Abstract
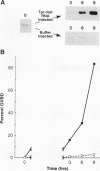
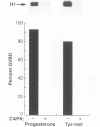
tpr-met, a tyrosine kinase oncogene, is the activated form of the met proto-oncogene that encodes the receptor for hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. The tpr-met product (p65tpr-met) was tested for its ability to induce meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes. While src and abl tyrosine kinase oncogene products have previously been shown to be inactive in this assay, p65tpr-met efficiently induced maturation-promoting factor (MPF) activation and germinal vesicle breakdown (GVBD) together with the associated increase in ribosomal S6 subunit phosphorylation. tpr-met-mediated MPF activation and GVBD was dependent on the endogenous c-mosxe, while the increase in S6 protein phosphorylation was not significantly affected by the loss of mos function. The phosphodiesterase inhibitor 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine inhibits tpr-met-mediated GVBD at concentrations that prevent insulin- but not progesterone-induced oocyte maturation. Moreover, maturation triggered by tpr-met is also inhibited by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. This is the first demonstration that a tyrosine kinase oncogene product, p65tpr-met, can induce meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes and activate MPF through a mos-dependent pathway, possibly the insulin or insulinlike growth factor 1 pathway.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allende C. C., Bravo R., Allende J. E. Comparison of in vivo and in vitro properties of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase of amphibian oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4662–4666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allende C. C., Hinrichs M. V., Santos E., Allende J. E. Oncogenic ras protein induces meiotic maturation of amphibian oocytes in the presence of protein synthesis inhibitors. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 18;234(2):426–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett C. B., Schroetke R. M., Van der Hoorn F. A., Nordeen S. K., Maller J. L. Ha-rasVal-12,Thr-59 activates S6 kinase and p34cdc2 kinase in Xenopus oocytes: evidence for c-mosxe-dependent and -independent pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):310–315. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Broek D., Wigler M. ras proteins can induce meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Kuo C. J., Erikson R. L. Identification of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase regulated by transformation and growth-promoting stimuli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14373–14376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Faletto D. L., Chan A. M., Kmiecik T. E., Vande Woude G. F., Aaronson S. A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1846706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Pelech S. L., Blenis J. Mitogen-activated Swiss mouse 3T3 RSK kinases I and II are related to pp44mpk from sea star oocytes and participate in the regulation of pp90rsk activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4981–4985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Pelech S. L., Krebs E. G. Activation of multiple protein kinases during the burst in protein phosphorylation that precedes the first meiotic cell division in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2009–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I., Nebreda A. R., Yew N., Sass P., Paules R., Santos E., Wigler M., Vande Woude G. F. The ras oncoprotein and M-phase activity. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):74–76. doi: 10.1126/science.1829549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I., Paules R. S., Vande Woude G. F. A characterization of cytostatic factor activity from Xenopus eggs and c-mos-transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):329–335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande A. K., Kung H. F. Insulin induction of Xenopus laevis oocyte maturation is inhibited by monoclonal antibody against p21 ras proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1285–1288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Etr M., Schorderet-Slatkine S., Baulieu E. E. Meiotic maturation in Xenopus laevis oocytes initiated by insulin. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1397–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.472755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Stefanovic D., Blenis J., Erikson R. L., Maller J. L. Antibodies to Xenopus egg S6 kinase II recognize S6 kinase from progesterone- and insulin-stimulated Xenopus oocytes and from proliferating chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3147–3155. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L. Structure, expression, and regulation of protein kinases involved in the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6007–6010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Wu M., Gerhart J. C., Martin G. S. Cell cycle tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 and a microtubule-associated protein kinase homolog in Xenopus oocytes and eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1965–1971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finidori-Lepicard J., Schorderet-Slatkine S., Hanoune J., Baulieu E. E. Progesterone inhibits membrane-bound adenylate cyclase in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):255–257. doi: 10.1038/292255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Pickham K. M., Kanki J. P., Lee B. A., Pena S. V., Donoghue D. J. Xenopus homolog of the mos protooncogene transforms mammalian fibroblasts and induces maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5805–5809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Minshull J., Lohka M., Glotzer M., Hunt T., Maller J. L. Cyclin is a component of maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90599-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelerstein S., Shapira H., Dascal N., Yekuel R., Oron Y. Is a decrease in cyclic AMP a necessary and sufficient signal for maturation of amphibian oocytes? Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi E., Stoker M. Hepatocyte growth factor--scatter factor: mitogen, motogen, and met. Cancer Cells. 1991 Jun;3(6):227–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzatti-Haces M., Seth A., Park M., Copeland T., Oroszlan S., Vande Woude G. F. Characterization of the TPR-MET oncogene p65 and the MET protooncogene p140 protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Wickens M. P. The use of Xenopus oocytes for the expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:370–386. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. E., Cameron S., Toda T., Wigler M., Zoller M. J. Expression in Escherichia coli of BCY1, the regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8636–8642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata T., Kung H. F. Modulation of maturation and ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation in Xenopus oocytes by microinjection of oncogenic ras protein and protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):880–886. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanki J. P., Donoghue D. J. Progression from meiosis I to meiosis II in Xenopus oocytes requires de novo translation of the mosxe protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruppa J., Darmer D., Kalthoff H., Richter D. The phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 from progesterone-stimulated Xenopus laevis oocytes. Kinetic studies and phosphopeptide analysis. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 1;129(3):537–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Foulkes J. G., Erikson E., Baltimore D. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 on serine after microinjection of the Abelson murine leukemia virus tyrosine-specific protein kinase into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):272–276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Krebs E. G. Progesterone-stimulated meiotic cell division in Xenopus oocytes. Induction by regulatory subunit and inhibition by catalytic subunit of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1712–1718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L. Regulation of amphibian oocyte maturation. Cell Differ. 1985 Jun;16(4):211–221. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(85)90570-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J., Wu M., Gerhart J. C. Changes in protein phosphorylation accompanying maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):295–312. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui Y., Clarke H. J. Oocyte maturation. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;57:185–282. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61464-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Arion D., Golsteyn R., Pines J., Brizuela L., Hunt T., Beach D. Cyclin is a component of the sea urchin egg M-phase specific histone H1 kinase. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2275–2282. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miake-Lye R., Newport J., Kirschner M. Maturation-promoting factor induces nuclear envelope breakdown in cycloheximide-arrested embryos of Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):81–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Santos E. Induction by NGF of meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes expressing the trk proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):558–561. doi: 10.1126/science.1850550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Thomas G., Maller J. L. Increased phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2937–2941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opresko L. K., Wiley H. S. Functional reconstitutional of the human epidermal growth factor receptor system in Xenopus oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1661–1671. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M., Dean M., Cooper C. S., Schmidt M., O'Brien S. J., Blair D. G., Vande Woude G. F. Mechanism of met oncogene activation. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90564-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Sanghera J., Pelech S., Aebersold R., Cooper J. A. Tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of homologous protein kinases during oocyte maturation and mitogenic activation of fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2517–2528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. A similar pool of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Xenopus oocytes is stimulated by insulin, insulin-like growth factor 1, and [Val12,Thr59]Ha-ras protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):856–861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L., Gibbs J. B. Transforming ras proteins accelerate hormone-induced maturation and stimulate cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1689–1696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. Inhibition of Xenopus oocyte adenylate cyclase by progesterone and 2',5'-dideoxyadenosine is associated with slowing of guanine nucleotide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7935–7941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. Inhibition of Xenopus oocyte adenylate cyclase by progesterone: a novel mechanism of action. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1985;19:179–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. Progesterone inhibits adenylate cyclase in Xenopus oocytes. Action on the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6368–6373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Daar I., Oskarsson M., Showalter S. D., Vande Woude G. F. The product of the mos proto-oncogene as a candidate "initiator" for oocyte maturation. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):643–646. doi: 10.1126/science.2474853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Oskarsson M., Copeland T., Brumbaugh J., Vande Woude G. F. Function of c-mos proto-oncogene product in meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):519–525. doi: 10.1038/335519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Watanabe N., Vande Woude G. F., Ikawa Y. The c-mos proto-oncogene product is a cytostatic factor responsible for meiotic arrest in vertebrate eggs. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):512–518. doi: 10.1038/342512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. D. The induction of oocyte maturation: transmembrane signaling events and regulation of the cell cycle. Development. 1989 Dec;107(4):685–699. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Erikson R. L., Maller J. L. Microinjection of pp60v-src into Xenopus oocytes increases phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and accelerates the rate of progesterone-induced meiotic maturation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1631–1634. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Otto A. M. The effect of serum, EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin on S6 phosphorylation and the initiation of protein and DNA synthesis. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]