Abstract
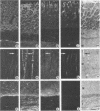
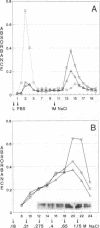
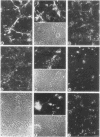
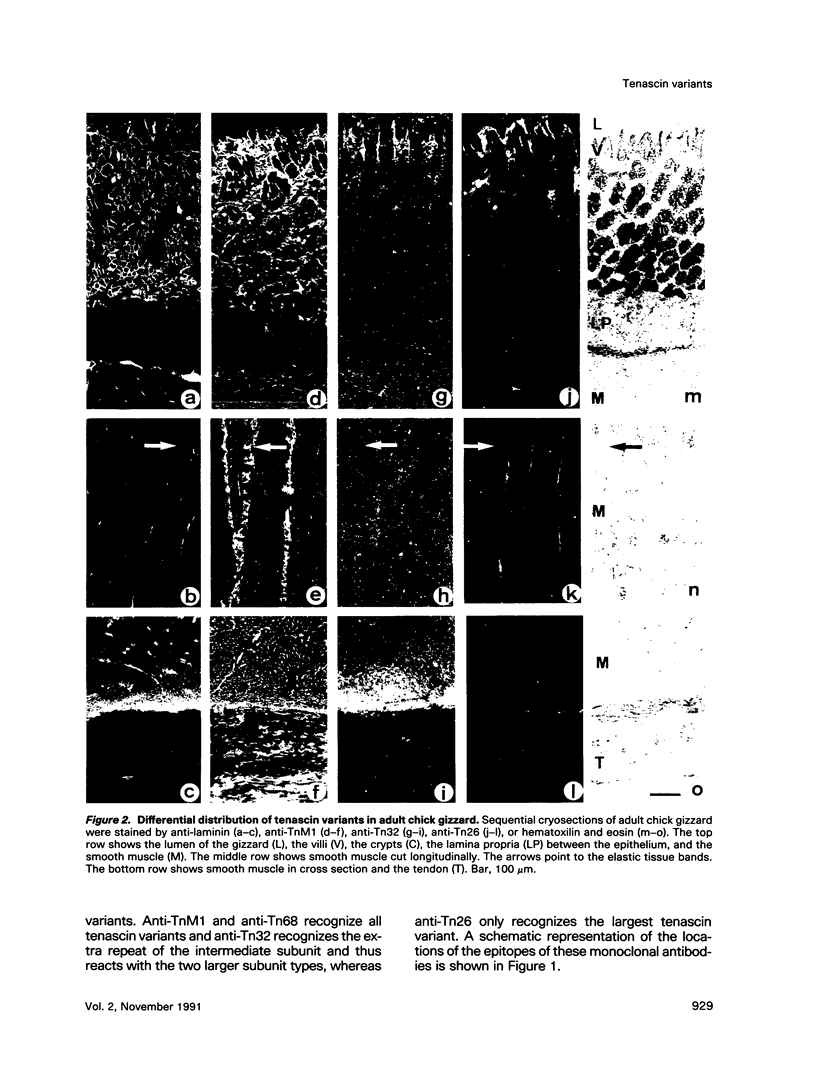
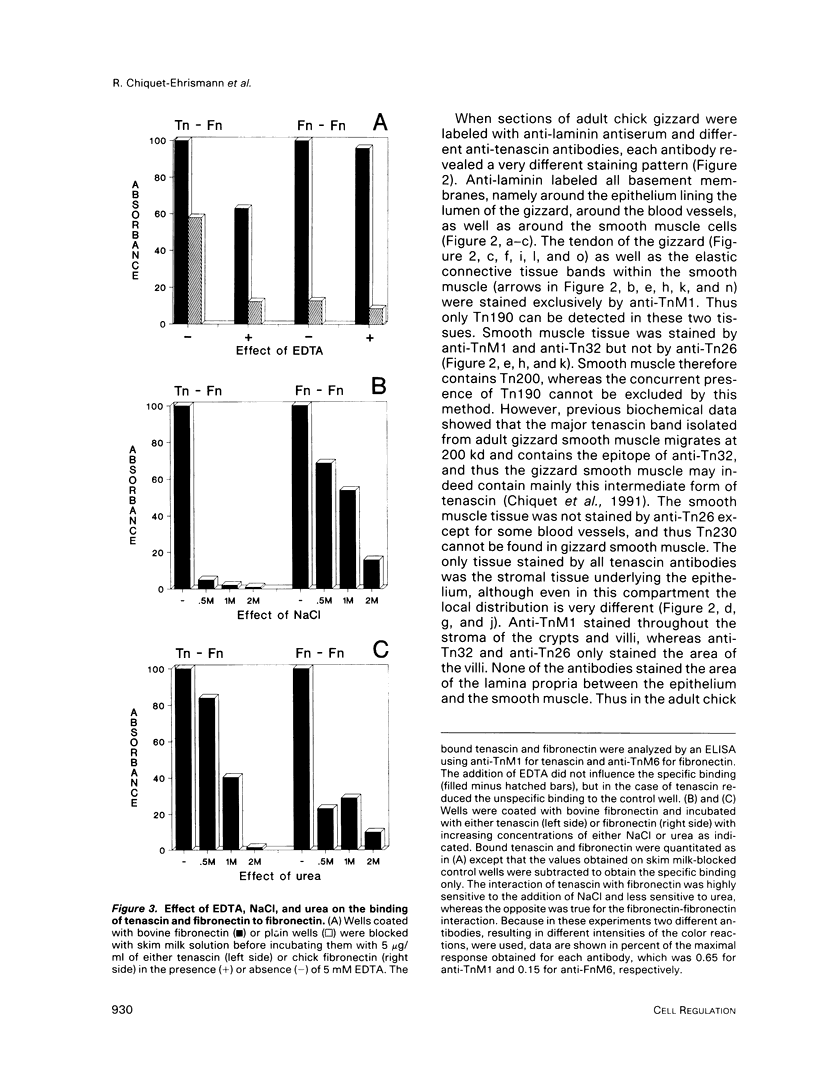
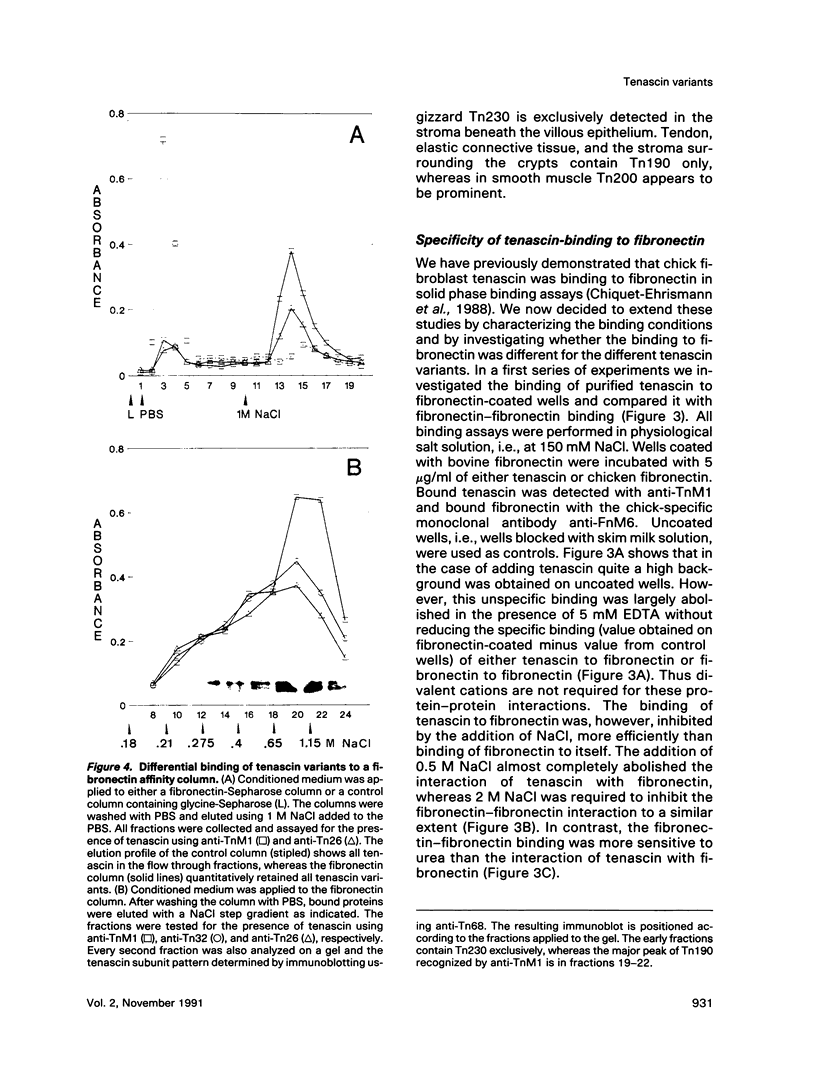
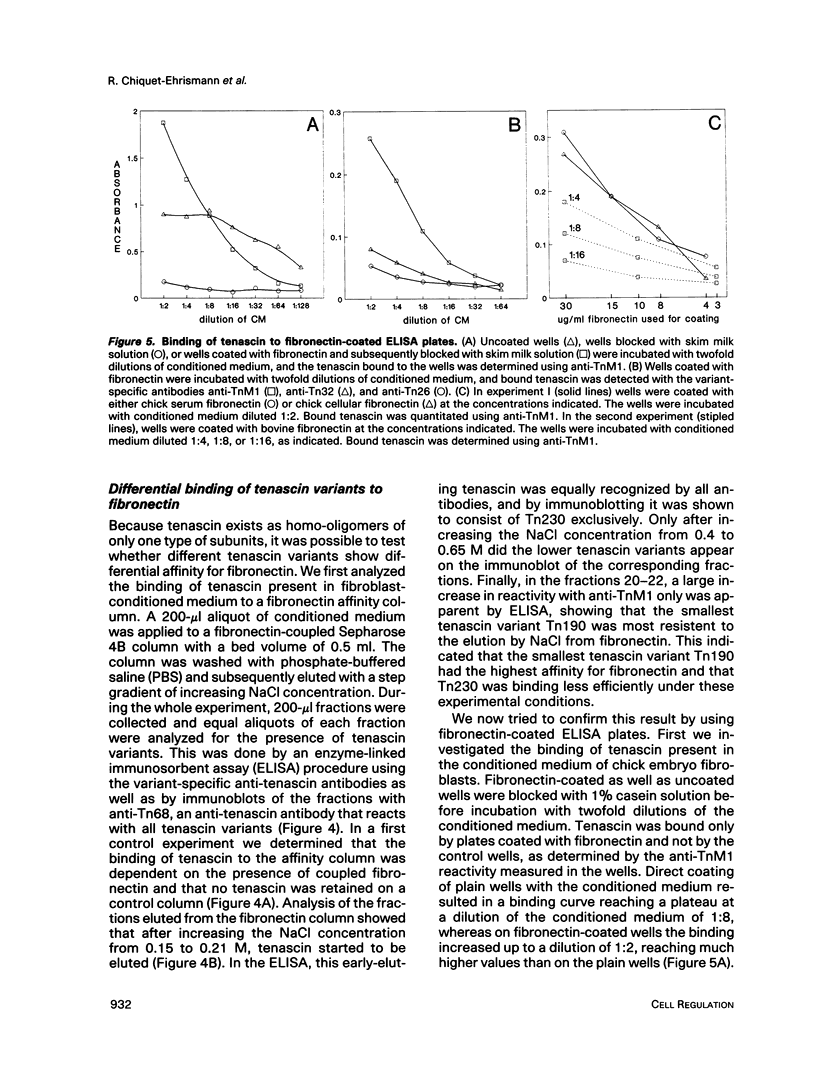
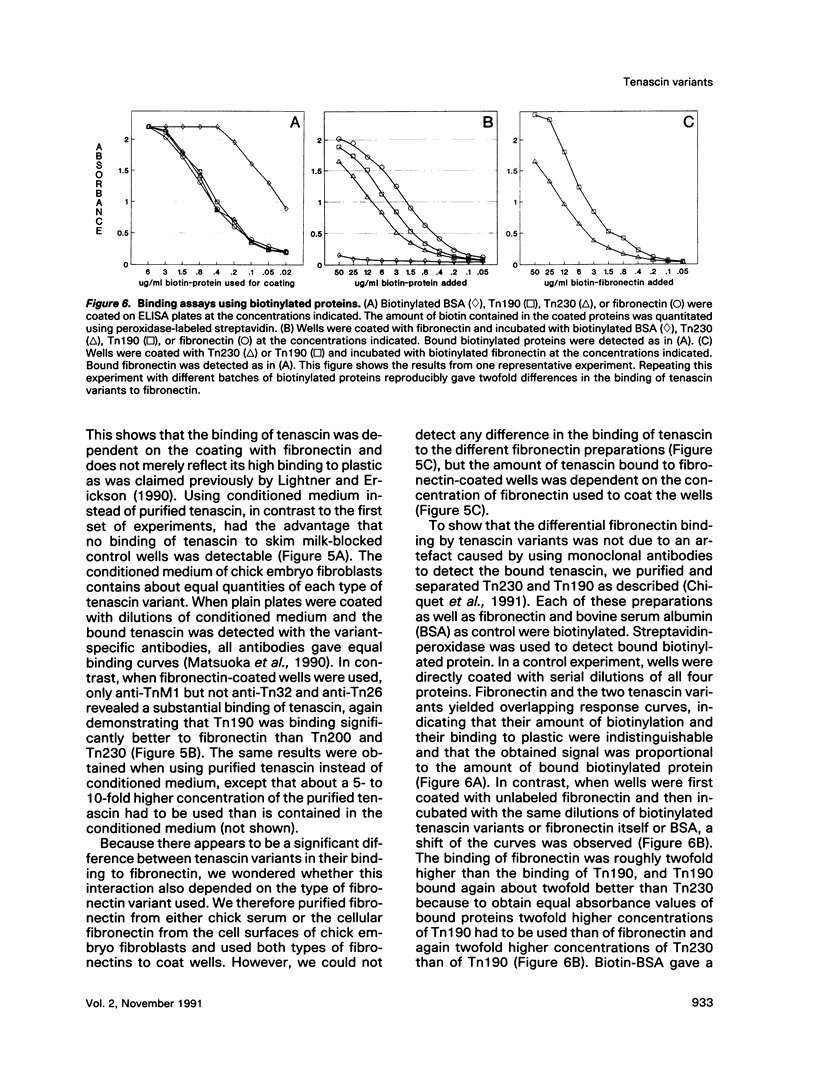
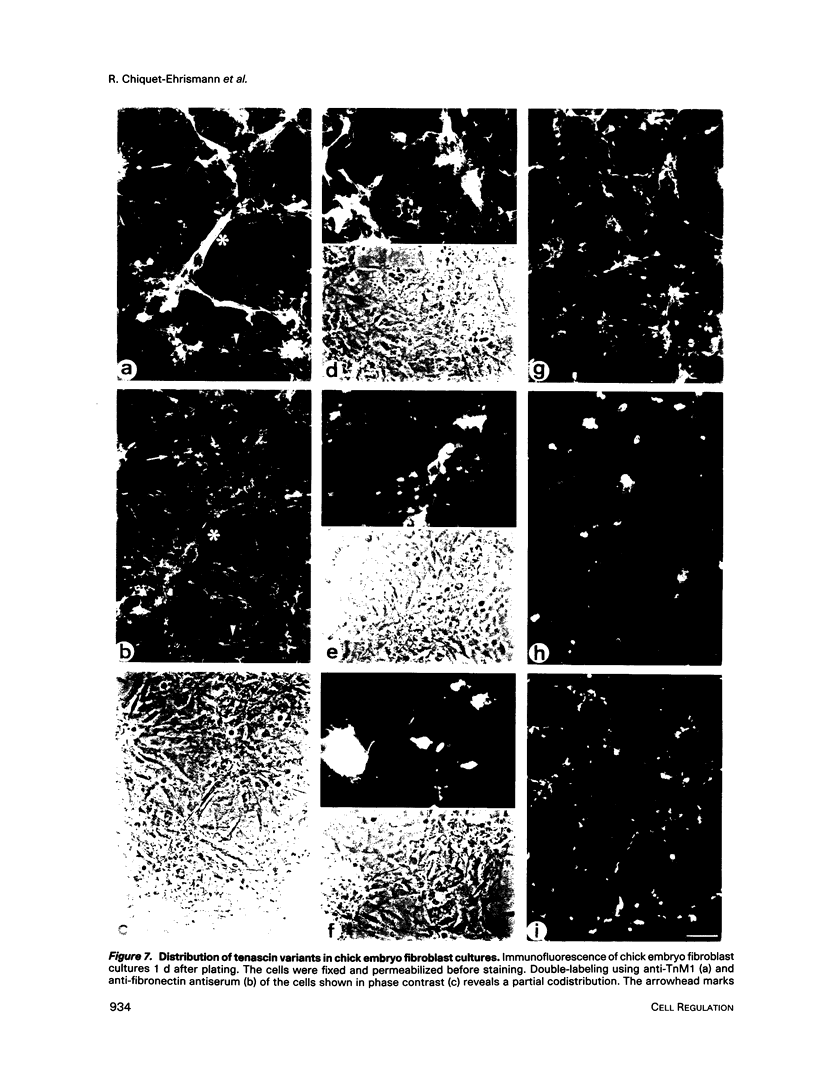
In the chicken, three tenascin variants have been characterized that are generated by alternative splicing of 3 of its 11 fibronectin type III repeats. Using monoclonal antibodies that react with common regions versus extra repeats of tenascin, we could distinguish and separate tenascin variants and investigate their interaction with fibronectin using multiple experimental procedures. Interestingly, in all assays used the smallest tenascin variant bound more strongly to fibronectin than the larger ones. These biochemical data were paralleled by the observation that in chick embryo fibroblast cultures only the smallest form of tenascin could be detected in the fibronectin-rich extracellular matrix network laid down by the cells. Furthermore, each tissue present in adult chicken gizzard contained a distinct set of tenascin variants. Those tissues particularly rich in extracellular matrix, such as the tendon, contained the smallest tenascin only. Intermediate-sized tenascin was present in smooth muscle, whereas the largest form was exclusively detectable underneath the epithelial lining of the villi. Thus it appears that cell type-specific forms of tenascin exist that are appropriate for the functional requirements of the respective extracellular matrices.