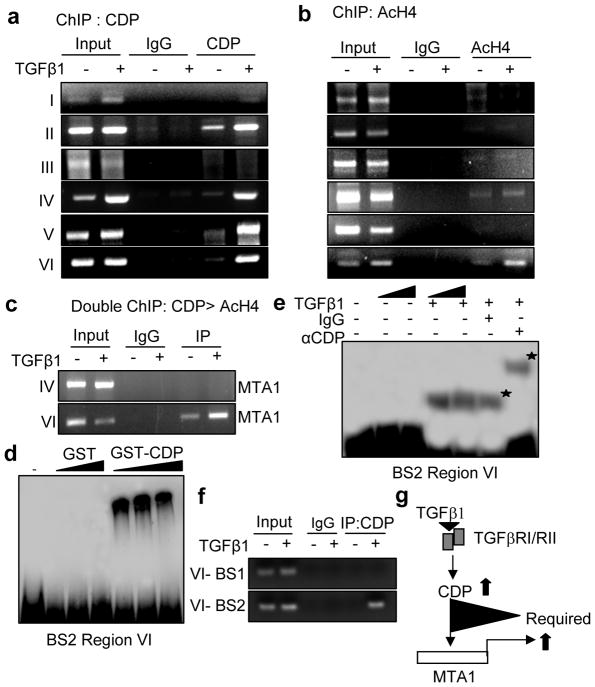
Figure 3.
TGF-β1 induces MTA1 expression through CDP. (a) Recruitment of CDP on to the mouse MTA1 promoter in HC11 cells treated with TGF-β1. HC11 cells stimulated with TGF-β1 were treated with 1% formaldehyde to cross link the histones to DNA and lysed by sonication, immunoprecipitated either by anti-CDP antibody or IgG antibody. The immunoprecipitants were then collected by adding beads, washed, eluted the DNA from the beads and purified DNA was subjected to PCR (b) Recruitment of Acetyl histone H4 (AcH4) on to mouse MTA1 promoter in HC11 cells treated with TGF-β1. ChIP analysis was carried out with AcH4 antibody as described earlier. (c) Recruitment of CDP followed by AcH4 complex onto MTA1 promoter (−3368 to −3604) by sequential double ChIP assay in HC11 cells treated with TGF-β1. The first ChIP was carried out with anti-CDP antibody followed by second ChIP with anti-AcH4 antibody. (d) EMSA analysis of GST-CDP binding to the binding site 2 (BS2) of region VI of mouse MTA1 promoter in the nuclear extracts prepared from TGF-β1 stimulated HC11 cells. (e) EMSA analysis showing super shift with CDP antibody on BS2 of region VI of mouse MTA1 promoter in the nuclear extract prepared from TGF-β1 stimulated HC11 cells. (f) Recruitment of CDP on to the BS2 of region VI of mouse MTA1 promoter in the nuclear extracts prepared from the HC11 cells treated with TGF-β1. (g) Model diagram showing the requirement of CDP for the induction of MTA1 expression by TGF-β1. Panels a–f, cells were treated with 2ng/ml of TGF-β1 for 12 hrs.