Description
A 55-year-old man presented with a 1-day history of vomiting, epigastric pain and bloating. He reported a weight loss of 3 stone over the last year through dieting, leaving him with a body mass index of 17. An abdominal examination revealed upper abdominal tenderness and distension. Blood tests showed a white cell count of 14.9×109/l but no other abnormalities.
An abdominal CT scan showed massive gastric and proximal duodenal dilation (figure 1), with compression of the duodenal lumen between the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) (figure 2). The left renal vein was also compressed by the SMA close to its origin (figure 3), resulting in a left-sided varicocoele. On further questioning, the patient denied experiencing haematuria. Gastroduodenoscopy did not identify any intrinsic obstruction.
Figure 1.
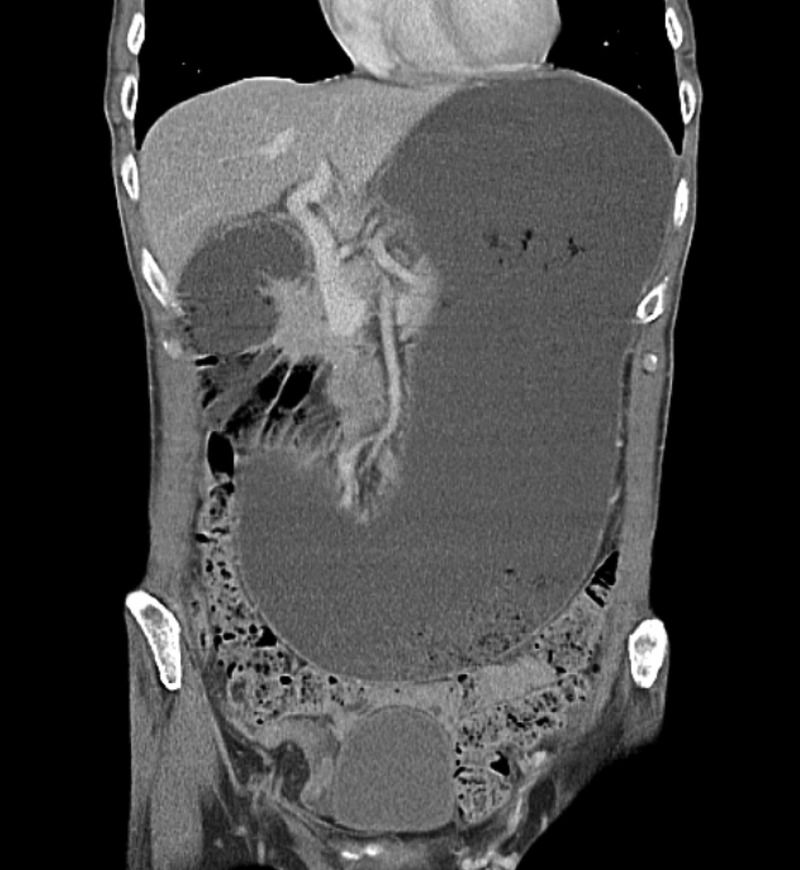
Sagittal CT scan showing massive dilation of the stomach and proximal duodenum.
Figure 2.
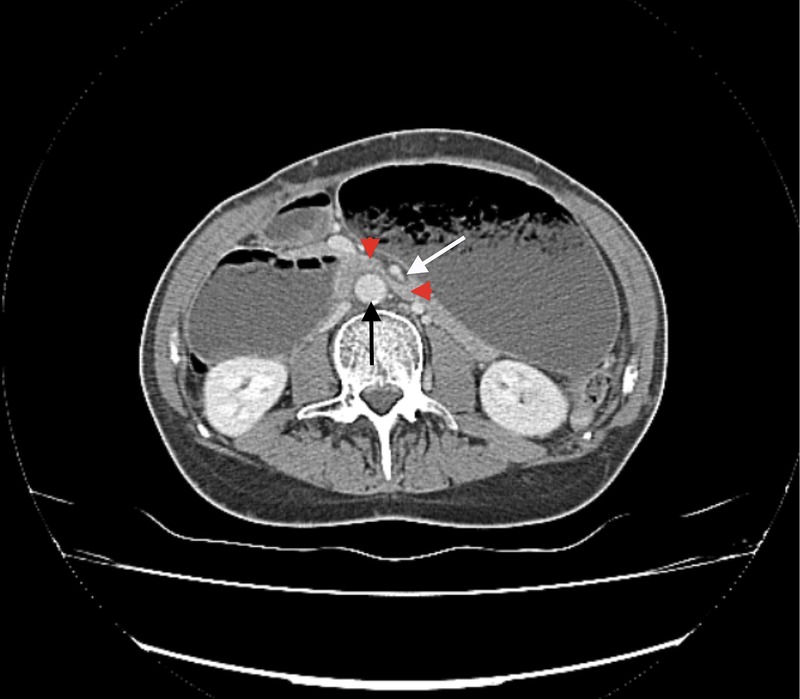
Axial CT section demonstrating duodenal compression (red arrows) between the abdominal aorta (black arrow) and superior mesenteric artery (white arrow).
