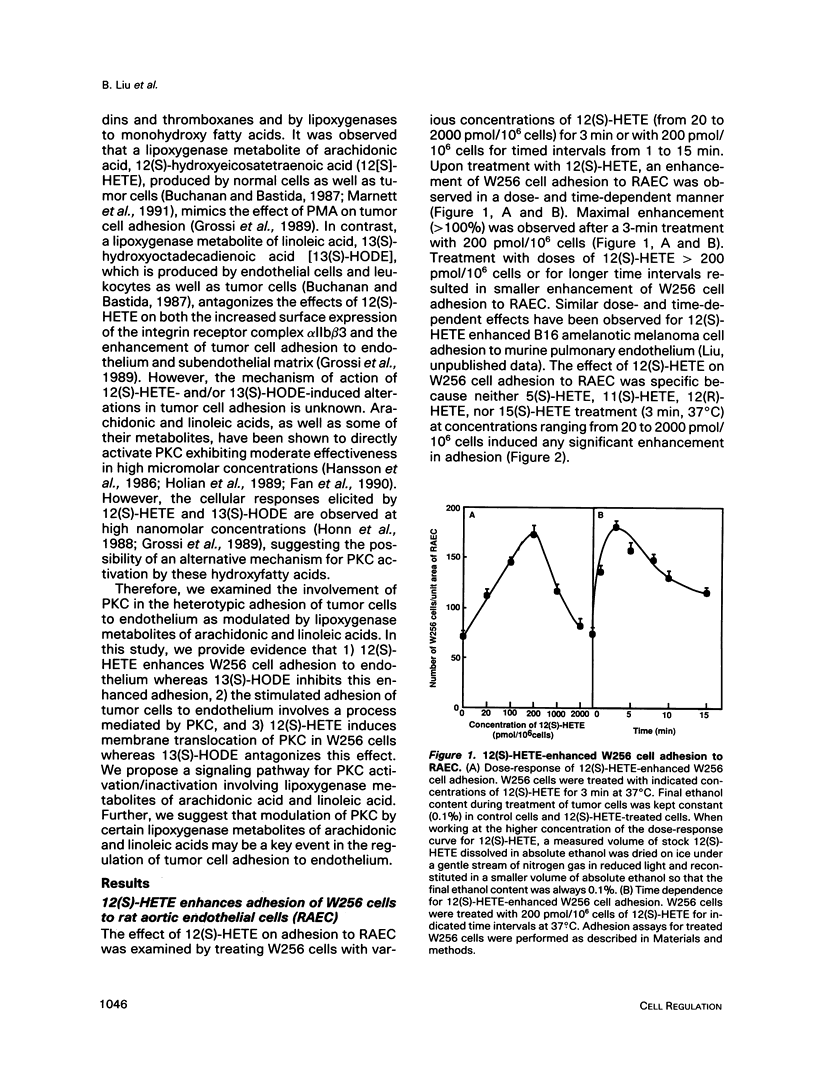
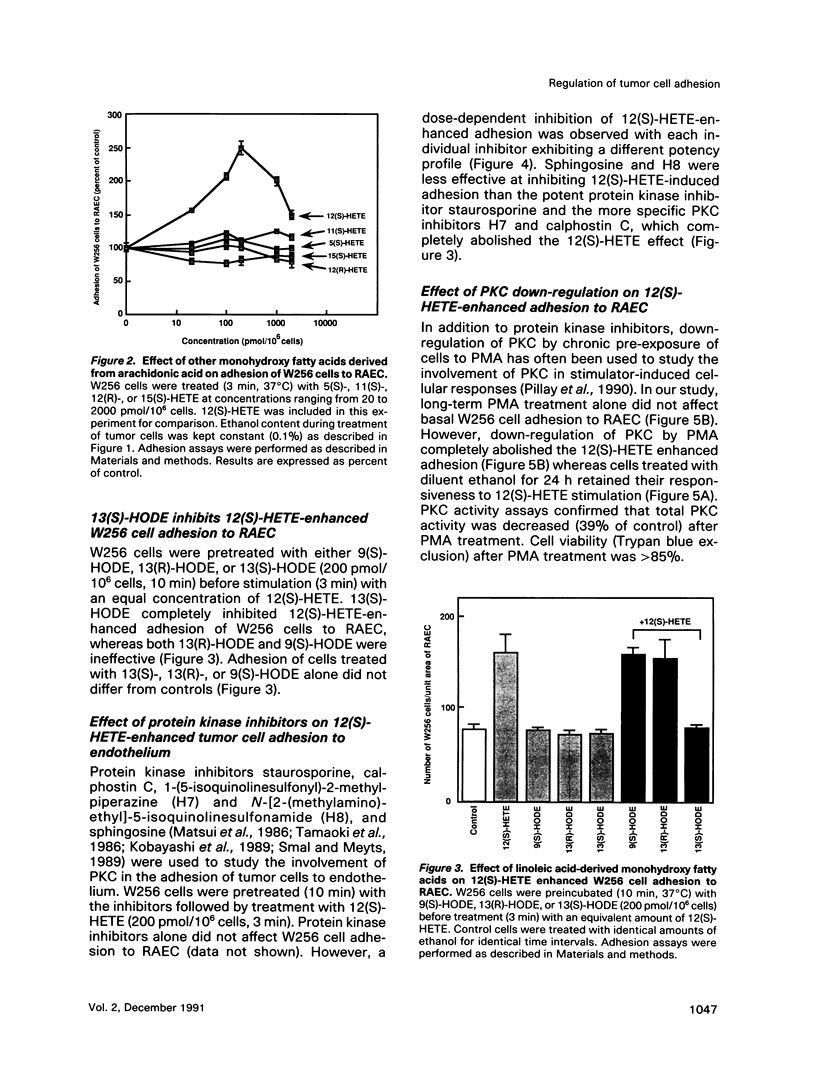
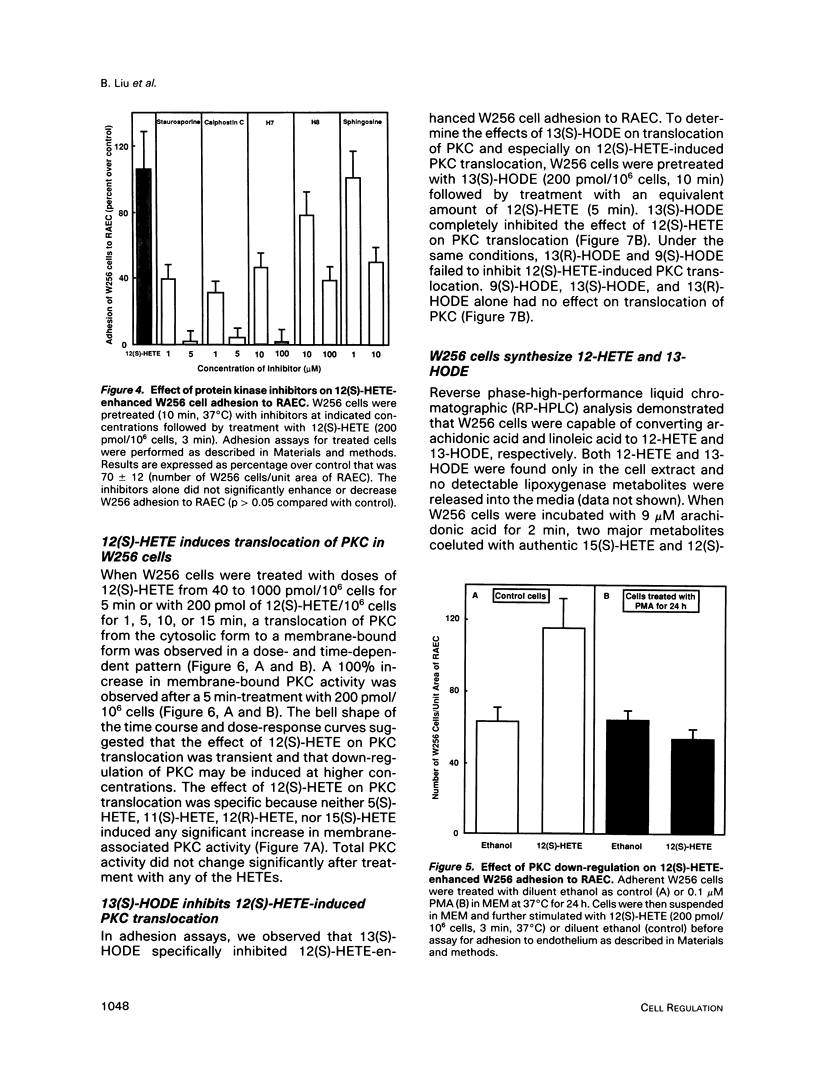
Abstract
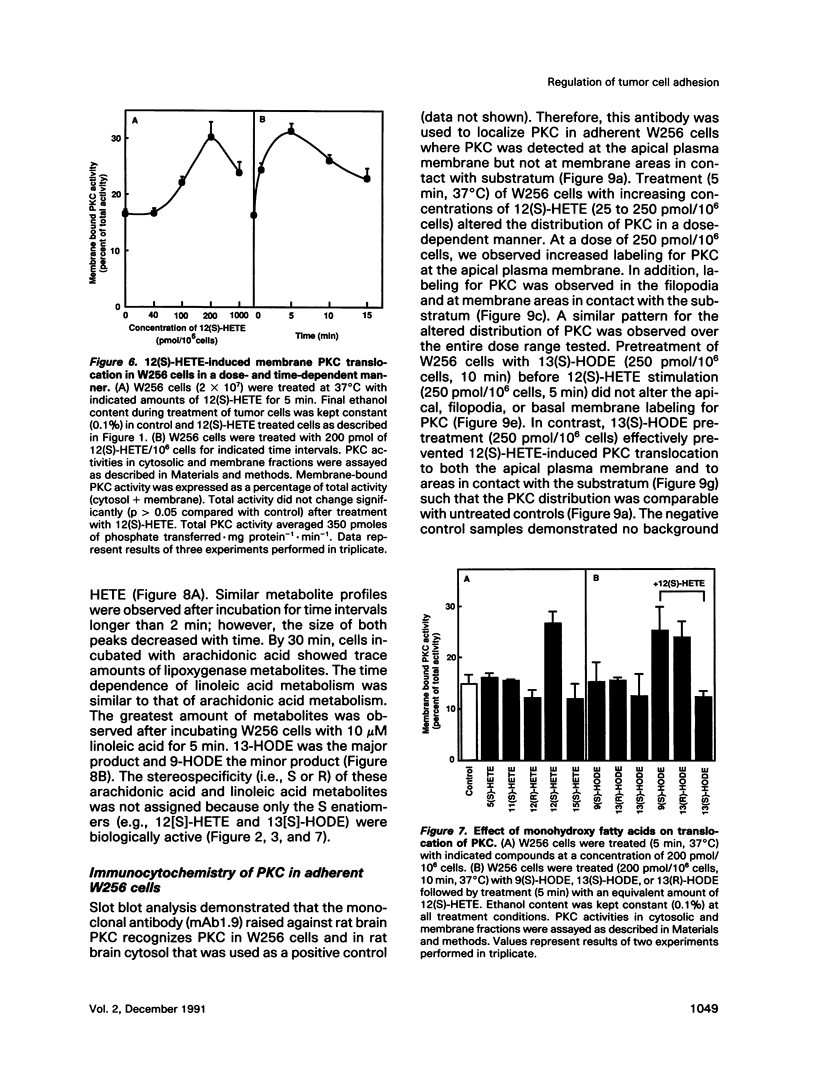
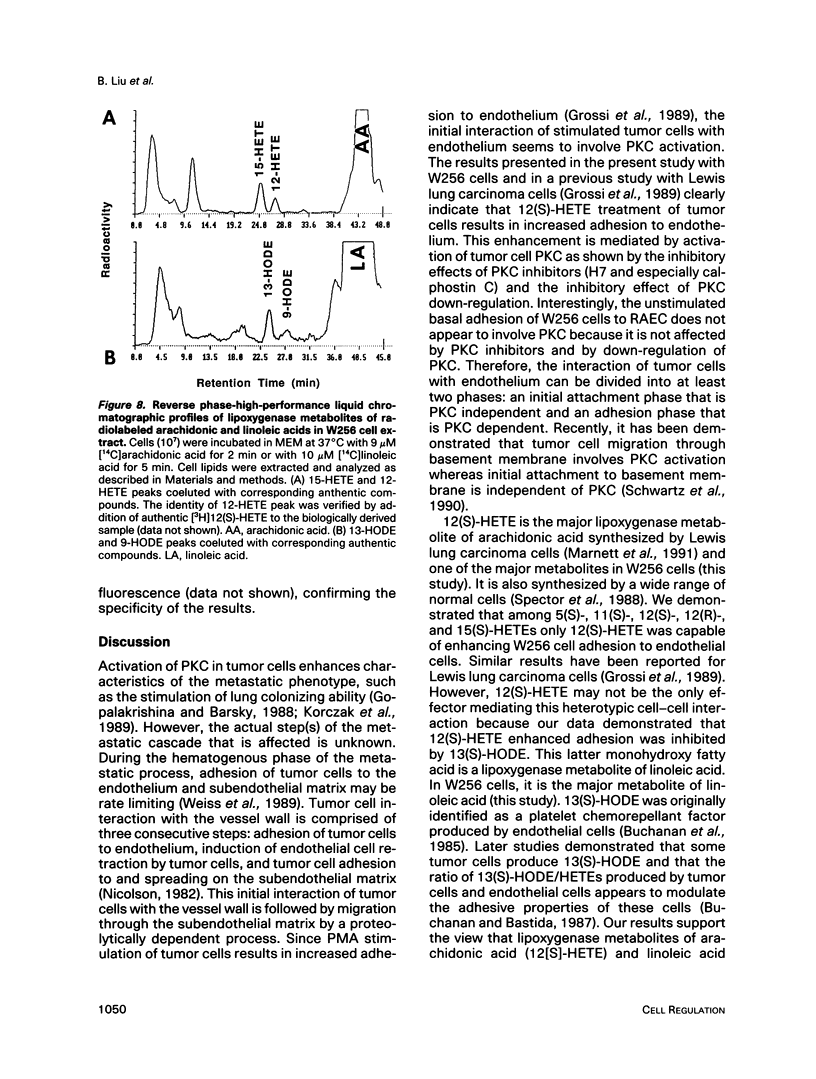
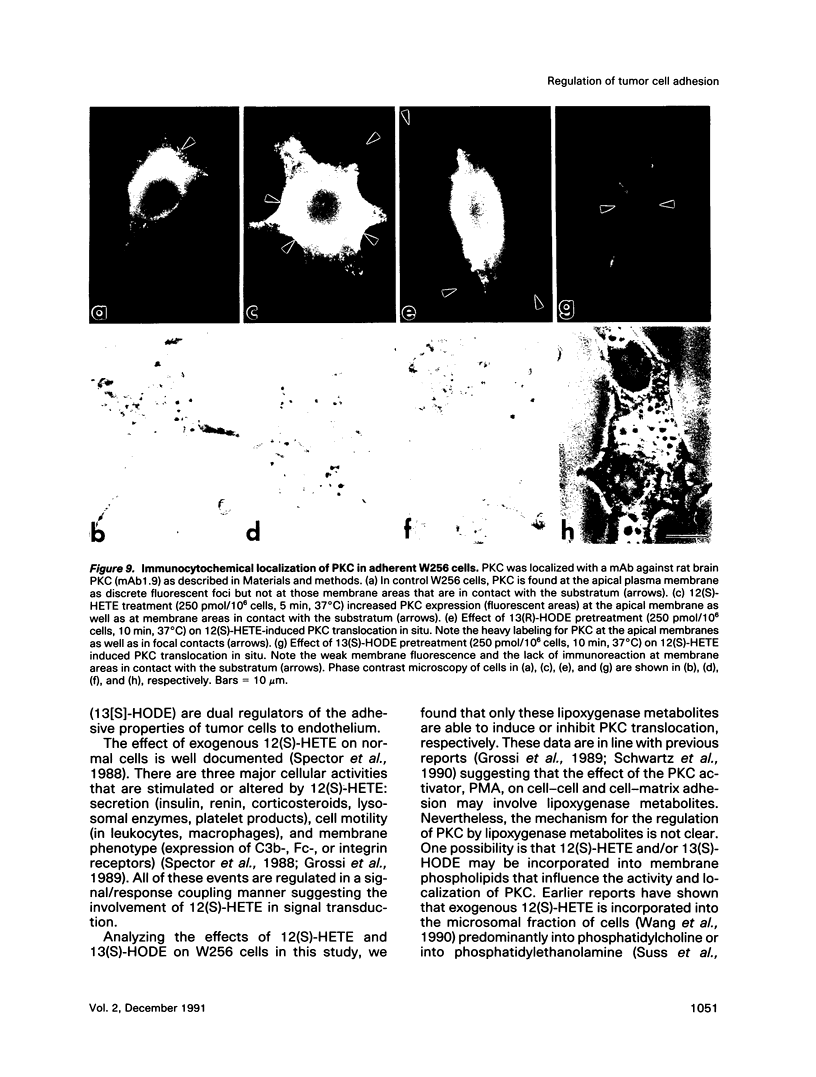
12(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12[S]-HETE) and 13(S)-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13[S]-HODE), lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid and linoleic acid, respectively, previously have been suggested to regulate tumor cell adhesion to endothelium during metastasis. Adhesion of rat Walker carcinosarcoma (W256) cells to a rat endothelial cell monolayer was enhanced after treatment with 12(S)-HETE and this 12(S)-HETE enhanced adhesion was blocked by 13(S)-HODE. Protein kinase inhibitors, staurosporine, calphostin C, and 1-(5-isoquinoline-sulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine, inhibited the 12(S)-HETE enhanced W256 cell adhesion. Depleting W256 cells of protein kinase C (PKC) with phorbol 12-myristate-13-acetate abolished their ability to respond to 12(S)-HETE. Treatment of W256 cells with 12(S)-HETE induced a 100% increase in membrane-associated PKC activity whereas 13(S)-HODE inhibited the effect of 12(S)-HETE on PKC translocation. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis revealed that in W256 cells 12-HETE and 13-HODE were two of the major lipoxygenase metabilites of arachidonic acid and linoleic acid, respectively. Therefore, these two metabolites may provide an alternative signaling pathway for the regulation of PKC. Further, these findings suggest that the regulation of tumor cell adhesion to endothelium by 12(S)-HETE and 13(S)-HODE may be a PKC-dependent process.