Abstract
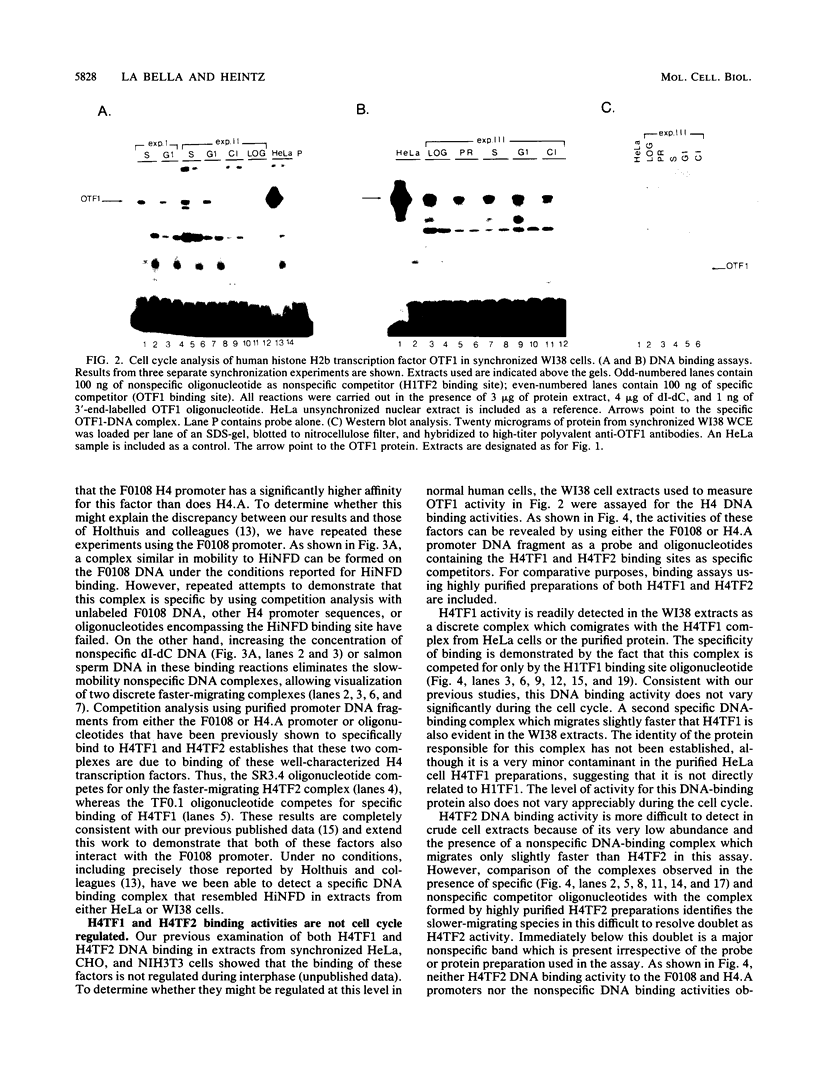
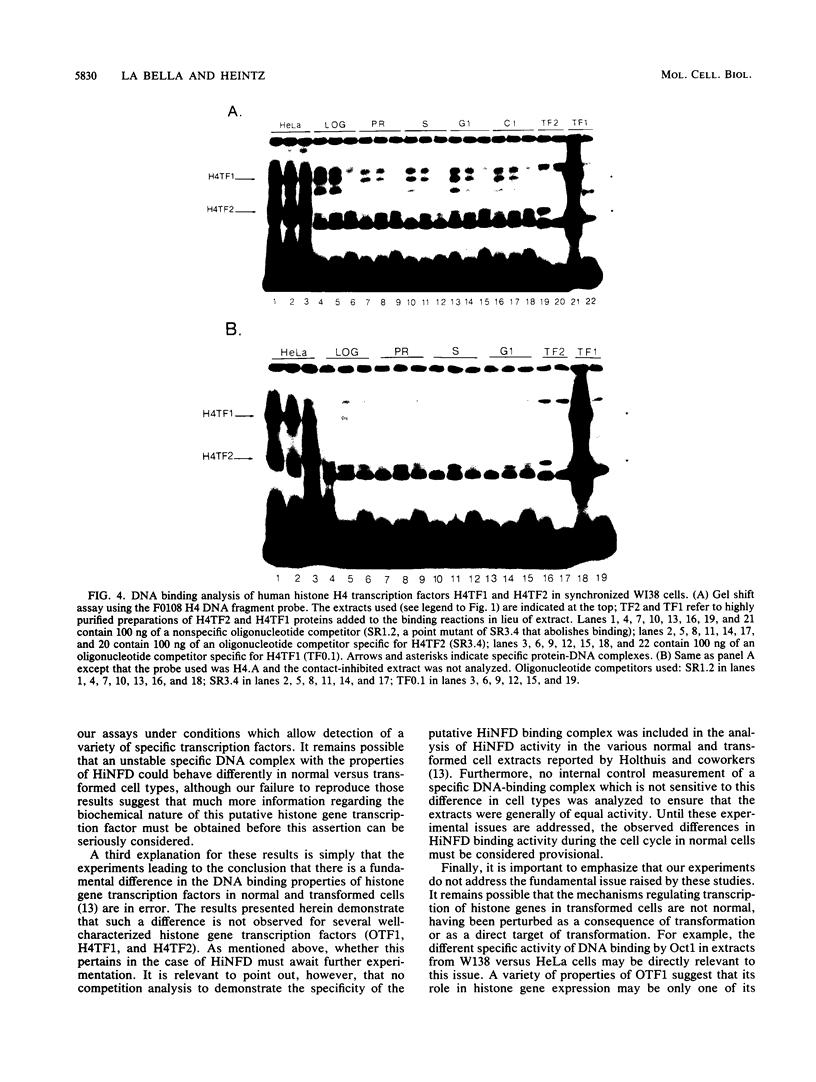
Transcriptional regulation of mammalian histone genes during S phase is achieved through activation of specific factors which interact with subtype-specific histone gene promoter sequences. It has previously been shown that in HeLa cells this induction is not mediated by obligatory changes in the DNA binding activity of histone gene transcription factors as cells progress through the cell cycle. Recently, it has been reported that the DNA binding properties of a putative histone gene transcription factor may be quite different in normal and transformed cells (J. Holthuis, T. A. Owen, A. J. van Wijnen, K. L. Wright, A. Ramsey-Ewing, M. B. Kennedy, R. Carter, S. C. Cosenza, K. J. Soprano, J. B. Lian, J. L. Stein, and G. S. Stein, Science 247:1454-1457, 1990). To determine whether the properties of well-characterized histone gene transcription factors are altered in transformed versus normal cells, we have examined the DNA binding activity of human histone transcription factors during the WI38 (a primary line of normal human fetal lung fibroblasts) cell cycle. The results demonstrate that the properties of Oct1, H4TF1, and H4TF2 are similar in WI38 and HeLa cells and that their DNA binding activities are constitutive during interphase of both normal and transformed cell lines. Although it remains possible that these factors are directly or indirectly perturbed as a result of cellular transformation, it appears unlikely that transformation results in gross changes in DNA binding activity as cells progress toward division.
Full text
PDF



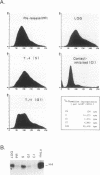
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artishevsky A., Delegeane A. M., Lee A. S. Use of a cell cycle mutant to delineate the critical period for the control of histone mRNA levels in the mammalian cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2364–2369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso O., Heintz N. Regulated expression of mammalian histone H4 genes in vivo requires a trans-acting transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5622–5626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Hanly S. M., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Distinct transcription factors bind specifically to two regions of the human histone H4 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7241–7245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. Purification of the human histone H4 gene-specific transcription factors H4TF-1 and H4TF-2. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1700–1712. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. RNA polymerase II transcription factors H4TF-1 and H4TF-2 require metal to bind specific DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4582–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Wells J. R. Maximal binding levels of an H1 histone gene-specific factor in S-phase correlate with maximal H1 gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4576–4578. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisle A. J., Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F., Johnson L. F. Regulation of histone mRNA production and stability in serum-stimulated mouse 3T6 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):1920–1929. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.1920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallinari P., La Bella F., Heintz N. Characterization and purification of H1TF2, a novel CCAAT-binding protein that interacts with a histone H1 subtype-specific consensus element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1566–1575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F. Rapid reversible changes in the rate of histone gene transcription and histone mRNA levels in mouse myeloma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):351–357. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. The regulation of histone gene expression during the cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 26;1088(3):327–339. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthuis J., Owen T. A., van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Ramsey-Ewing A., Kennedy M. B., Carter R., Cosenza S. C., Soprano K. J., Lian J. B. Tumor cells exhibit deregulation of the cell cycle histone gene promoter factor HiNF-D. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1454–1457. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Sharma A., Lee A. S., Maxson R. Cell cycle regulation of H2b histone octamer DNA-binding activity in Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):869–873. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Bella F., Gallinari P., McKinney J., Heintz N. Histone H1 subtype-specific consensus elements mediate cell cycle-regulated transcription in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1982–1990. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBella F., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Cell-cycle regulation of a human histone H2b gene is mediated by the H2b subtype-specific consensus element. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):32–39. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeks-Wagner D., Hartwell L. H. Normal stoichiometry of histone dimer sets is necessary for high fidelity of mitotic chromosome transmission. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90483-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. B., Segil N., Heintz N. Differential phosphorylation of the transcription factor Oct1 during the cell cycle. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1022–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.1887216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells D. E. Compilation analysis of histones and histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986;14 (Suppl):r119–r149. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.suppl.r119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. A nuclear protein with affinity for the 5' flanking region of a cell cycle dependent human H4 histone gene in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1679–1698. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Human H4 histone gene transcription requires the proliferation-specific nuclear factor HiNF-D. Auxiliary roles for HiNF-C (Sp1-like) and HiNF-A (high mobility group-like). J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):15034–15042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]