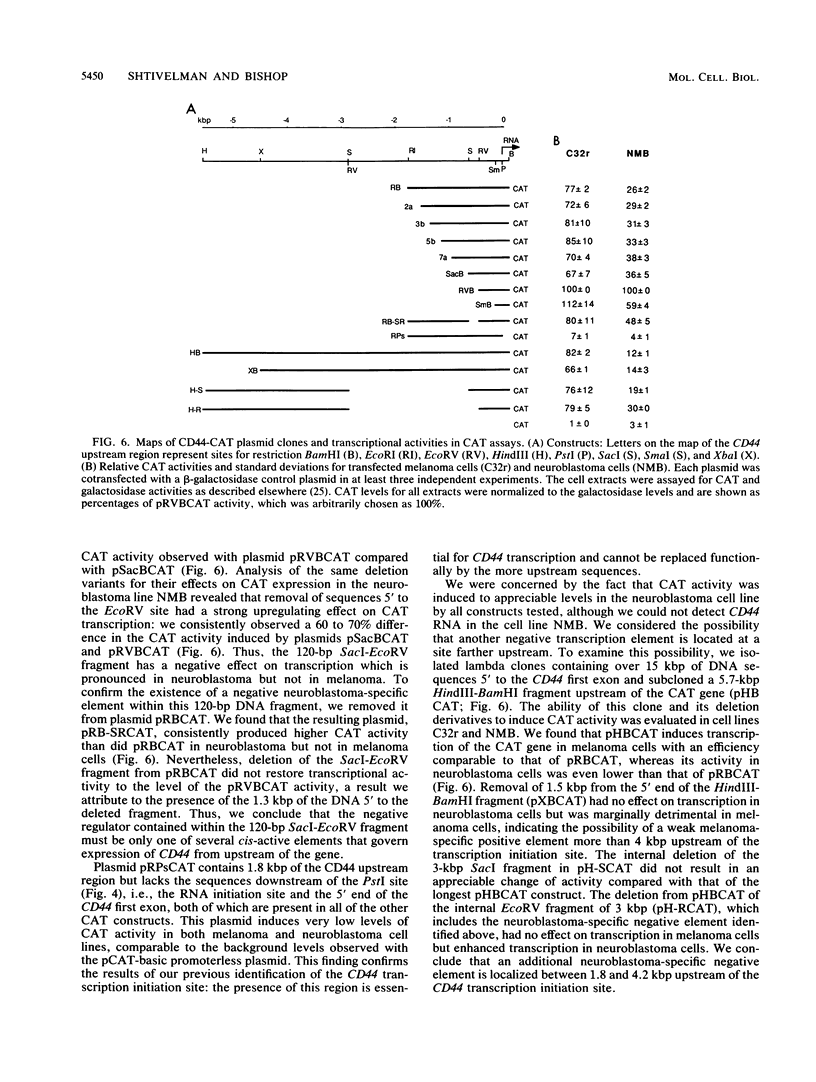
Abstract
We have used cDNA subtractive cloning to identify a group of human genes that are expressed in diverse differentiated derivatives of neural crest origin but not in neuroblastoma cell lines. One of these genes was identified as CD44, which encodes an integral membrane glycoprotein that serves as the principal receptor for hyaluronate and participates in specific cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix interactions. The repression of CD44 expression in neuroblastoma cell lines might be relevant to their high metastatic potential. We have cloned full-length cDNAs corresponding to CD44 trancscripts and identified a novel splice variant of CD44 lacking 31 amino acids of the extracellular domain. As a first step toward analysis of CD44 downregulation in neuroblastoma cells, we have mapped the CD44 RNA initiation site and analyzed the structure of the upstream regulatory region. We constructed a series of plasmids containing different amounts of CD44 upstream regulatory region linked to the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene and then analyzed their ability to promote transcription in neuroblastoma and melanoma cells. We found that a DNA segment including about 150 bp of the CD44 upstream region and the 5' end of the gene itself was sufficient to induce substantial transcription of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in both neuroblastoma and melanoma cells. Several upstream cis-acting elements contribute to the downregulation of CD44 in neuroblastoma cells, the most prominent being a 120-bp DNA fragment located 450 bp upstream to the RNA initiation site. Our data suggest that multiple factors might be involved in downregulation of CD44 in neuroblastoma cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akeson R., Bernards R. N-myc down regulates neural cell adhesion molecule expression in rat neuroblastoma. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2012–2016. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruffo A., Stamenkovic I., Melnick M., Underhill C. B., Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1303–1313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90694-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belitsos P. C., Hildreth J. E., August J. T. Homotypic cell aggregation induced by anti-CD44(Pgp-1) monoclonal antibodies and related to CD44(Pgp-1) expression. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1661–1670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., Dessain S. K., Weinberg R. A. N-myc amplification causes down-modulation of MHC class I antigen expression in neuroblastoma. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90636-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur G. M., Sekhon G., Goldstein M. N. Chromosomal aberrations in human neuroblastomas. Cancer. 1977 Nov;40(5):2256–2263. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197711)40:5<2256::aid-cncr2820400536>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Wayner E. A. Characterization of the class III collagen receptor, a phosphorylated, transmembrane glycoprotein expressed in nucleated human cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4193–4201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. J., Hutchins G. M., Cohen P. S., Helman L. J., Mennie R. J., Israel M. A. Human neuroblastoma tumor cell lines correspond to the arrested differentiation of chromaffin adrenal medullary neuroblasts. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Apr;1(4):149–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culty M., Miyake K., Kincade P. W., Sikorski E., Butcher E. C., Underhill C., Silorski E. The hyaluronate receptor is a member of the CD44 (H-CAM) family of cell surface glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2765–2774. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert F., Feder M., Balaban G., Brangman D., Lurie D. K., Podolsky R., Rinaldt V., Vinikoor N., Weisband J. Human neuroblastomas and abnormalities of chromosomes 1 and 17. Cancer Res. 1984 Nov;44(11):5444–5449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. A., Butcher E. C. Identification of mRNA that encodes an alternative form of H-CAM(CD44) in lymphoid and nonlymphoid tissues. Immunogenetics. 1990;32(6):389–397. doi: 10.1007/BF00241632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. A., Zhou D. F., Picker L. J., Minty C. N., Bargatze R. F., Ding J. F., Butcher E. C. A human lymphocyte homing receptor, the hermes antigen, is related to cartilage proteoglycan core and link proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90639-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günthert U., Hofmann M., Rudy W., Reber S., Zöller M., Haussmann I., Matzku S., Wenzel A., Ponta H., Herrlich P. A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to rat carcinoma cells. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90403-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Telen M. J., Hale L. P., Denning S. M. CD44--a molecule involved in leukocyte adherence and T-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1989 Dec;10(12):423–428. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Cohen D. I., Nielsen E. A., Davis M. M. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding T cell-specific membrane-associated proteins. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):149–153. doi: 10.1038/308149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet S., Groux H., Caillou B., Valentin H., Prieur A. M., Bernard A. CD44 contributes to T cell activation. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):798–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idzerda R. L., Carter W. G., Nottenburg C., Wayner E. A., Gallatin W. M., St John T. Isolation and DNA sequence of a cDNA clone encoding a lymphocyte adhesion receptor for high endothelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4659–4663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen S., Reichert R. A., Gallatin W. M., Bargatze R. F., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. Homing receptors and the control of lymphocyte migration. Immunol Rev. 1986 Jun;91:39–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewinsohn D. M., Nagler A., Ginzton N., Greenberg P., Butcher E. C. Hematopoietic progenitor cell expression of the H-CAM (CD44) homing-associated adhesion molecule. Blood. 1990 Feb 1;75(3):589–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake K., Medina K. L., Hayashi S., Ono S., Hamaoka T., Kincade P. W. Monoclonal antibodies to Pgp-1/CD44 block lympho-hemopoiesis in long-term bone marrow cultures. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):477–488. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake K., Underhill C. B., Lesley J., Kincade P. W. Hyaluronate can function as a cell adhesion molecule and CD44 participates in hyaluronate recognition. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):69–75. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Nakache M., Butcher E. C. Monoclonal antibodies to human lymphocyte homing receptors define a novel class of adhesion molecules on diverse cell types. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):927–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal A., Patil N., Chao M. A constitutive promoter directs expression of the nerve growth factor receptor gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3160–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Van Seventer G. A., Siraganian R., Wahl L., Shaw S. Dual role of the CD44 molecule in T cell adhesion and activation. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2457–2463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidell N., Altman A., Haussler M. R., Seeger R. C. Effects of retinoic acid (RA) on the growth and phenotypic expression of several human neuroblastoma cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Oct;148(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld K. H., Ishii D. N. Nerve growth factor effects and receptors in cultured human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):375–391. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinelli W., Sonnenfeld K. H., Ishii D. N. Effects of phorbol ester tumor promoters and nerve growth factor on neurite outgrowth in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Dec;42(12):5067–5073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T., Meyer J., Idzerda R., Gallatin W. M. Expression of CD44 confers a new adhesive phenotype on transfected cells. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90714-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Amiot M., Pesando J. M., Seed B. A lymphocyte molecule implicated in lymph node homing is a member of the cartilage link protein family. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1057–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90638-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Aruffo A., Amiot M., Seed B. The hematopoietic and epithelial forms of CD44 are distinct polypeptides with different adhesion potentials for hyaluronate-bearing cells. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):343–348. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Duband J. L., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in early chicken embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6737–6741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos M., Scarpa S., Ross R. A., Triche T. J. Differentiation of human neuroblastoma recapitulates neural crest development. Study of morphology, neurotransmitter enzymes, and extracellular matrix proteins. Am J Pathol. 1987 Sep;128(3):484–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weith A., Martinsson T., Cziepluch C., Brüderlein S., Amler L. C., Berthold F., Schwab M. Neuroblastoma consensus deletion maps to 1p36.1-2. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1989 Nov;1(2):159–166. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870010209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Triche T. J., Knutsen T., Miser J., Kao-Shan S., Tsai S., Israel M. A. Cytogenetic characterization of selected small round cell tumors of childhood. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 Apr 1;21(3):185–208. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. F., Ding J. F., Picker L. J., Bargatze R. F., Butcher E. C., Goeddel D. V. Molecular cloning and expression of Pgp-1. The mouse homolog of the human H-CAM (Hermes) lymphocyte homing receptor. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3390–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]