Figure 3.
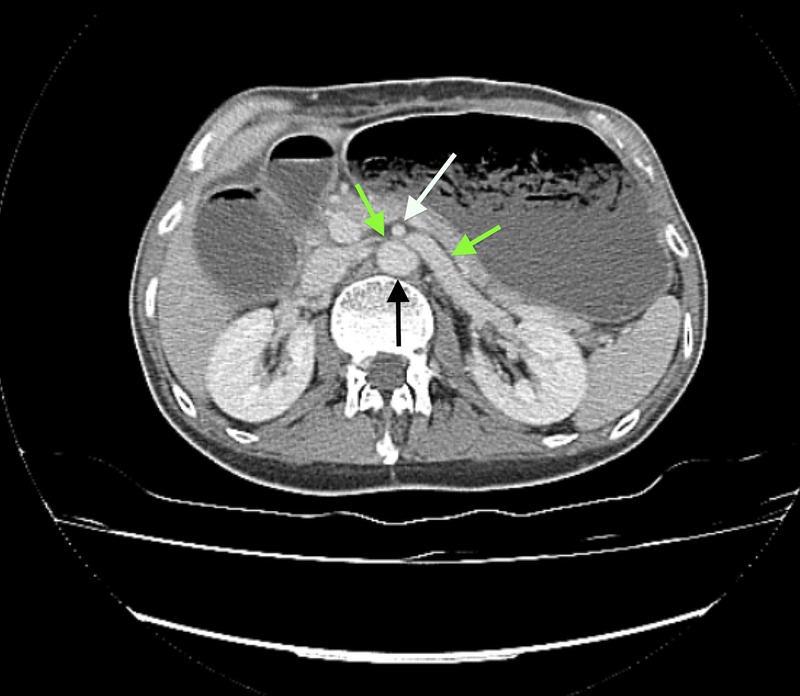
Axial CT section showing proximal dilatation and compression of the left renal vein (green arrows) between the abdominal aorta (black arrow) and superior mesenteric artery (white arrow).
SMA syndrome, or aortomesenteric compression, occurs when an abnormally acute angle is formed between the abdominal aorta and the SMA, causing an extrinsic compression of the third part of the duodenum.1 As in this case, the condition most commonly affects underweight individuals with a history of rapid weight loss. It is characterised by clinical features of high gastrointestinal tract obstruction in the absence of any intrinsic blockage on endoscopy. The treatment involves nutritional support and surgery, in the form of duodenojejunostomy, if required.
The ‘nutcracker phenomenon’ describes compression of the left renal vein between the aorta and the SMA at its origin. Affected patients may be asymptomatic or experience haematuria and pain; a left-sided varicocoele may also be present.2 Conservative management is often sufficient, but endovascular stenting is the treatment of choice if required.
Learning points.
Superior mesenteric artery syndrome is an uncommon cause of high gastrointestinal tract obstruction, and should be suspected when endoscopic examination does not reveal an intrinsic obstruction.
The ‘nutcracker syndrome’ should be considered as an uncommon cause of haematuria, particularly when a left sided varicocoele is also present.
Footnotes
Competing interests: None.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Ahmed AR, Taylor I. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome. Postgrad Med J 1997;73:776–8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kurklinsky AK, Rooke TW. Nutcracker phenomenon and nutcracker syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc 2010;85:552–9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