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aufderheide E., Ekblom P. Tenascin during gut development: appearance in the mesenchyme, shift in molecular forms, and dependence on epithelial-mesenchymal interactions. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2341–2349. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaldo P., Russo V., Bucciotti F., Doliana R., Colombatti A. Structural and functional features of the alpha 3 chain indicate a bridging role for chicken collagen VI in connective tissues. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 6;29(5):1245–1254. doi: 10.1021/bi00457a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Kalla P., Pearson C. A., Beck K., Chiquet M. Tenascin interferes with fibronectin action. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R. What distinguishes tenascin from fibronectin? FASEB J. 1990 Jun;4(9):2598–2604. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.9.1693347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet M., Fambrough D. M. Chick myotendinous antigen. I. A monoclonal antibody as a marker for tendon and muscle morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1926–1936. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet M., Fambrough D. M. Chick myotendinous antigen. II. A novel extracellular glycoprotein complex consisting of large disulfide-linked subunits. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1937–1946. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet M., Vrucinić-Filipi N., Schenk S., Beck K., Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Isolation of chick tenascin variants and fragments. A C-terminal heparin-binding fragment produced by cleavage of the extra domain from the largest subunit splicing variant. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):379–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Pan T. C., Conway D., Kuo H. J., Glanville R. W., Timpl R., Mann K., Deutzmann R. Sequence analysis of alpha 1(VI) and alpha 2(VI) chains of human type VI collagen reveals internal triplication of globular domains similar to the A domains of von Willebrand factor and two alpha 2(VI) chain variants that differ in the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1939–1946. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Zhang R. Z., Pan T. C., Stokes D., Conway D., Kuo H. J., Glanville R., Mayer U., Mann K., Deutzmann R. Mosaic structure of globular domains in the human type VI collagen alpha 3 chain: similarity to von Willebrand factor, fibronectin, actin, salivary proteins and aprotinin type protease inhibitors. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):385–393. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08122.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrismann R., Chiquet M., Turner D. C. Mode of action of fibronectin in promoting chicken myoblast attachment. Mr = 60,000 gelatin-binding fragment binds native fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4056–4062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P., Bourdon M. A. Tenascin: an extracellular matrix protein prominent in specialized embryonic tissues and tumors. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:71–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faissner A., Kruse J., Kühn K., Schachner M. Binding of the J1 adhesion molecules to extracellular matrix constituents. J Neurochem. 1990 Mar;54(3):1004–1015. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb02350.