Abstract
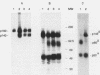
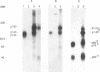
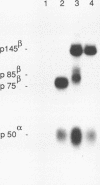
The MET proto-oncogene encodes a transmembrane tyrosine kinase of 190 kDa (p190MET), which has recently been identified as the receptor for hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. p190MET is a heterodimer composed of two disulfide-linked chains of 50 kDa (p50 alpha) and 145 kDa (p145 beta). We have produced four different monoclonal antibodies that are specific for the extracellular domain of the Met receptor. These antibodies immunoprecipitate with p190MET two additional Met proteins of 140 and 130 kDa. The first protein (p140MET) is membrane bound and is composed of an alpha chain (p50 alpha) and an 85-kDa C-terminal truncated beta chain (p85 beta). The second protein (p130MET) is released in the culture supernatant and consists of an alpha chain (p50 alpha) and a 75-kDa C-terminal truncated beta chain (p75 beta). Both truncated forms lack the tyrosine kinase domain. p140MET and p130MET are consistently detected in vivo, together with p190MET, in different cell lines or their culture supernatants. p140MET is preferentially localized at the cell surface, where it is present in roughly half the amount of p190MET. The two C-terminal truncated forms of the Met receptor are also found in stable transfectants expressing the full-length MET cDNA, thus showing that they originate from posttranslational proteolysis. This process is regulated by protein kinase C activation. Together, these data suggest that the production of the C-terminal truncated Met forms may have a physiological role in modulating the Met receptor function.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu A., Raghunath M., Bishayee S., Das M. Inhibition of tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor by a truncated receptor form that binds to EGF: role for interreceptor interaction in kinase regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):671–677. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beguin Y., Huebers H. A., Josephson B., Finch C. A. Transferrin receptors in rat plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):637–640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Faletto D. L., Chan A. M., Kmiecik T. E., Vande Woude G. F., Aaronson S. A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1846706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. S., Park M., Blair D. G., Tainsky M. A., Huebner K., Croce C. M., Vande Woude G. F. Molecular cloning of a new transforming gene from a chemically transformed human cell line. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):29–33. doi: 10.1038/311029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Park M., Le Beau M. M., Robins T. S., Diaz M. O., Rowley J. D., Blair D. G., Vande Woude G. F. The human met oncogene is related to the tyrosine kinase oncogenes. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):385–388. doi: 10.1038/318385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J. Epidermal growth factor-induced truncation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17641–17644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiStefano P. S., Johnson E. M., Jr Identification of a truncated form of the nerve growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):270–274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Ligand and protein kinase C downmodulate the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor by independent mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2890–2896. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga R., Seto Y., Mizushima S., Nagata S. Three different mRNAs encoding human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8702–8706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandino L., Di Renzo M. F., Giordano S., Bussolino F., Comoglio P. M. Protein kinase-c activation inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation of the c-met protein. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):721–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatanaga T., Hwang C. D., Kohr W., Cappuccini F., Lucci J. A., 3rd, Jeffes E. W., Lentz R., Tomich J., Yamamoto R. S., Granger G. A. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor (soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor) for tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin obtained from the serum ultrafiltrates of human cancer patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8781–8784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano S., Di Renzo M. F., Ferracini R., Chiadò-Piat L., Comoglio P. M. p145, a protein with associated tyrosine kinase activity in a human gastric carcinoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3510–3517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano S., Di Renzo M. F., Narsimhan R. P., Cooper C. S., Rosa C., Comoglio P. M. Biosynthesis of the protein encoded by the c-met proto-oncogene. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1383–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano S., Ponzetto C., Di Renzo M. F., Cooper C. S., Comoglio P. M. Tyrosine kinase receptor indistinguishable from the c-met protein. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):155–156. doi: 10.1038/339155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzatti-Haces M., Seth A., Park M., Copeland T., Oroszlan S., Vande Woude G. F. Characterization of the TPR-MET oncogene p65 and the MET protooncogene p140 protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Separate endocytic pathways of kinase-defective and -active EGF receptor mutants expressed in same cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1541–1548. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lee P. L., Lu J., Williams L. T. Diverse forms of a receptor for acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4728–4736. