Abstract
Neurokinins are a family of neuropeptides with widespread distribution mediating a broad spectrum of physiological actions through three distinct receptor subtypes: NK-1, NK-2, and NK-3. We investigated some of the second messenger and cellular processes under control by the recombinant bovine NK-2 receptor stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. In this system the NK-2 receptor displays its expected pharmacological characteristics, and the physiological agonist neurokinin A stimulates several cellular responses. These include 1) transient inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) formation and Ca2+ mobilization, 2) increased out put of arachidonic acid and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), 3) enhanced cyclic AMP (cAMP) generation, 4) increased de novo DNA synthesis, and 5) an induction of the "immediate early" genes c-fos and c-jun. Although NK-2 receptor-mediated IP3 formation involves activation of a pertussis toxin-insensitive G-protein, increased cAMP production is largely a secondary response and can be at least partially attributed to autocrine stimulation by endogenously generated eicosanoids, particularly PGE2. This is the first demonstration that a single recombinant neurokinin receptor subtype can regulate, either directly or indirectly, multiple signal transduction pathways and suggests several potential important mediators of neurokinin actions under physiological conditions.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J., Burch R. M., Jelsema C. L. Receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase A2 via GTP-binding proteins: arachidonic acid and its metabolites as second messengers. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Mar;11(3):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capponi A. M., Lew P. D., Jornot L., Vallotton M. B. Correlation between cytosolic free Ca2+ and aldosterone production in bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells. Evidence for a difference in the mode of action of angiotensin II and potassium. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8863–8869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate R. L., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Tizard R., Farber N. M., Cheung A., Ninfa E. G., Frey A. Z., Gash D. J., Chow E. P. Isolation of the bovine and human genes for Müllerian inhibiting substance and expression of the human gene in animal cells. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):685–698. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90783-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin B. R., Brann M. R., Buckley N. J., Ma A. L., Bonner T. I., Axelrod J. Stimulation of arachidonic acid release and inhibition of mitogenesis by cloned genes for muscarinic receptor subtypes stably expressed in A9 L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8698–8702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Kobilka B. K., Daniel K. W., Nolan R. D., Lapetina E. Y., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Multiple second messenger pathways of alpha-adrenergic receptor subtypes expressed in eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):63–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dam T. V., Escher E., Quirion R. Evidence for the existence of three classes of neurokinin receptors in brain. Differential ontogeny of neurokinin-1, neurokinin-2 and neurokinin-3 binding sites in rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 21;453(1-2):372–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
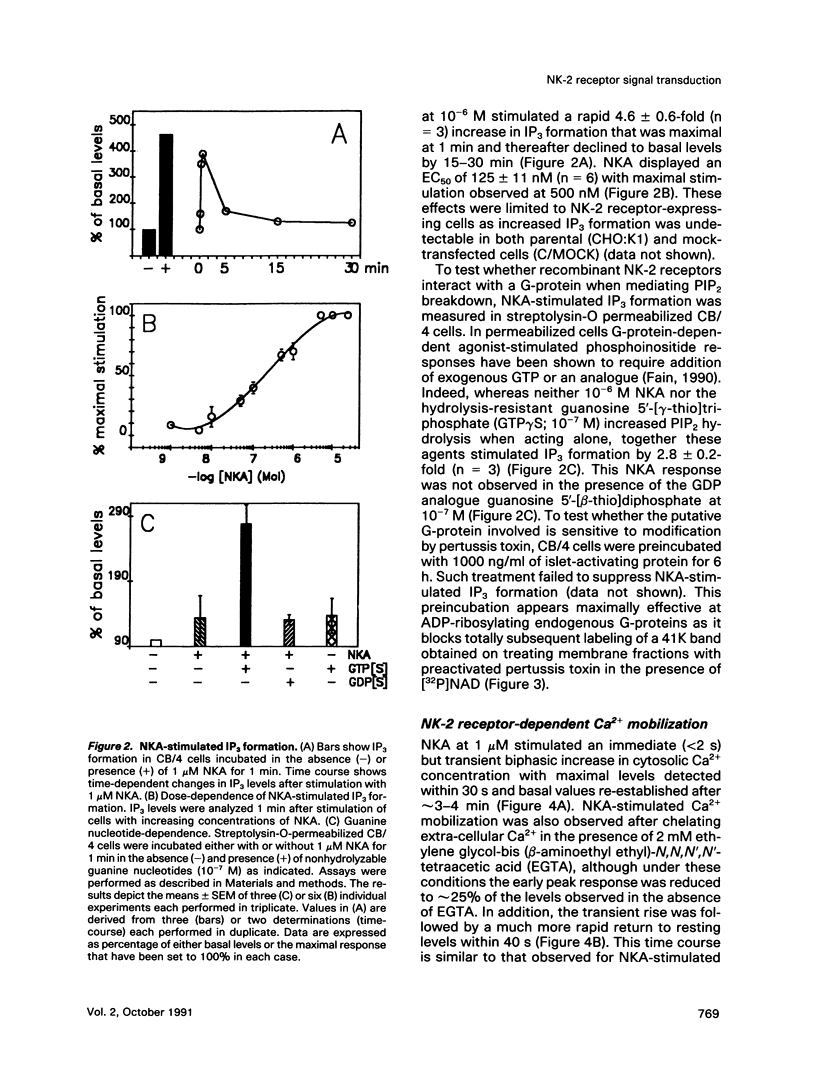
