Abstract
A novel serine/threonine protein kinase (termed rac-PK) has recently been identified and cloned from cDNA libraries derived from the human cell lines MCF-7 and WI38. A second form of this protein kinase, termed rac protein kinase beta, has been identified from cDNAs derived from the same cell lines. These two closely related forms show 90% homology, although the beta form with a predicted Mr 60,200 has a carboxyl terminal extension of 40 amino acids in comparison to the alpha form. This extension has a high serine content with 11 serine residues in the last 30 amino acids. The beta form of the protein has been shown by both in vitro translation and bacterial expression to be approximately 5000 Da larger than the alpha form. rac protein kinase beta is encoded by a 3.4-kb transcript and the alpha form is encoded by a 3.2-kb mRNA. Using gene-specific probes both transcripts were detected in all cell types analyzed, although levels of expression were different for the two forms. The catalytic domain of rac protein kinase beta shows a high degree of homology to both the protein kinase C and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase families, and hence rac protein kinases appear to represent a new subfamily of the second messenger serine/threonine protein kinases.
Full text
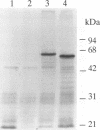
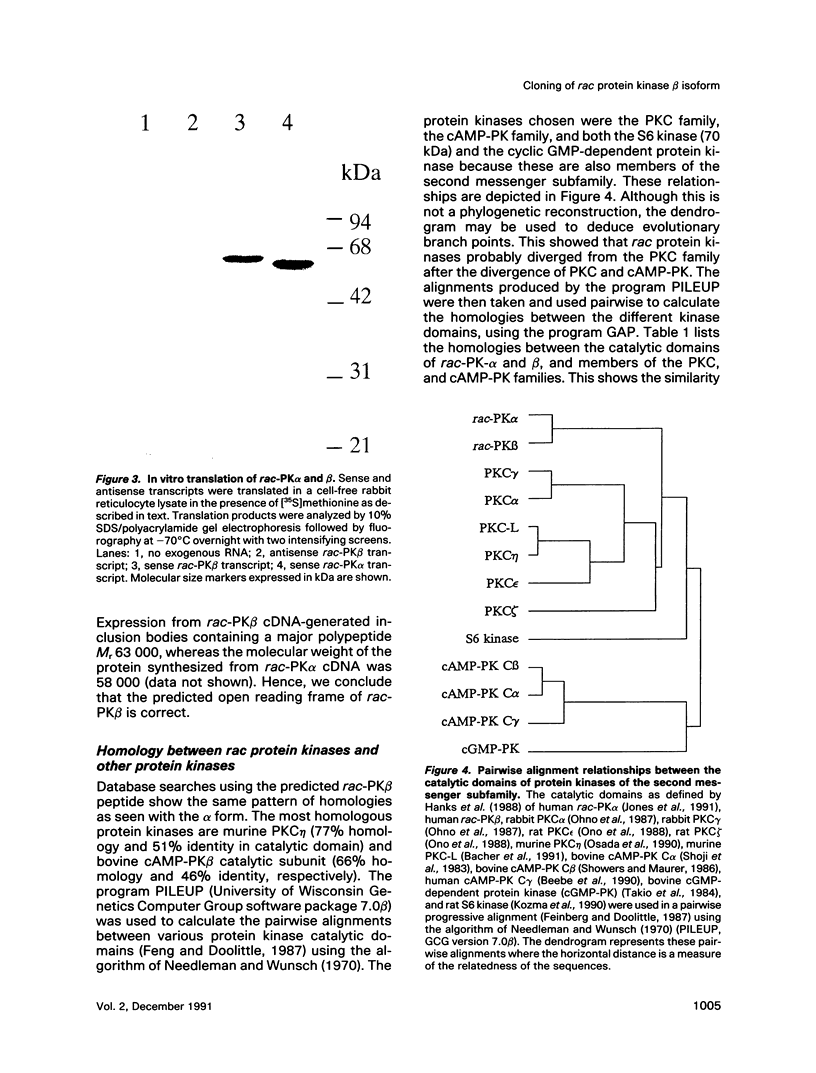
PDF



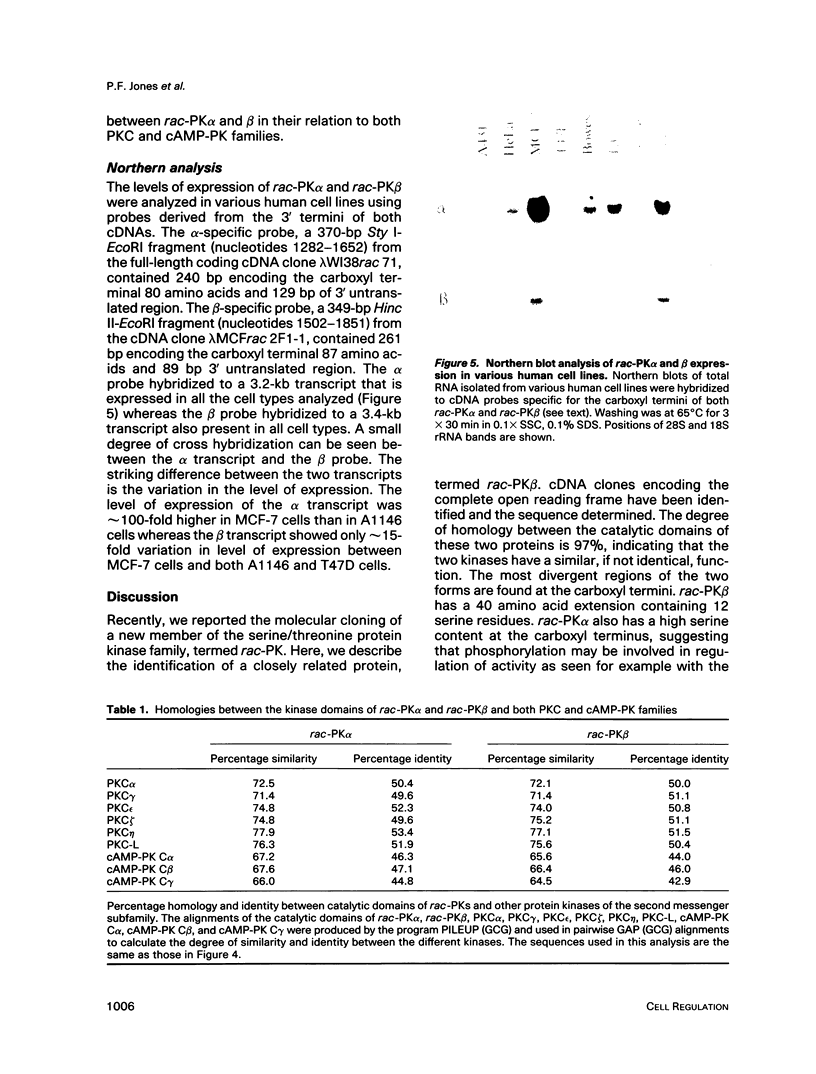



Images in this article
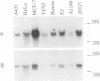
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacher N., Zisman Y., Berent E., Livneh E. Isolation and characterization of PKC-L, a new member of the protein kinase C-related gene family specifically expressed in lung, skin, and heart. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):126–133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Siegmann M., Thomas G. S6 kinase in quiescent Swiss mouse 3T3 cells is activated by phosphorylation in response to serum treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7154–7158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebe S. J., Oyen O., Sandberg M., Frøysa A., Hansson V., Jahnsen T. Molecular cloning of a tissue-specific protein kinase (C gamma) from human testis--representing a third isoform for the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):465–475. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. S., Zoller M. J. Identification of electrostatic interactions that determine the phosphorylation site specificity of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5329–5334. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K. Homology probing: identification of cDNA clones encoding members of the protein-serine kinase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):388–392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase C contains a pseudosubstrate prototope in its regulatory domain. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1726–1728. doi: 10.1126/science.3686012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. F., Jakubowicz T., Pitossi F. J., Maurer F., Hemmings B. A. Molecular cloning and identification of a serine/threonine protein kinase of the second-messenger subfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4171–4175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khew-Goodall Y., Hemmings B. A. Tissue-specific expression of mRNAs encoding alpha- and beta-catalytic subunits of protein phosphatase 2A. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 10;238(2):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):414–420. doi: 10.1126/science.1862343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma S. C., Ferrari S., Bassand P., Siegmann M., Totty N., Thomas G. Cloning of the mitogen-activated S6 kinase from rat liver reveals an enzyme of the second messenger subfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7365–7369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M., Stein M., Beach D. The product of the mei3+ gene, expressed under control of the mating-type locus, induces meiosis and sporulation in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):729–736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen D. A., Shapiro D. J. Preparation of capped RNA transcripts using T7 RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5936–5936. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Kawasaki H., Imajoh S., Suzuki K., Inagaki M., Yokokura H., Sakoh T., Hidaka H. Tissue-specific expression of three distinct types of rabbit protein kinase C. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):161–166. doi: 10.1038/325161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. The structure, expression, and properties of additional members of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osada S., Mizuno K., Saido T. C., Akita Y., Suzuki K., Kuroki T., Ohno S. A phorbol ester receptor/protein kinase, nPKC eta, a new member of the protein kinase C family predominantly expressed in lung and skin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22434–22440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Titani K. Amino acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of bovine type II adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3702–3709. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showers M. O., Maurer R. A. A cloned bovine cDNA encodes an alternate form of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16288–16291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J., Hemmings B. A. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding two isoforms of the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7215–7220. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Wade R. D., Smith S. B., Krebs E. G., Walsh K. A., Titani K. Guanosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase, a chimeric protein homologous with two separate protein families. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4207–4218. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Hol W. G. Predicted nucleotide-binding properties of p21 protein and its cancer-associated variant. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):842–844. doi: 10.1038/302842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]