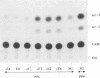
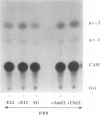
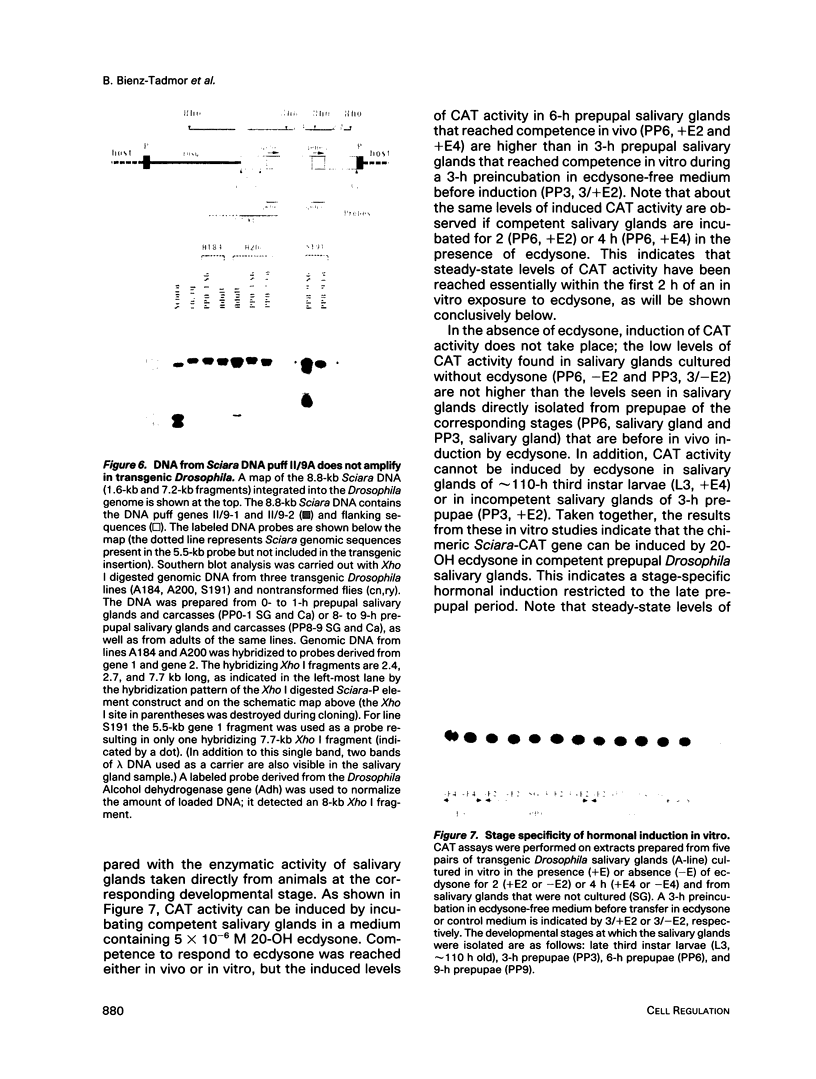
Abstract
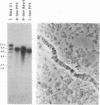
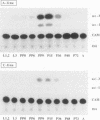
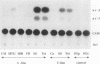
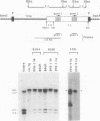
DNA puffs occur in Sciarid salivary gland chromosomes; they are sites of DNA amplification and intense transcription and they appear to encode secreted structural proteins needed for pupation. In this report we have used P-element transformation of Drosophila to study regulation of a Sciara DNA puff gene. We found that a 718-bp promoter fragment of DNA puff gene II/9-1 from Sciara coprophila directs expression of the bacterial reporter gene CAT in late prepupal salivary glands of transgenic Drosophila melanogaster. The identical tissue and analogous stage specificity indicate that some aspects of the ecdysone response are evolutionarily conserved between Drosophila and Sciara. When transgenic salivary glands are cultured in vitro, CAT activity is rapidly induced by ecdysone, suggesting direct control of gene expression by the ecdysone receptor. Putative stage-specific factors limit expression of the chimeric Sciara-CAT gene in transgenic Drosophila to late prepupae but not to third instar larvae when ecdysone titers are also high.
