Abstract
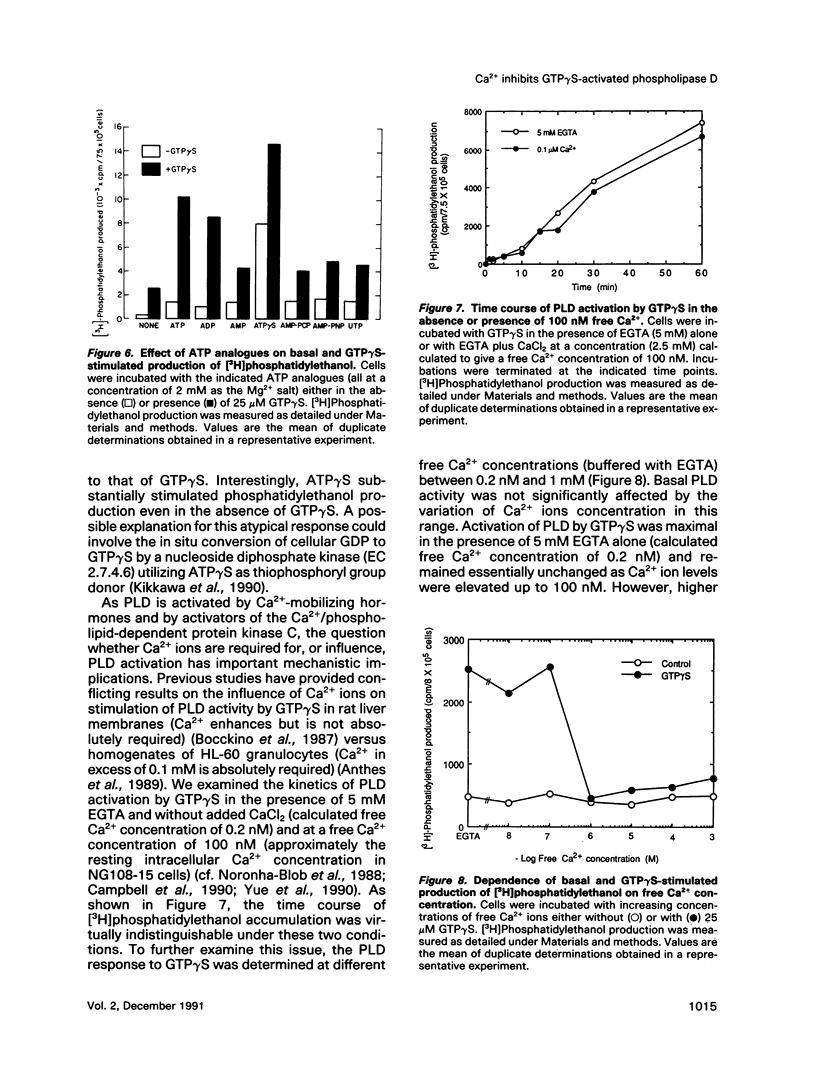
We have investigated the regulation of phospholipase D (PLD) activity by guanine nucleotides and Ca2+ in cells of the NG108-15 neuroblastoma X glioma line that were permeabilized with digitonin. The nonhydrolyzable GTP analogue guanosine-5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) (GTP gamma S) caused a nearly sixfold increase (EC50 = 3 microM) in production of [3H]phosphatidylethanol (specific product of the PLD transphosphatidylation reaction). Other GTP analogues were less effective than GTP gamma S, and guanosine-5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate) inhibited PLD activation by GTP gamma S. Both basal and GTP gamma S-stimulated PLD activities were potentiated by MgATP and Mg2+. Adenosine-5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) and ADP also potentiated the effect of GTP gamma S, but non-phosphorylating analogues of ATP had no such effect. The activation of PLD by GTP gamma S did not require Ca2+ and was independent of free Ca2+ ions up to a concentration of 100 nM (resting intracellular concentration). Higher Ca2+ concentrations (greater than or equal to 1 microM) completely inhibited PLD activation by GTP gamma S. It is concluded that elevated intracellular Ca2+ concentrations may negatively modulate PLD activation by a guanine nucleotide-binding protein, thus affecting receptor-PLD coupling in neural-derived cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthes J. C., Eckel S., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Phospholipase D in homogenates from HL-60 granulocytes: implications of calcium and G protein control. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):657–664. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Anthes J. C. The regulation and cellular functions of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):281–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2690281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Abramowitz J., Brown A. M. Receptor-effector coupling by G proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):163–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Phosphatidate accumulation in hormone-treated hepatocytes via a phospholipase D mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15309–15315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. D., Subramaniam S., Kotlikoff M. I., Williamson J. R., Fluharty S. J. Cyclic AMP inhibits inositol polyphosphate production and calcium mobilization in neuroblastoma X glioma NG108-15 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;38(2):282–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalifa V., Möhn H., Liscovitch M. A neutral phospholipase D activity from rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. Identification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17512–17519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claro E., Wallace M. A., Lee H. M., Fain J. N. Carbachol in the presence of guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) stimulates the breakdown of exogenous phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate, and phosphatidylinositol by rat brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18288–18295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M. The formation of phosphatidylglycerol and other phospholipids by the transferase activity of phospholipase D. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):205–210. doi: 10.1042/bj1020205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:367–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich Y. H., Snider R. M., Kornecki E., Garfield M. G., Lenox R. H. Modulation of neuronal signal transduction systems by extracellular ATP. J Neurochem. 1988 Jan;50(1):295–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb13263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Yoshimoto K. K., Eversole-Cire P., Simon M. I. Identification of a GTP-binding protein alpha subunit that lacks an apparent ADP-ribosylation site for pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3066–3070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamprecht B., Glaser T., Reiser G., Bayer E., Propst F. Culture and characteristics of hormone-responsive neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:316–341. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa S., Takahashi K., Takahashi K., Shimada N., Ui M., Kimura N., Katada T. Conversion of GDP into GTP by nucleoside diphosphate kinase on the GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21536–21540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Kanfer J. N. Phosphatidylethanol formation via transphosphatidylation by rat brain synaptosomal phospholipase D. J Neurochem. 