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashles O., Yarden Y., Fischer R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. A dominant negative mutation suppresses the function of normal epidermal growth factor receptors by heterodimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1454–1463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Conway D., Parada L. F., Barbacid M. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase gene codes for a second neurogenic receptor that lacks the catalytic kinase domain. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):647–656. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90476-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno T., Brewer M. T., Baker S. L., Schwartz P. E., King M. W., Hale K. K., Squires C. H., Thompson R. C., Vannice J. L. A second tumor necrosis factor receptor gene product can shed a naturally occurring tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8331–8335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. G., Tepper M. A., Clairmont K. B., Perregaux S. B., Czech M. P. Serum form of the rat insulin-like growth factor II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor is truncated in the carboxyl-terminal domain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3256–3261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemas D. S., Lindberg R. A., Hunter T. trkB, a neural receptor protein-tyrosine kinase: evidence for a full-length and two truncated receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):143–153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley B., Beckmann M. P., March C. J., Idzerda R. L., Gimpel S. D., VandenBos T., Friend D., Alpert A., Anderson D., Jackson J. The murine interleukin-4 receptor: molecular cloning and characterization of secreted and membrane bound forms. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):335–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Vigna E., Ferracini R., Longati P., Gandino L., Prat M., Comoglio P. M. The tyrosine kinase encoded by the MET proto-oncogene is activated by autophosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1793–1803. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Vigna E., Narsimhan R. P., Gaudino G., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. K., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) stimulates the tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor encoded by the proto-oncogene c-MET. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):501–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Weidner K. M., Vigna E., Gaudino G., Bardelli A., Ponzetto C., Narsimhan R. P., Hartmann G., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. K. Scatter factor and hepatocyte growth factor are indistinguishable ligands for the MET receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2867–2878. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M., Dean M., Cooper C. S., Schmidt M., O'Brien S. J., Blair D. G., Vande Woude G. F. Mechanism of met oncogene activation. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90564-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M., Dean M., Kaul K., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Vande Woude G. Sequence of MET protooncogene cDNA has features characteristic of the tyrosine kinase family of growth-factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6379–6383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Giordano S., Peverali F., Della Valle G., Abate M. L., Vaula G., Comoglio P. M. c-met is amplified but not mutated in a cell line with an activated met tyrosine kinase. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):553–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat M., Medico E., Piantino P., Bretti S., Rossini F. P., Comoglio P. M. The monoclonal antibody-defined CAR-3 antigen is a serological marker associated with pancreatic carcinoma. Int J Biol Markers. 1988 Jan-Mar;3(1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat M., Rossino P., Bussolati G., Morra I., Comoglio P. M. Production of monoclonal antibodies for the immunohistochemical detection of gastric carcinomas. Cancer Detect Prev. 1987;10(3-4):293–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Kutny R. M. Structure-function relationships for the IL 2-receptor system. IV. Analysis of the sequence and ligand-binding properties of soluble Tac protein. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):855–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih Y. J., Baynes R. D., Hudson B. G., Flowers C. H., Skikne B. S., Cook J. D. Serum transferrin receptor is a truncated form of tissue receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19077–19081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest P. R., Cooper C. S., Major G. N. The activated human met gene encodes a protein tyrosine kinase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81142-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest P. R., Stratton M. R., Cooper C. S. Structure of the met protein and variation of met protein kinase activity among human tumour cell lines. Br J Cancer. 1988 Jul;58(1):3–7. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno H., Colbert H., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Inhibition of PDGF beta receptor signal transduction by coexpression of a truncated receptor. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):844–848. doi: 10.1126/science.1851331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W., Gill G. N., Spiess J. Production of an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Science. 1984 Apr 20;224(4646):294–297. doi: 10.1126/science.6324343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabrecky J. R., Lam T., McKenzie S. J., Carney W. The extracellular domain of p185/neu is released from the surface of human breast carcinoma cells, SK-BR-3. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1716–1720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]