Abstract
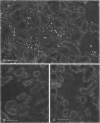
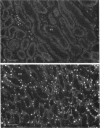
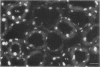
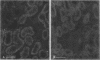
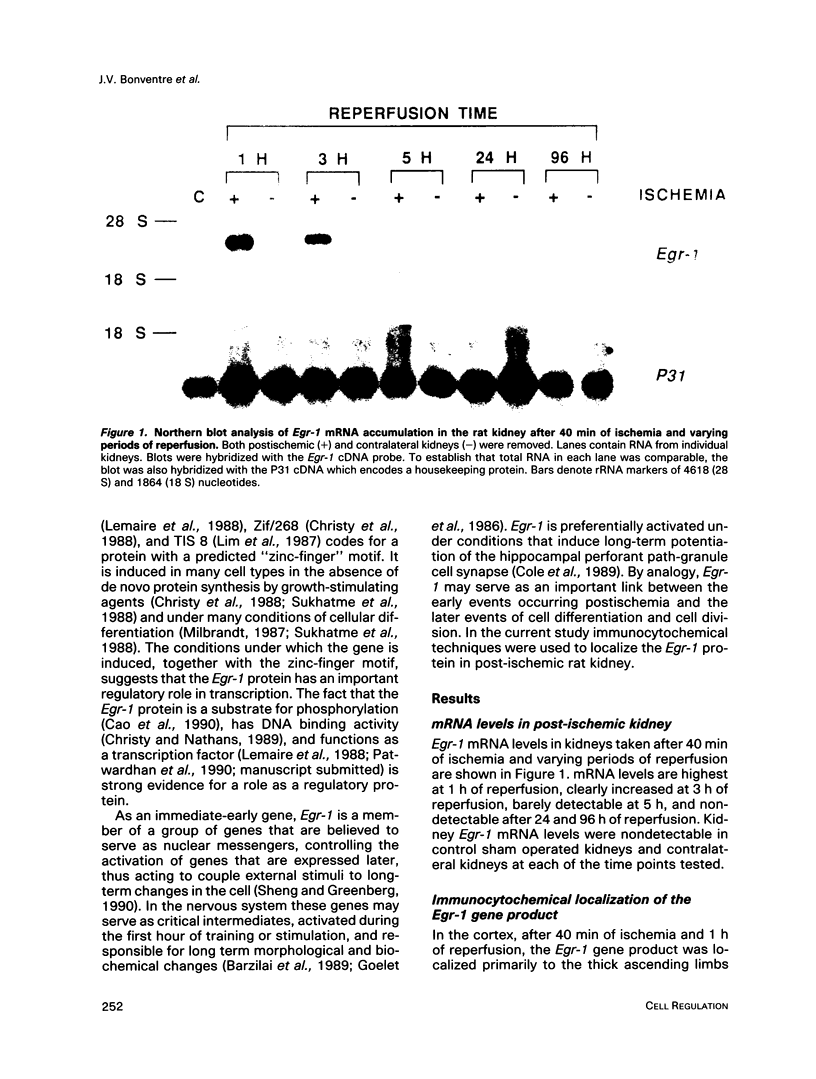
Egr-1 is an "immediate early" gene that is induced by growth factors and agents that induce differentiation and encodes a protein with a "zinc-finger" motif. This protein is believed to be involved in transcriptional regulation. Because the fate of the kidney, and hence the organism, after an ischemic insult is dependent upon cellular repair, differentiation, and proliferation, we examined whether there was expression of the Egr-1 protein after an ischemic insult to the rat kidney. We have previously reported that Egr-1 mRNA accumulates to high levels in mouse kidneys after 30 min of ischemia and 1 h of reperfusion. In the present study, performed in rats, we show that Egr-1 mRNA transiently accumulates to very high levels after 40 min of ischemia and 1 h of reperfusion, is decreased by 3 h, and is nondetectable by 24 h of reperfusion. Reperfusion is required for Egr-1 protein accumulation to occur. The Egr-1 protein was localized by immunohistochemical techniques primarily to the nuclei of the thick ascending limbs and principal cells of the collecting ducts in the cortex and medulla. The subcellular localization was exclusively nuclear. There was some staining of the glomerular tuft and staining was particularly prominent in the parietal epithelial cells. In parallel to the accumulation of Egr-1 mRNA, the expression of the protein was transient and was no longer apparent after 5 h of reperfusion. The Egr-1 protein may play an important role in regulation of the response to ischemia of those segments of the nephron that are highly susceptible to oxygen deprivation and have a high level of intrinsic plasticity. It is possible that this protein may modulate cellular processes important for the ultimate ability of these critical nephron segments to recover from an ischemic insult.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barzilai A., Kennedy T. E., Sweatt J. D., Kandel E. R. 5-HT modulates protein synthesis and the expression of specific proteins during long-term facilitation in Aplysia sensory neurons. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1577–1586. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. G., Madsen K. M., Davis R. G., Tisher C. C. Response of the medullary thick ascending limb to hypothyroidism in the rat. Am J Pathol. 1985 Aug;120(2):215–221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouby N., Bankir L. Effect of high protein intake on sodium, potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase activity in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop in the rat. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 Mar;74(3):319–329. doi: 10.1042/cs0740319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouby N., Bankir L., Trinh-Trang-Tan M. M., Minuth W. W., Kriz W. Selective ADH-induced hypertrophy of the medullary thick ascending limb in Brattleboro rats. Kidney Int. 1985 Sep;28(3):456–466. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezis M., Rosen S., Silva P., Epstein F. H. Renal ischemia: a new perspective. Kidney Int. 1984 Oct;26(4):375–383. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Gluck S., Hartwig J. Structure of the novel membrane-coating material in proton-secreting epithelial cells and identification as an H+ATPase. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1637–1648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X. M., Koski R. A., Gashler A., McKiernan M., Morris C. F., Gaffney R., Hay R. V., Sukhatme V. P. Identification and characterization of the Egr-1 gene product, a DNA-binding zinc finger protein induced by differentiation and growth signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1931–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B. A., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated in mouse 3T3 cells by serum growth factors encodes a protein with "zinc finger" sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7857–7861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B., Nathans D. DNA binding site of the growth factor-inducible protein Zif268. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. J., Saffen D. W., Baraban J. M., Worley P. F. Rapid increase of an immediate early gene messenger RNA in hippocampal neurons by synaptic NMDA receptor activation. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):474–476. doi: 10.1038/340474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelet P., Castellucci V. F., Schacher S., Kandel E. R. The long and the short of long-term memory--a molecular framework. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):419–422. doi: 10.1038/322419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R. Extracellular signals, transcriptional responses and cellular specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Nov;14(11):455–458. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes H. D., Cieslinski D. A., Coimbra T. M., Messana J. M., Galvao C. Epidermal growth factor enhances renal tubule cell regeneration and repair and accelerates the recovery of renal function in postischemic acute renal failure. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1757–1761. doi: 10.1172/JCI114359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Bulger R. E., Trump B. F., Nagle R. B. Effects of transient hypotension on the structure and function of rat kidney. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1976 Nov 2;22(2):121–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02889210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire P., Revelant O., Bravo R., Charnay P. Two mouse genes encoding potential transcription factors with identical DNA-binding domains are activated by growth factors in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4691–4695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim R. W., Varnum B. C., Herschman H. R. Cloning of tetradecanoyl phorbol ester-induced 'primary response' sequences and their expression in density-arrested Swiss 3T3 cells and a TPA non-proliferative variant. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):263–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. A nerve growth factor-induced gene encodes a possible transcriptional regulatory factor. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):797–799. doi: 10.1126/science.3672127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitoris B. A., Hoilien C. A., Dahl R., Ahnen D. J., Wilson P. D., Kim J. Characterization of ischemia-induced loss of epithelial polarity. J Membr Biol. 1988 Dec;106(3):233–242. doi: 10.1007/BF01872161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER J., MacDOWELL M., TRACY A. The pathogenesis of acute renal failure associated with traumatic and toxic injury; renal ischemia, nephrotoxic damage and the ischemic episode. J Clin Invest. 1951 Dec;30(121):1307–1439. doi: 10.1172/JCI102550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette A. J., Malt R. A., Sukhatme V. P., Bonventre J. V. Expression of two "immediate early" genes, Egr-1 and c-fos, in response to renal ischemia and during compensatory renal hypertrophy in mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):766–771. doi: 10.1172/JCI114502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellmayer A., Uedelhoven W. M., Weber P. C., Bonventre J. V. Endogenous non-cyclooxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid modulate growth and mRNA levels of immediate-early response genes in rat mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3800–3807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanley P. F., Rosen M. D., Brezis M., Silva P., Epstein F. H., Rosen S. Topography of focal proximal tubular necrosis after ischemia with reflow in the rat kidney. Am J Pathol. 1986 Mar;122(3):462–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90106-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukhatme V. P., Cao X. M., Chang L. C., Tsai-Morris C. H., Stamenkovich D., Ferreira P. C., Cohen D. R., Edwards S. A., Shows T. B., Curran T. A zinc finger-encoding gene coregulated with c-fos during growth and differentiation, and after cellular depolarization. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90485-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukhatme V. P., Kartha S., Toback F. G., Taub R., Hoover R. G., Tsai-Morris C. H. A novel early growth response gene rapidly induced by fibroblast, epithelial cell and lymphocyte mitogens. Oncogene Res. 1987 Sep-Oct;1(4):343–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodor L., Peleg D., Meyuhas O. P31, a mammalian housekeeping protein encoded by a multigene family containing a high proportion of pseudogenes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 13;826(2-3):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Bernard D. B., Donohoe J. F., Levinsky N. G. Ischemic damage and repair in the rat proximal tubule: differences among the S1, S2, and S3 segments. Kidney Int. 1978 Jul;14(1):31–49. doi: 10.1038/ki.1978.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. R., Honrath U. Inner medullary collecting duct function in ischemic acute renal failure. Clin Invest Med. 1988 Jun;11(3):157–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]