Full text
PDF







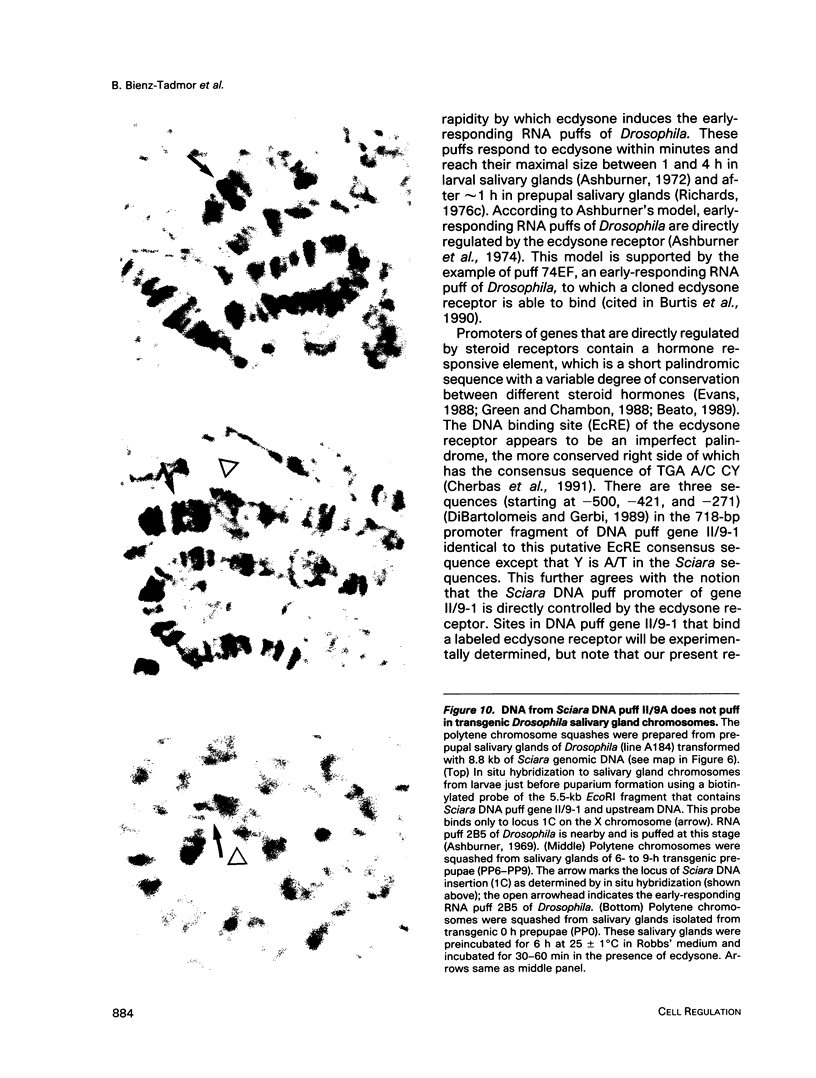




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amabis D. C., Amabis J. M. Effects of ecdysterone in polytene chromosomes of Trichosia pubescens. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Induction of puffs in polytene chromosomes of in vitro cultured salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster by ecdysone and echysone analogues. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 14;230(15):222–224. doi: 10.1038/newbio230222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. I. Autosomal puffing patterns in a laboratory stock of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1967;21(4):398–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00336950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. II. The X-chromosome puffing patterns of D. melanogaster and D. simulans. Chromosoma. 1969;27(1):47–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00326110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. VI. Induction by ecdysone in salivary glands of D. melanogaster cultured in vitro. Chromosoma. 1972;38(3):255–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00290925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Puffs, genes, and hormones revisited. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90205-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Richards G. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. III. Consequences of ecdysone withdrawal. Dev Biol. 1976 Dec;54(2):241–255. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90302-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Dependence upon ecdysone concentration. Dev Biol. 1973 Nov;35(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. II. The effects of inhibitors of protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1974 Jul;39(1):141–157. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(74)80016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainbridge S. P., Bownes M. Staging the metamorphosis of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1981 Dec;66:57–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao A. T., Guild G. M. Molecular analysis of the ecdysterone-inducible 2B5 "early' puff in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):143–150. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04188.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherbas L., Lee K., Cherbas P. Identification of ecdysone response elements by analysis of the Drosophila Eip28/29 gene. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):120–131. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse H. V., Keyl H. G. Extra replications in the "DNA-puffs" of Sciara coprophila. Chromosoma. 1968 Nov;25(3):357–364. doi: 10.1007/BF01183126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse H. V. The role of ecdysone in DNA-puff formation and DNA synthesis in the polytene chromosomes of Sciara coprophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):971–978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBartolomeis S. M., Gerbi S. A. Molecular characterization of DNA puff II/9A genes in Sciara coprophila. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):531–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90129-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GABRUSEWYCZ-GARCIA N. CYTOLOGICAL AND AUTORADIOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN SCIARA COPROPHILA SALIVARY GLAND CHROMOSOMES. Chromosoma. 1964 Aug 14;15:312–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00321517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrusewycz-García N., Kleinfeld R. G. A study of the nucleolar material in Sciara coprophila. J Cell Biol. 1966 May;29(2):347–359. doi: 10.1083/jcb.29.2.