Abstract
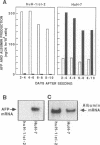
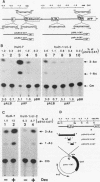
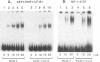
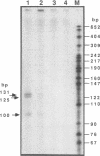
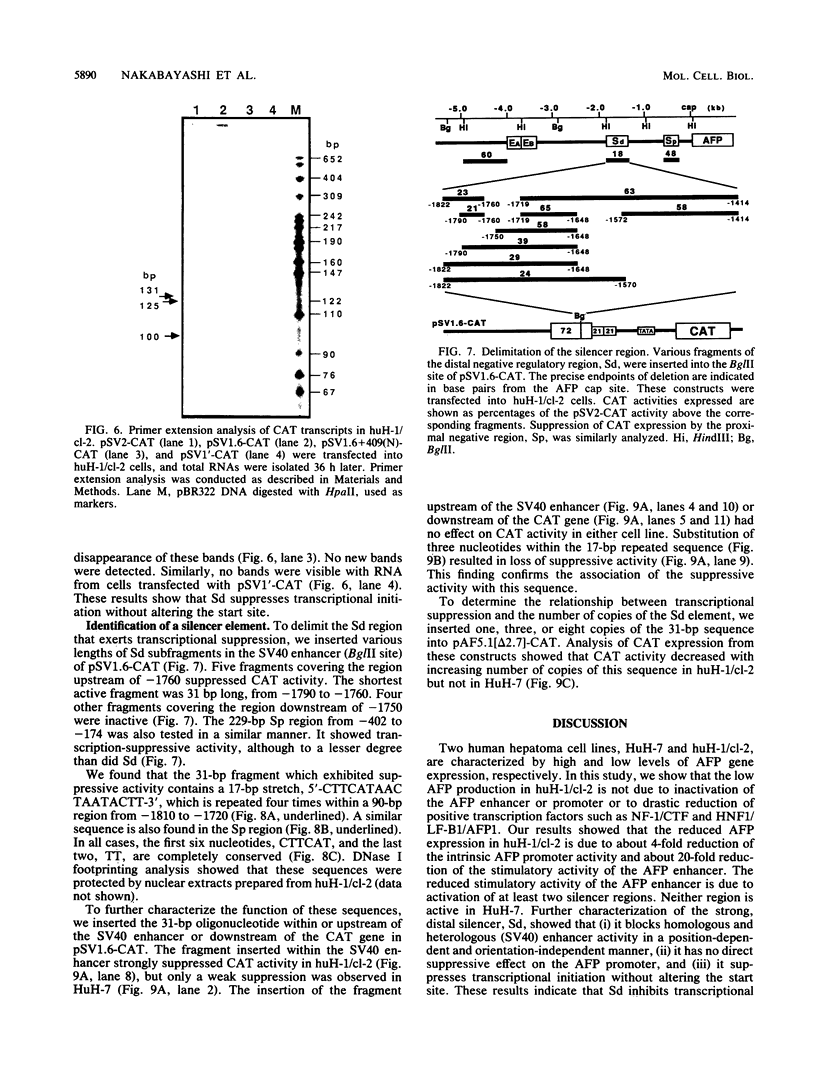
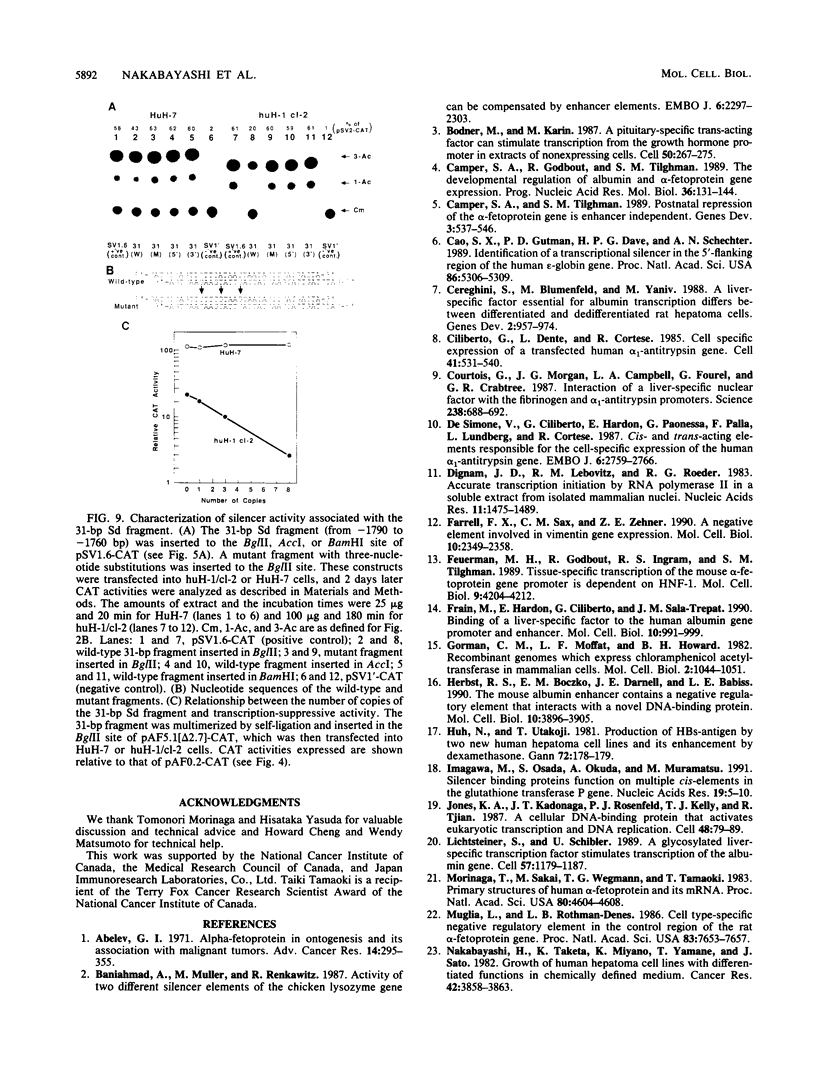
A large percentage of human hepatomas produce alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), but the levels of AFP expression vary greatly among hepatomas. To understand the molecular basis for this variation, we analyzed transcriptional regulatory activities associated with the 5'-flanking region of the AFP gene in two human hepatoma cell lines, HuH-7 and huH-1/cl-2, which produce a high and a low level of AFP, respectively. We found that the low level of AFP production in huH-1/cl-2 is due to the action of at least two silencer regions located between the enhancer and the promoter of the AFP gene. In contrast, no silencer activity is expressed in HuH-7. We identified 5'-CTTCATAACTAATACTT-3' to be a core sequence responsible for the negative regulatory activity. This sequence is repeated four times in a strong, distal silencer region, Sd, whereas one copy is present in a weak, proximal silencer region, Sp. The silencer reduces transcriptional initiation by blocking enhancer activation of the AFP promoter in a position-dependent manner. The silencer functions in the presence of positive transcription factors and may play a key role in developmental repression as well as variable expression of the AFP gene in hepatomas.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelev G. I. Alpha-fetoprotein in ontogenesis and its association with malignant tumors. Adv Cancer Res. 1971;14:295–358. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Muller M., Steiner C., Renkawitz R. Activity of two different silencer elements of the chicken lysozyme gene can be compensated by enhancer elements. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2297–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02504.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Karin M. A pituitary-specific trans-acting factor can stimulate transcription from the growth hormone promoter in extracts of nonexpressing cells. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper S. A., Godbout R., Tilghman S. M. The developmental regulation of albumin and alpha-fetoprotein gene expression. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1989;36:131–143. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper S. A., Tilghman S. M. Postnatal repression of the alpha-fetoprotein gene is enhancer independent. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):537–546. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao S. X., Gutman P. D., Dave H. P., Schechter A. N. Identification of a transcriptional silencer in the 5'-flanking region of the human epsilon-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5306–5309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dente L., Cortese R. Cell-specific expression of a transfected human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):531–540. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Morgan J. G., Campbell L. A., Fourel G., Crabtree G. R. Interaction of a liver-specific nuclear factor with the fibrinogen and alpha 1-antitrypsin promoters. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):688–692. doi: 10.1126/science.3499668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone V., Ciliberto G., Hardon E., Paonessa G., Palla F., Lundberg L., Cortese R. Cis- and trans-acting elements responsible for the cell-specific expression of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2759–2766. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell F. X., Sax C. M., Zehner Z. E. A negative element involved in vimentin gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2349–2358. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerman M. H., Godbout R., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. Tissue-specific transcription of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene promoter is dependent on HNF-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4204–4212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frain M., Hardon E., Ciliberto G., Sala-Trepat J. M. Binding of a liver-specific factor to the human albumin gene promoter and enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):991–999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Boczko E. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. The mouse albumin enhancer contains a negative regulatory element that interacts with a novel DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3896–3905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huh N., Utakoji T. Production of HBs-antigen by two new human hepatoma cell lines and its enhancement by dexamethasone. Gan. 1981 Feb;72(1):178–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Osada S., Okuda A., Muramatsu M. Silencer binding proteins function on multiple cis-elements in the glutathione transferase P gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):5–10. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Schibler U. A glycosylated liver-specific transcription factor stimulates transcription of the albumin gene. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1179–1187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morinaga T., Sakai M., Wegmann T. G., Tamaoki T. Primary structures of human alpha-fetoprotein and its mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4604–4608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muglia L., Rothman-Denes L. B. Cell type-specific negative regulatory element in the control region of the rat alpha-fetoprotein gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7653–7657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Taketa K., Miyano K., Yamane T., Sato J. Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res. 1982 Sep;42(9):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Taketa K., Yamane T., Miyazaki M., Miyano K., Sato J. Phenotypical stability of a human hepatoma cell line, HuH-7, in long-term culture with chemically defined medium. Gan. 1984 Feb;75(2):151–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Taketa K., Yamane T., Oda M., Sato J. Hormonal control of alpha-fetoprotein secretion in human hepatoma cell lines proliferating in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res. 1985 Dec;45(12 Pt 1):6379–6383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Watanabe K., Saito A., Otsuru A., Sawadaishi K., Tamaoki T. Transcriptional regulation of alpha-fetoprotein expression by dexamethasone in human hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):266–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura N., Burt D. W., Paul M., Dzau V. J. Negative control elements and cAMP responsive sequences in the tissue-specific expression of mouse renin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):56–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai M., Morinaga T., Urano Y., Watanabe K., Wegmann T. G., Tamaoki T. The human alpha-fetoprotein gene. Sequence organization and the 5' flanking region. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5055–5060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadaishi K., Morinaga T., Tamaoki T. Interaction of a hepatoma-specific nuclear factor with transcription-regulatory sequences of the human alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5179–5187. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen R. A., Goswami S. K., Mascareno E., Kumar A., Siddiqui M. A. Tissue-specific transcription of the cardiac myosin light-chain 2 gene is regulated by an upstream repressor element. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1676–1685. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J. A nonchromatographic assay for expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in eucaryotic cells. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner C., Muller M., Baniahmad A., Renkawitz R. Lysozyme gene activity in chicken macrophages is controlled by positive and negative regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4163–4178. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urano Y., Watanabe K., Sakai M., Tamaoki T. The human albumin gene. Characterization of the 5' and 3' flanking regions and the polymorphic gene transcripts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3244–3251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacher J., Tilghman S. M. Dominant negative regulation of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene in adult liver. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1732–1735. doi: 10.1126/science.1702902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Saito A., Tamaoki T. Cell-specific enhancer activity in a far upstream region of the human alpha-fetoprotein gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4812–4818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]