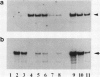
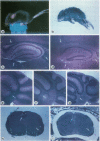
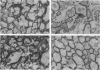
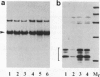
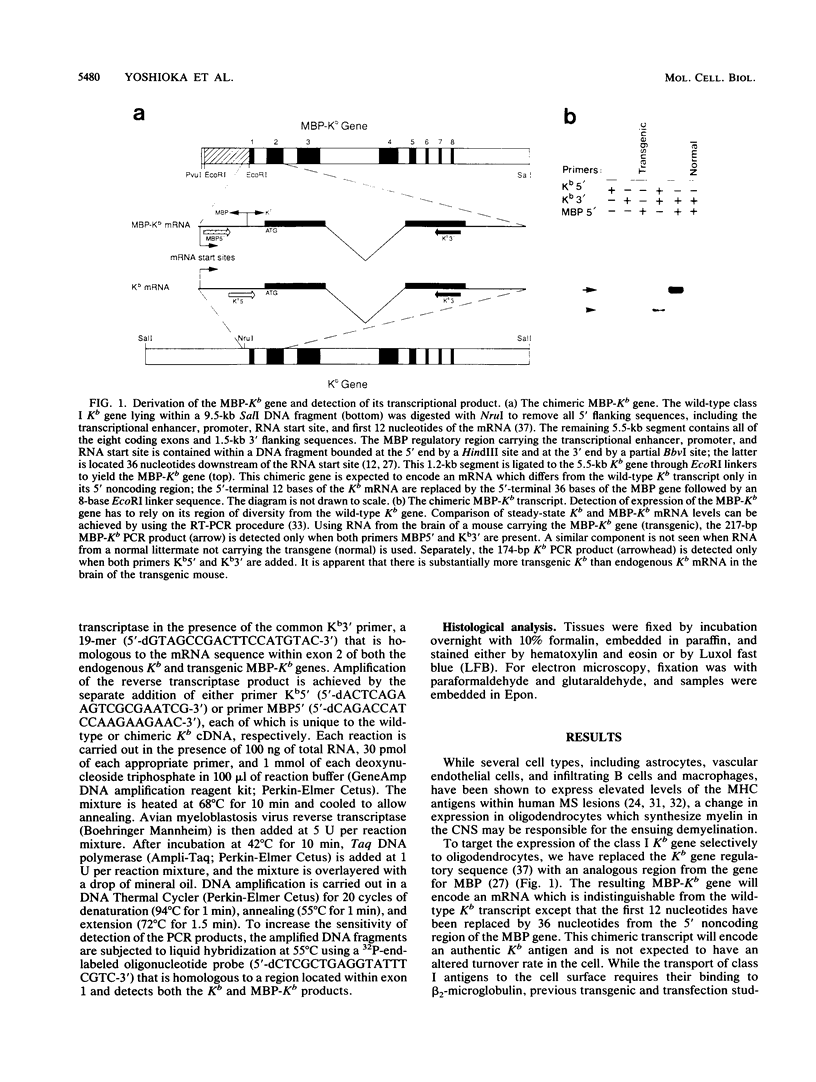
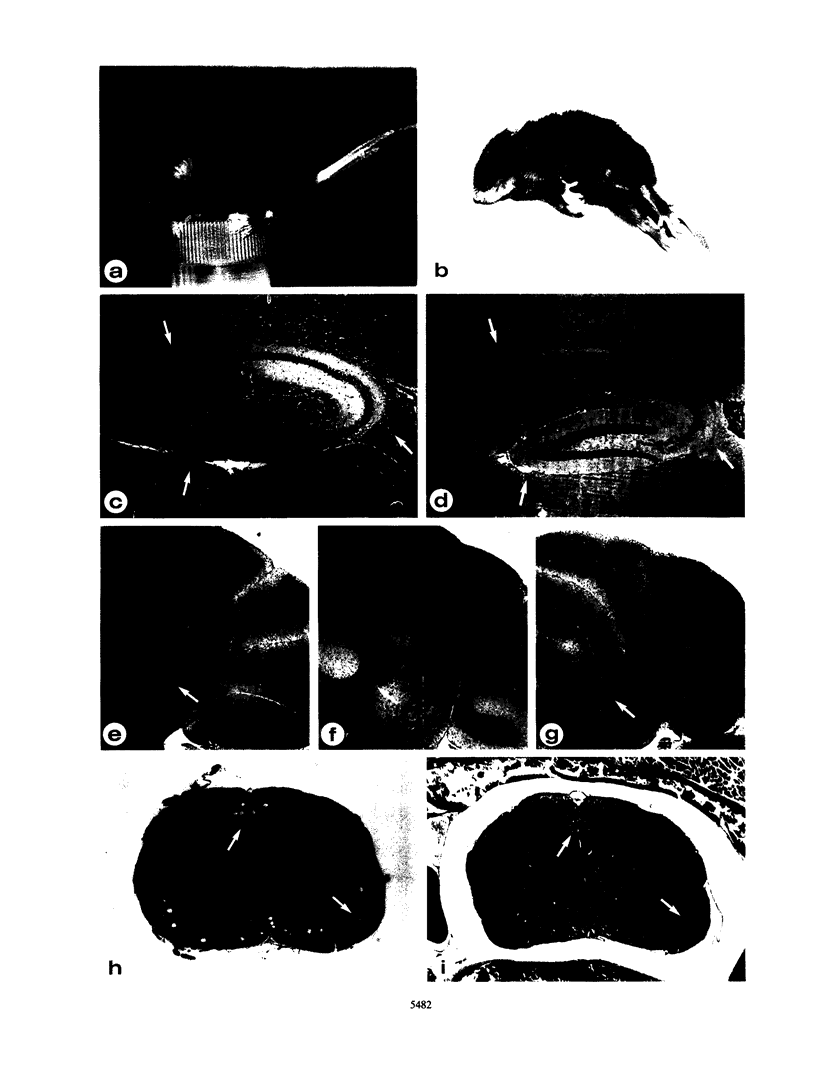
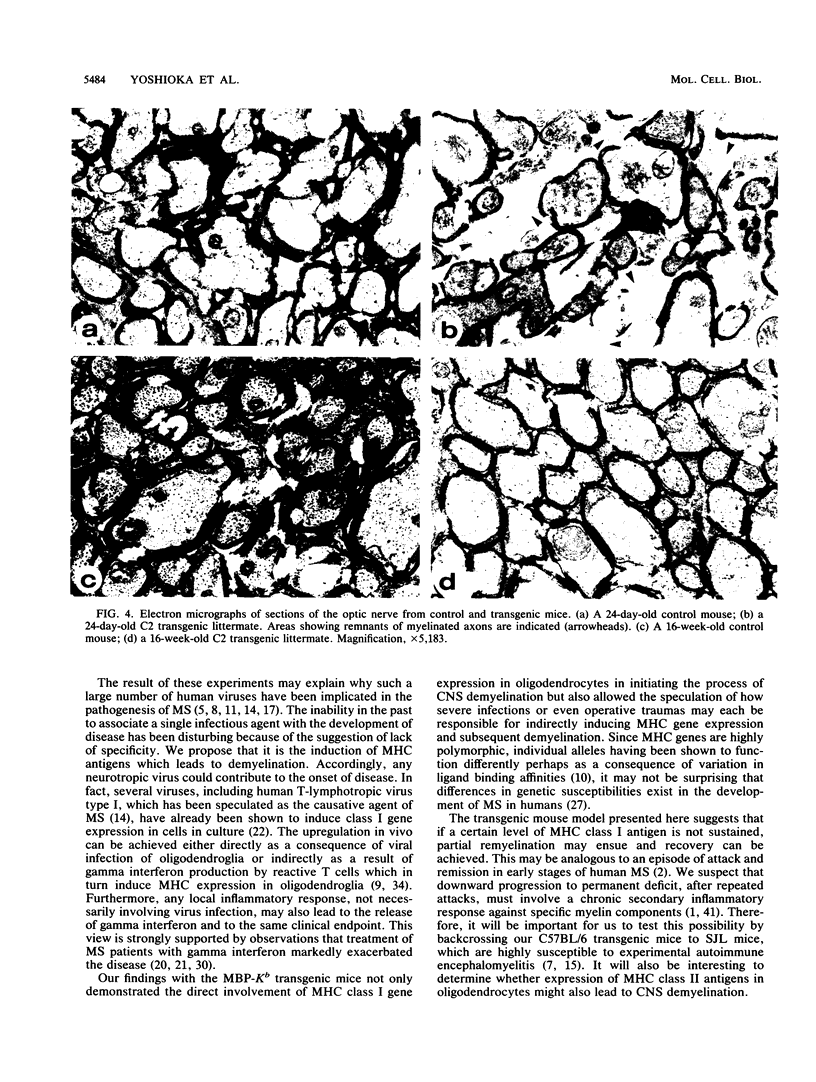
Abstract
A common feature of demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis in humans and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rodents is the marked elevation in the expression of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens in the involved sites. By specific targeting of a syngeneic MHC class I gene to oligodendrocytes, we have generated transgenic mice which not only exhibit severe involuntary tremors and develop tonic seizures but also show extensive demyelination in both the brain and the spinal cord. The fact that demyelination in these mice occurs in the absence of immune infiltration dismisses an autoimmune involvement but suggests that the MHC class I antigens play a direct role in inducing disease. Our findings lend support to the possibility that demyelinating diseases are induced by infectious agents such as viruses which can either directly activate MHC gene expression in oligodendroglia or indirectly activate expression through the release by reactive T cells of gamma interferon in the brain.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allegretta M., Nicklas J. A., Sriram S., Albertini R. J. T cells responsive to myelin basic protein in patients with multiple sclerosis. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):718–721. doi: 10.1126/science.1689076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieberich C., Yoshioka T., Tanaka K., Jay G., Scangos G. Functional expression of a heterologous major histocompatibility complex class I gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4003–4009. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burks J. S., DeVald B. L., Jankovsky L. D., Gerdes J. C. Two coronaviruses isolated from central nervous system tissue of two multiple sclerosis patients. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):933–934. doi: 10.1126/science.7403860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier R. D., Eldridge R. Possible risk factors in multiple sclerosis as found in a national twin study. Arch Neurol. 1982 Mar;39(3):140–144. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510150010003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz R. B., Chou C. H., McFarlin D. E. Induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in PL/J and (SJL/J x PL/J)F1 mice by myelin basic protein and its peptides: localization of a second encephalitogenic determinant. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):191–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemachudha T., Griffin D. E., Giffels J. J., Johnson R. T., Moser A. B., Phanuphak P. Myelin basic protein as an encephalitogen in encephalomyelitis and polyneuritis following rabies vaccination. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):369–374. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. L., Panitch H. S., Johnson K. P. Lymphocytes from multiple sclerosis patients produce elevated levels of gamma interferon in vitro. J Clin Immunol. 1985 Nov;5(6):386–389. doi: 10.1007/BF00915335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höglund P., Ljunggren H. G., Ohlén C., Ahrlund-Richter L., Scangos G., Bieberich C., Jay G., Klein G., Kärre K. Natural resistance against lymphoma grafts conveyed by H-2Dd transgene to C57BL mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1469–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Griffin D. E., Hirsch R. L., Wolinsky J. S., Roedenbeck S., Lindo de Soriano I., Vaisberg A. Measles encephalomyelitis--clinical and immunologic studies. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):137–141. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki M., Sato M., Kimura M., Yokoyama M., Kobayashi K., Nomura T. Conversion of normal behavior to shiverer by myelin basic protein antisense cDNA in transgenic mice. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):593–595. doi: 10.1126/science.2456614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike K., Hinrichs S. H., Isselbacher K. J., Jay G. Transgenic mouse model for human gastric carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5615–5619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., DeFreitas E. C., Harper M. E., Sandberg-Wollheim M., Sheremata W. A., Robert-Guroff M., Saxinger C. W., Feinberg M. B., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Multiple sclerosis and human T-cell lymphotropic retroviruses. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):154–160. doi: 10.1038/318154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi E., Gilden D. H., Wroblewska Z., Rorke L. B., Weiss S. R. Experimental demyelination produced by the A59 strain of mouse hepatitis virus. Neurology. 1984 May;34(5):597–603. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.5.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisak R. P., Behan P. O., Zweiman B., Shetty T. Cell-mediated immunity to myelin basic protein in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neurology. 1974 Jun;24(6):560–564. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.6.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerenberg M., Hinrichs S. H., Reynolds R. K., Khoury G., Jay G. The tat gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 induces mesenchymal tumors in transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1324–1329. doi: 10.1126/science.2888190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T., Poduslo S. E. Myelination in rat brain: changes in myelin composition during brain maturation. J Neurochem. 1973 Oct;21(4):759–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panitch H. S., Hirsch R. L., Haley A. S., Johnson K. P. Exacerbations of multiple sclerosis in patients treated with gamma interferon. Lancet. 