Abstract
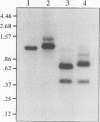
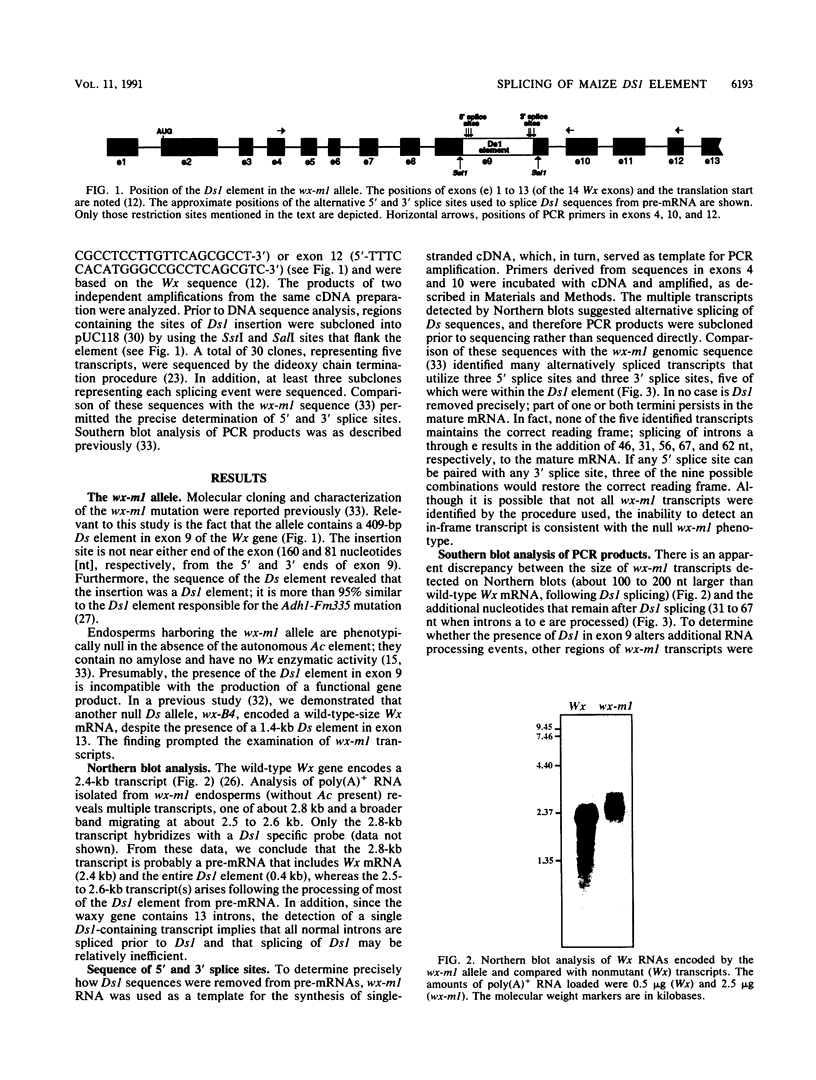
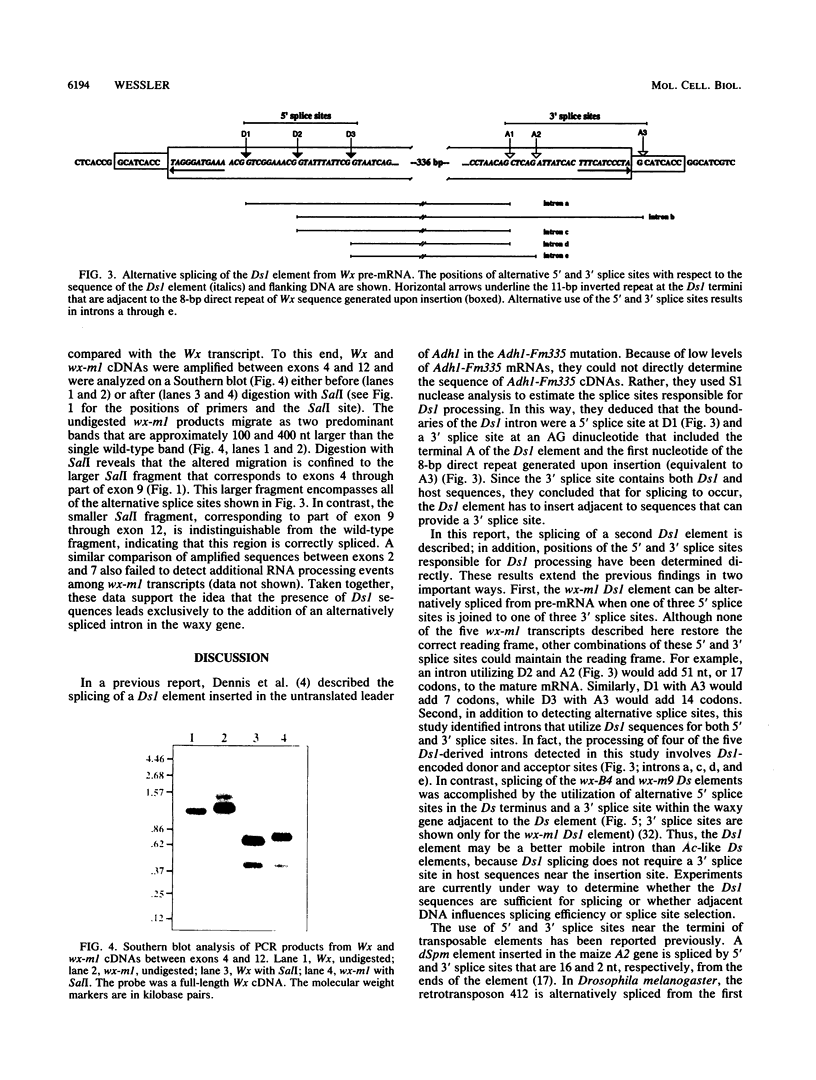
The null wx-ml allele contains a 409-bp Dissociation 1 (Ds1) element in exon 9 of the maize waxy (Wx) gene. In the absence of the autonomous Activator (Ac) element, the Ds1 element cannot transpose, and this allele encodes several Wx transcripts that arise following alternative splicing of Ds1 sequences from Wx pre-mRNA. Splicing involves the utilization of three 5' splice sites and three 3' splice sites. All but one of these splice sites are in Ds1 sequences near the ends of the element. The presence of 5' and 3' splice sites near the Ds1 termini and the element's small size and AT richness are features that distinguish Ds1 elements from all other known Ds elements. It is suggested that these features may enhance the ability of Ds1 to function as a mobile intron.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustin S., Müller M. W., Schweyen R. J. Reverse self-splicing of group II intron RNAs in vitro. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):383–386. doi: 10.1038/343383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Self-splicing of group I introns. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:543–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleaux L., D'Auriol L., Galibert F., Dujon B. Recognition and cleavage site of the intron-encoded omega transposase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6022–6026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Wessler S., Shure M. Isolation of the transposable maize controlling elements Ac and Ds. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridell R. A., Pret A. M., Searles L. L. A retrotransposon 412 insertion within an exon of the Drosophila melanogaster vermilion gene is spliced from the precursor RNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):559–566. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Filipowicz W. The AU-rich sequences present in the introns of plant nuclear pre-mRNAs are required for splicing. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):473–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hehl R., Baker B. Induced transposition of Ds by a stable Ac in crosses of transgenic tobacco plants. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):53–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00330942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Dujon B. An intron-encoded protein is active in a gene conversion process that spreads an intron into a mitochondrial gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambowitz A. M. Infectious introns. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menssen A., Höhmann S., Martin W., Schnable P. S., Peterson P. A., Saedler H., Gierl A. The En/Spm transposable element of Zea mays contains splice sites at the termini generating a novel intron from a dSpm element in the A2 gene. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3051–3057. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07501.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mörl M., Schmelzer C. Integration of group II intron bI1 into a foreign RNA by reversal of the self-splicing reaction in vitro. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):629–636. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90666-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON O. E., RINES H. W. The enzymatic deficiency in the waxy mutant of maize. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Oct 31;9:297–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson O. E., Klein A. S. Characterization of an spm-controlled bronze-mutable allele in maize. Genetics. 1984 Apr;106(4):769–779. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.4.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterman J. C., Schwartz D. Analysis of a controlling-element mutation at the adh locus of maize. Genetics. 1981 Oct;99(2):267–273. doi: 10.1093/genetics/99.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock W. J., Dennis E. S., Gerlach W. L., Sachs M. M., Schwartz D. Insertion and excision of Ds controlling elements in maize. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:347–354. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiefelbein J. W., Raboy V., Fedoroff N. V., Nelson O. E., Jr Deletions within a defective suppressor-mutator element in maize affect the frequency and developmental timing of its excision from the bronze locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4783–4787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. On the origin of RNA splicing and introns. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. D., Gerlach W. L., Peacock W. J., Schwartz D. Molecular analysis of ds controlling element mutations at the adh1 locus of maize. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1265–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4642.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varagona M., Wessler S. R. Implications for the cis-requirements for Ds transposition based on the sequence of the wxB4 Ds element. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Feb;220(3):414–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00391747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. R., Baran G., Varagona M., Dellaporta S. L. Excision of Ds produces waxy proteins with a range of enzymatic activities. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2427–2432. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. R., Baran G., Varagona M. The maize transposable element Ds is spliced from RNA. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):916–918. doi: 10.1126/science.3039661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. R. Phenotypic diversity mediated by the maize transposable elements Ac and Spm. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):399–405. doi: 10.1126/science.2845581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]