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover D. M., Zaha A., Stocker A. J., Santelli R. V., Pueyo M. T., De Toledo S. M., Lara F. J. Gene amplification in Rhynchosciara salivary gland chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2947–2951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Polytene chromosomes. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1987;14:27–58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-47783-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsialis S. A., Spoerel N., Leviten M., Kafatos F. C. A short 5'-flanking DNA region is sufficient for developmentally correct expression of moth chorion genes in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7987–7991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W., Komitopoulou K., Kafatos F. C. Mutants suppressing in trans chorion gene amplification in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3773–3777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks S., Wakimoto B., Spradling A. Replication and expression of an X-linked cluster of Drosophila chorion genes. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):294–305. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90372-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G. P. The control of prepupal puffing patterns in vitro; implications for prepupal ecdysone titres in Drosophilia melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1976 Jan;48(1):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. IV. The mid prepupal period. Dev Biol. 1976 Dec;54(2):256–263. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90303-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. V. The late prepupal puffs. Dev Biol. 1976 Dec;54(2):264–275. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90304-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G. The radioimmune assay of ecdysteroid titres in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Mar;21(3):181–197. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Pelham H. R. An ecdysone response element in the Drosophila hsp27 promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3729–3734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. A. Maintenance of imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster in chemically defined media. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jun;41(3):876–885. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.3.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudkin G. T., Corlette S. L. DISPROPORTIONATE SYNTHESIS OF DNA IN A POLYTENE CHROMOSOME REGION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957 Nov 15;43(11):964–968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.43.11.964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A., Hogness D. S. The E75 ecdysone-inducible gene responsible for the 75B early puff in Drosophila encodes two new members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):204–219. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker A. J., Pavan C. The influence of ecdysterone on gene amplification, DNA synthesis, and puff formation in the salivary gland chromosomes of Rhynchosciara hollaenderi. Chromosoma. 1974 Apr 9;45(3):295–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00283413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Burtis K. C., Hogness D. S. Spatial and temporal patterns of E74 transcription during Drosophila development. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urness L. D., Thummel C. S. Molecular interactions within the ecdysone regulatory hierarchy: DNA binding properties of the Drosophila ecdysone-inducible E74A protein. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90287-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakimoto B. T., Kalfayan L. J., Spradling A. C. Developmentally regulated expression of Drosophila chorion genes introduced at diverse chromosomal positions. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):33–45. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90404-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]