1987 Apr 18;1(8538):893–895. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92863-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panitch H. S., Hirsch R. L., Schindler J., Johnson K. P. Treatment of multiple sclerosis with gamma interferon: exacerbations associated with activation of the immune system. Neurology. 1987 Jul;37(7):1097–1102. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.7.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada M., Suzumura A., Yoshida M., Marunouchi T. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I trans activator induces class I major histocompatibility complex antigen expression in glial cells. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):4002–4006. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.4002-4006.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Blanchette B. W., Bhan A. K., Colvin R. B. The immunopathology of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. II. Endothelial cell Ia increases prior to inflammatory cell infiltration. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2402–2407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman L., Rosenbaum J. T., Sriram S., McDevitt H. O. In vivo effects of antibodies to immune response gene products: prevention of experimental allergic encephalitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7111–7114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzumura A., Lavi E., Weiss S. R., Silberberg D. H. Coronavirus infection induces H-2 antigen expression on oligodendrocytes and astrocytes. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):991–993. doi: 10.1126/science.3010460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Roach A., Teplow D. B., Prusiner S. B., Hood L. Cloning and characterization of the myelin basic protein gene from mouse: one gene can encode both 14 kd and 18.5 kd MBPs by alternate use of exons. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Appella E., Jay G. Developmental activation of the H-2K gene is correlated with an increase in DNA methylation. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):457–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Isselbacher K. J., Khoury G., Jay G. Reversal of oncogenesis by the expression of a major histocompatibility complex class I gene. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):26–30. doi: 10.1126/science.3975631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Lebon P. Multiple sclerosis: involvement of interferons in lesion pathogenesis. Ann Neurol. 1988 Aug;24(2):243–251. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Raine C. S., McFarlin D. E. Acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the mouse: immunopathology of the developing lesion. Cell Immunol. 1985 Mar;91(1):240–254. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Scheinberg L. C., Raine C. S. On the presence of Ia-positive endothelial cells and astrocytes in multiple sclerosis lesions and its relevance to antigen presentation. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Apr;8(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(85)80043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veres G., Gibbs R. A., Scherer S. E., Caskey C. T. The molecular basis of the sparse fur mouse mutation. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.3603027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vervliet G., Claeys H., Van Haver H., Carton H., Vermylen C., Meulepas E., Billiau A. Interferon production and natural killer (NK) activity in leukocyte cultures from multiple sclerosis patients. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Jul;60(1):137–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel J., Hinrichs S. H., Reynolds R. K., Luciw P. A., Jay G. The HIV tat gene induces dermal lesions resembling Kaposi's sarcoma in transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):606–611. doi: 10.1038/335606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Golden L., Zakut R., Mellor A., Fahrner K., Kvist S., Flavell R. A. The DNA sequence of the H-2kb gene: evidence for gene conversion as a mechanism for the generation of polymorphism in histocompatibilty antigens. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):453–462. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Bartlett P. F., Clark-Lewis I., McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Schrader J. W. Interferon-gamma induces the expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on brain cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Feb-Mar;7(5-6):255–278. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(84)80026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woyciechowska J. L., Trapp B. D., Patrick D. H., Shekarchi I. C., Leinikki P. O., Sever J. L., Holmes K. V. Acute and subacute demyelination induced by mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 in C3H mice. J Exp Pathol. 1984 Fall;1(4):295–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka T., Bieberich C., Scangos G., Jay G. A transgenic class I antigen is recognized as self and functions as a restriction element. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3861–3867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaller D. M., Osman G., Kanagawa O., Hood L. Prevention and treatment of murine experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with T cell receptor V beta-specific antibodies. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):1943–1955. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller N. K., Hunkeler M. J., Campagnoni A. T., Sprague J., Lazzarini R. A. Characterization of mouse myelin basic protein messenger RNAs with a myelin basic protein cDNA clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):18–22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]