1987 May;48(5):1597–1603. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie Y., Liscovitch M. Activation of phospholipase D by sphingoid bases in NG108-15 neural-derived cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3868–3872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie Y., Piterman O., Liscovitch M. Inhibition of phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase activity by sphingosine. Dual action of sphingosine in diacylglycerol signal termination. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 17;277(1-2):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80796-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Amsterdam A. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone activates phospholipase D in ovarian granulosa cells. Possible role in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11762–11767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Blusztajn J. K., Freese A., Wurtman R. J. Stimulation of choline release from NG108-15 cells by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):81–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2410081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M. Phosphatidylethanol biosynthesis in ethanol-exposed NG108-15 neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells. Evidence for activation of a phospholipase D phosphatidyl transferase activity by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1450–1456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M. Signal-dependent activation of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis: role of phospholipase D. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Apr;19(2):402–407. doi: 10.1042/bst0190402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löffelholz K. Receptor regulation of choline phospholipid hydrolysis. A novel source of diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 May 15;38(10):1543–1549. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone activates a Ca2+-dependent polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in permeable GH3 cells. GTP gamma S potentiation by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2918–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. W., Michaelis K. P2-purinergic agonists stimulate phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylcholine in endothelial cells. Evidence for activation of phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8847–8856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., McKenzie F. R., McClue S. J., Mitchell F. M., Mullaney I. Guanine nucleotide binding proteins in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid, NG108-15, cells. Regulation of expression and function. Int J Biochem. 1990;22(7):701–707. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(90)90004-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nirenberg M., Wilson S., Higashida H., Rotter A., Krueger K., Busis N., Ray R., Kenimer J. G., Adler M. Modulation of synapse formation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):794–799. doi: 10.1126/science.6314503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noronha-Blob L., Richard C., U'Prichard D. C. Voltage-sensitive calcium channels in differentiated neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid (NG108-15) cells: characterization by quin 2 fluorescence. J Neurochem. 1988 May;50(5):1381–1390. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Phospholipase D catalyzes phospholipid metabolism in chemotactic peptide-stimulated HL-60 granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12472–12477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M., Downs R. W., Jr Guanine nucleotides: key regulators of hormone receptor-adenylate cyclase interaction. Endocr Rev. 1981 Summer;2(3):275–305. doi: 10.1210/edrv-2-3-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Chae H. Z., Rhee S. G., Exton J. H. Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):516–518. doi: 10.1038/350516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tettenborn C. S., Mueller G. C. Phorbol esters activate the pathway for phosphatidylethanol synthesis in differentiating HL-60 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 12;931(2):242–250. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing R. J., Prpic V., Jiang H., Exton J. H. Hormone-stimulated polyphosphoinositide breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue T. L., Gleason M. M., Lysko P. G., Feuerstein G. Effect of endothelins on cytosolic free calcium concentration in neuroblastoma NG108-15 and NCB-20 cells. Neuropeptides. 1990 Sep;17(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(90)90134-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]