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra H., Hatfield J. S., Chang Y. S., Grossi I. M., Fitzgerald L. A., O'Gara C. Y., Marnett L. J., Diglio C. A., Taylor J. D., Honn K. V. Role of tumor cytoskeleton and membrane glycoprotein IRGpIIb/IIIa in platelet adhesion to tumor cell membrane and tumor cell-induced platelet aggregation. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 1;48(13):3787–3800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diglio C. A., Grammas P., Giacomelli F., Wiener J. Primary culture of rat cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Isolation, growth, and characterization. Lab Invest. 1982 Jun;46(6):554–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan X. T., Huang X. P., Da Silva C., Castagna M. Arachidonic acid and related methyl ester mediate protein kinase C activation in intact platelets through the arachidonate metabolism pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 29;169(3):933–940. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91983-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna R., Barsky S. H. Tumor promoter-induced membrane-bound protein kinase C regulates hematogenous metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):612–616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross E., Ruzicka T., von Restorff B., Stolz W., Klotz K. N. High-affinity binding and lack of growth-promoting activity of 12(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12(S)-HETE) in a human epidermal cell line. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Apr;94(4):446–451. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossi I. M., Fitzgerald L. A., Umbarger L. A., Nelson K. K., Diglio C. A., Taylor J. D., Honn K. V. Bidirectional control of membrane expression and/or activation of the tumor cell IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor and tumor cell adhesion by lipoxygenase products of arachidonic acid and linoleic acid. Cancer Res. 1989 Feb 15;49(4):1029–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson A., Serhan C. N., Haeggström J., Ingelman-Sundberg M., Samuelsson B. Activation of protein kinase C by lipoxin A and other eicosanoids. Intracellular action of oxygenation products of arachidonic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1215–1222. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90380-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holian O., Kumar R., Nyhus L. M. Fatty acyl esters potentiate fatty acid induced activation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 15;160(3):1110–1116. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honn K. V., Grossi I. M., Fitzgerald L. A., Umbarger L. A., Diglio C. A., Taylor J. D. Lipoxygenase products regulate IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor mediated adhesion of tumor cells to endothelial cells, subendothelial matrix and fibronectin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1988 Oct;189(1):130–135. doi: 10.3181/00379727-189-1-rc1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi E., Nakano H., Morimoto M., Tamaoki T. Calphostin C (UCN-1028C), a novel microbial compound, is a highly potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korczak B., Whale C., Kerbel R. S. Possible involvement of Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C activation in the induction of spontaneous metastasis by mouse mammary adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2597–2602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand A. B., Lawson J. A., Meyrick B. O., Blair I. A., Oates J. A. Substitution of 