T., Iwasaki M., Shigeta Y. Alteration of insulin-receptor kinase activity by high-fat feeding. Diabetes. 1988 Oct;37(10):1397–1404. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.10.1397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Haring H. U., Kasuga M., Kahn C. R. Kinetic properties and sites of autophosphorylation of the partially purified insulin receptor from hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):255–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y. The insulin receptor: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1989;24(3):217–269. doi: 10.3109/10409238909082554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]