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gretch D. R., Suter M., Stinski M. F. The use of biotinylated monoclonal antibodies and streptavidin affinity chromatography to isolate herpesvirus hydrophobic proteins or glycoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 15;163(1):270–277. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulcher J. R., Nies D. E., Marton L. S., Stefansson K. An alternatively spliced region of the human hexabrachion contains a repeat of potential N-glycosylation sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M. Molecular forms, binding functions, and developmental expression patterns of cytotactin and cytotactin-binding proteoglycan, an interactive pair of extracellular matrix molecules. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):519–532. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. A proteoglycan with HNK-1 antigenic determinants is a neuron-associated ligand for cytotactin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2523–2527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplony A., Zimmermann D. R., Fischer R. W., Imhof B. A., Odermatt B. F., Winterhalter K. H., Vaughan L. Tenascin Mr 220,000 isoform expression correlates with corneal cell migration. Development. 1991 Jun;112(2):605–614. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.2.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch M., Wehrle-Haller B., Baumgartner S., Spring J., Brubacher D., Chiquet M. Epithelial synthesis of tenascin at tips of growing bronchi and graded accumulation in basement membrane and mesenchyme. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Jun;194(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90368-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightner V. A., Erickson H. P. Binding of hexabrachion (tenascin) to the extracellular matrix and substratum and its effect on cell adhesion. J Cell Sci. 1990 Feb;95(Pt 2):263–277. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. J., Thesleff I., Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Tenascin is associated with chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation in vivo and promotes chondrogenesis in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2569–2579. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka Y., Spring J., Ballmer-Hofer K., Hofer U., Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Differential expression of tenascin splicing variants in the chick gizzard and in cell cultures. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson C. A., Pearson D., Shibahara S., Hofsteenge J., Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Tenascin: cDNA cloning and induction by TGF-beta. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):2977–2982. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J., Baule V. J., Rich C. B., Ginsburg C. D., Curtiss S. W., Foster J. A. Chick tropoelastin isoforms. From the gene to the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3697–3702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto A. L., Jones F. S., Cunningham B. A., Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M. Localization during development of alternatively spliced forms of cytotactin mRNA by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):685–698. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probstmeier R., Martini R., Schachner M. Expression of J1/tenascin in the crypt-villus unit of adult mouse small intestine: implications for its role in epithelial cell shedding. Development. 1990 Jun;109(2):313–321. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmivirta M., Elenius K., Vainio S., Hofer U., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Thesleff I., Jalkanen M. Syndecan from embryonic tooth mesenchyme binds tenascin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7733–7739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siri A., Carnemolla B., Saginati M., Leprini A., Casari G., Baralle F., Zardi L. Human tenascin: primary structure, pre-mRNA splicing patterns and localization of the epitopes recognized by two monoclonal antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):525–531. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:527–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring J., Beck K., Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Two contrary functions of tenascin: dissection of the active sites by recombinant tenascin fragments. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90294-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda K. K., Nishimura I., Sugrue S. P., Ninomiya Y., Olsen B. R. Embryonic chicken cornea and cartilage synthesize type IX collagen molecules with different amino-terminal domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7496–7500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller A., Beck S., Ekblom P. Amino acid sequence of mouse tenascin and differential expression of two tenascin isoforms during embryogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(2):355–362. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pastan I. The major cell surface glycoprotein of chick embryo fibroblasts is an agglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3158–3162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]