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid in the phosphoinositide signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7570–7577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marnett L. J., Leithauser M. T., Richards K. M., Blair I., Honn K. V., Yamamoto S., Yoshimoto T. Arachidonic acid metabolism of cytosolic fractions of Lewis lung carcinoma cells. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1991;21B:895–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Nakao Y., Koizumi T., Katakami Y., Fujita T. Inhibition of phorbol ester-induced phenotypic differentiation of HL-60 cells by 1-(5-isoquinolinylsulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine, a protein kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):583–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menter D. G., Steinert B. W., Sloane B. F., Gundlach N., O'Gara C. Y., Marnett L. J., Diglio C., Walz D., Taylor J. D., Honn K. V. Role of platelet membrane in enhancement of tumor cell adhesion to endothelial cell extracellular matrix. Cancer Res. 1987 Dec 15;47(24 Pt 1):6751–6762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Basbaum A. I., Koshland D. E., Jr Distinct cellular and regional localization of immunoreactive protein kinase C in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4660–4664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Metastatic tumor cell attachment and invasion assay utilizing vascular endothelial cell monolayers. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Mar;30(3):214–220. doi: 10.1177/30.3.7061823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brian C. A., Ward N. E. Biology of the protein kinase C family. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989 Dec;8(3):199–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00047337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillay T. S., Whittaker J., Siddle K. Phorbol ester-induced downregulation of protein kinase C potentiates insulin receptor tyrosine autophosphorylation: evidence for a major constitutive role in insulin receptor regulation. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Jun;18(3):494–495. doi: 10.1042/bst0180494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. S. Reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography of arachidonic acid metabolites formed by cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenases. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jul;148(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90628-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade U. F., Burmeister I., Engel R. Increased 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid content in lipopolysaccharide stimulated macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):695–700. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90986-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. K., Redwood S. M., Ohnuma T., Holland J. F., Droller M. J., Liu B. C. Inhibition of invasion of invasive human bladder carcinoma cells by protein kinase C inhibitor staurosporine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Nov 21;82(22):1753–1756. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.22.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearman M. S., Naor Z., Sekiguchi K., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. Selective activation of the gamma-subspecies of protein kinase C from bovine cerebellum by arachidonic acid and its lipoxygenase metabolites. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 30;243(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smal J., De Meyts P. Sphingosine, an inhibitor of protein kinase C, suppresses the insulin-like effects of growth hormone in rat adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4705–4709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. L. The eicosanoids and their biochemical mechanisms of action. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):315–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2590315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., Gordon J. A., Moore S. A. Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs). Prog Lipid Res. 1988;27(4):271–323. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(88)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Süss R., Arenberger P., Gross E. C., Ruzicka T. Regulation of 12(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12(S)-HETE) binding sites on human epidermal cells by interferon-gamma. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Dec;191(2):204–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90006-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. Cadherins: a molecular family important in selective cell-cell adhesion. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:237–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. X., Kaduce T. L., Spector A. A. Localization of 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid in endothelial cells. J Lipid Res. 1990 Dec;31(12):2265–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Orr F. W., Honn K. V. Interactions between cancer cells and the microvasculature: a rate-regulator for metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1989 Mar-Apr;7(2):127–167. doi: 10.1007/BF01787020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]