- Fain J. N. Regulation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 12;1053(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90029-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fargin A., Raymond J. R., Regan J. W., Cotecchia S., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Effector coupling mechanisms of the cloned 5-HT1A receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14848–14852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder C. C., Kanterman R. Y., Ma A. L., Axelrod J. A transfected m1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor stimulates adenylate cyclase via phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20356–20362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Nakamura M. I - Prostaglandin hyperalgesia, a cAMP/Ca2+ dependent process. Prostaglandins. 1979 Aug;18(2):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(79)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
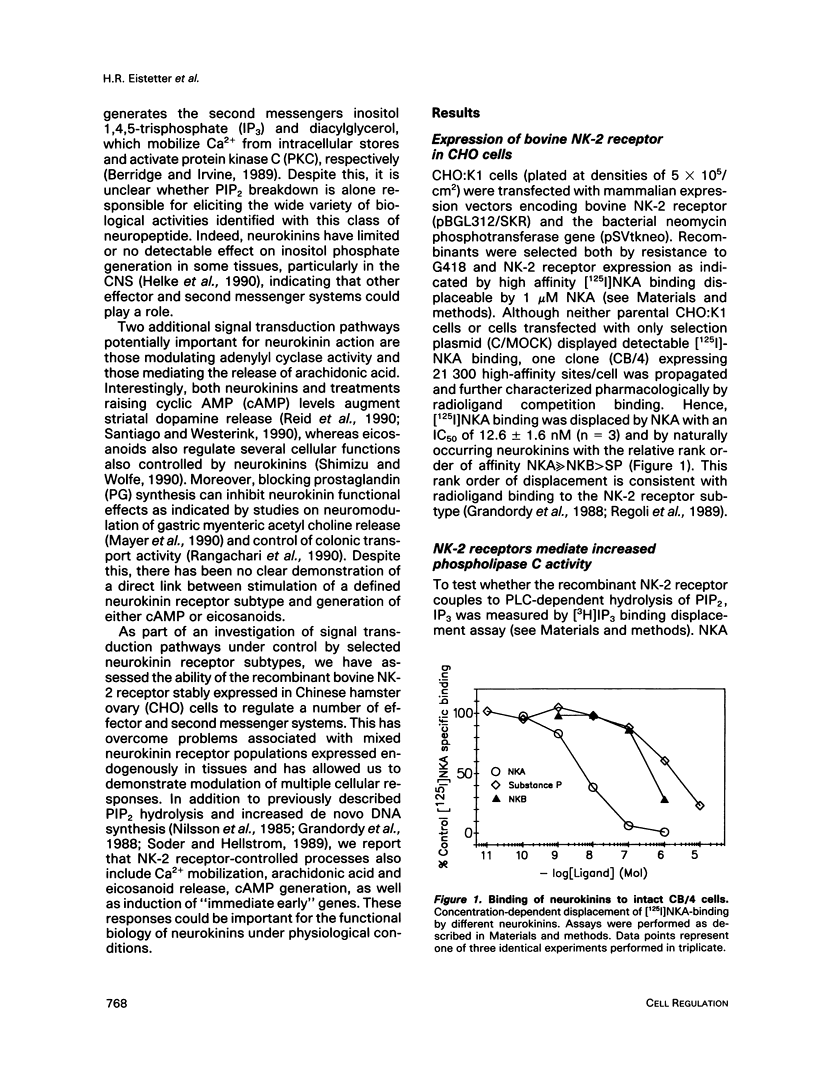
- Grandordy B. M., Frossard N., Rhoden K. J., Barnes P. J. Tachykinin-induced phosphoinositide breakdown in airway smooth muscle and epithelium: relationship to contraction. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):515–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guard S., Watson S. P., Maggio J. E., Too H. P., Watling K. J. Pharmacological analysis of [3H]-senktide binding to NK3 tachykinin receptors in guinea-pig ileum longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus and cerebral cortex membranes. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;99(4):767–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb13004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley M. R., Lee C. M., Michell R. H., Jones L. M. Similar effects of substance P and related peptides on salivation and on phosphatidylinositol turnover in rat salivary glands. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;18(1):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helke C. J., Krause J. E., Mantyh P. W., Couture R., Bannon M. J. Diversity in mammalian tachykinin peptidergic neurons: multiple peptides, receptors, and regulatory mechanisms. FASEB J. 1990 Apr 1;4(6):1606–1615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquot J., Dupuit F., Elbtaouri H., Hinnrasky J., Antonicelli F., Haye B., Puchelle E. Production of lipocortin-like proteins by cultured human tracheal submucosal gland cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 12;274(1-2):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81347-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masu Y., Nakayama K., Tamaki H., Harada Y., Kuno M., Nakanishi S. cDNA cloning of bovine substance-K receptor through oocyte expression system. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):836–838. doi: 10.1038/329836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishima Y., Nakata Y., Segawa T. Comparison of the effects of ions and GTP on substance P binding to membrane-bound and solubilized specific sites. J Neurochem. 1989 Nov;53(5):1428–1434. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb08534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura-Craig M., Smith T. W. Substance P and peripheral inflammatory hyperalgesia. Pain. 1989 Jul;38(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(89)90078-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson J., von Euler A. M., Dalsgaard C. J. Stimulation of connective tissue cell growth by substance P and substance K. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):61–63. doi: 10.1038/315061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta E. G., Ashkenazi A., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Differential regulation of PI hydrolysis and adenylyl cyclase by muscarinic receptor subtypes. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):434–437. doi: 10.1038/334434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangachari P. K., Prior T., McWade D. Epithelial and mucosal preparations from canine colon: responses to substance P. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Sep;254(3):1076–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Dion S., Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Tousignant C., Jukic D., D'Orleans-Juste P., Drapeau G. Selective agonists for receptors of substance P and related neurokinins. Biopolymers. 1989 Jan;28(1):81–90. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid M. S., Herrera-Marschitz M., Hökfelt T., Ohlin M., Valentino K. L., Ungerstedt U. Effects of intranigral substance P and neurokinin A on striatal dopamine release--I. Interactions with substance P antagonists. Neuroscience. 1990;36(3):643–658. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90007-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. F., Aursudkij B., Barnes P. J. Effects of tachykinins on mucus secretion in human bronchi in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 19;174(2-3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90322-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago M., Westerink B. H. Role of adenylate cyclase in the modulation of the release of dopamine: a microdialysis study in the striatum of the rat. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):169–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A. Nuclear protooncogene products: fine-tuned components of signal transduction pathways. Cell Signal. 1990;2(3):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90049-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90106-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigemoto R., Yokota Y., Tsuchida K., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a rat neuromedin K receptor cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Wolfe L. S. Arachidonic acid cascade and signal transduction. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Hepler J. R., Brown K. O., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.1846707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söder O., Hellström P. M. The tachykinins neurokinin A and physalaemin stimulate murine thymocyte proliferation. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;90(1):91–96. doi: 10.1159/000235006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Muca C., Magni M., Albert P., Bunzow J., Meldolesi J., Civelli O. Differential coupling of dopaminergic D2 receptors expressed in different cell types. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in LtK- fibroblasts, hyperpolarization, and cytosolic-free Ca2+ concentration decrease in GH4C1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10320–10326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Lopez-Belmonte J. Interactions between the vascular peptide endothelin-1 and sensory neuropeptides in gastric mucosal injury. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):950–954. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota Y., Sasai Y., Tanaka K., Fujiwara T., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Kakizuka A., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA for rat substance P receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17649–17652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]