Abstract
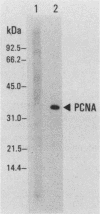
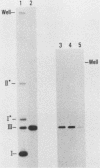
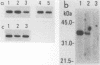
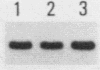
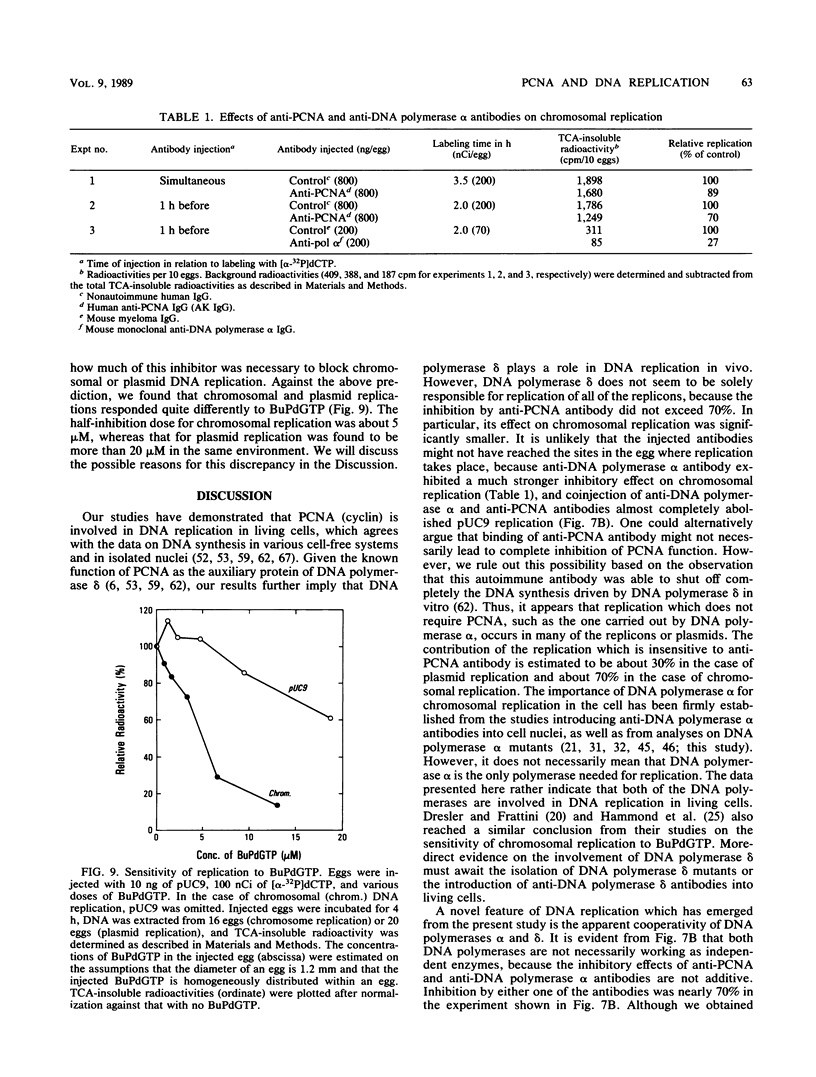
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) (also called cyclin) is known to stimulate the activity of DNA polymerase delta but not the other DNA polymerases in vitro. We injected a human autoimmune antibody against PCNA into unfertilized eggs of Xenopus laevis and examined the effects of this antibody on the replication of injected plasmid DNA as well as egg chromosomes. The anti-PCNA antibody inhibited plasmid replication by up to 67%, demonstrating that PCNA is involved in plasmid replication in living cells. This result further implies that DNA polymerase delta is necessary for plasmid replication in vivo. Anti-PCNA antibody alone did not block plasmid replication completely, but the residual replication was abolished by coinjection of a monoclonal antibody against DNA polymerase alpha. Anti-DNA polymerase alpha alone inhibited plasmid replication by 63%. Thus, DNA polymerase alpha is also required for plasmid replication in this system. In similar studies on the replication of egg chromosomes, the inhibition by anti-PCNA antibody was only 30%, while anti-DNA polymerase alpha antibody blocked 73% of replication. We concluded that the replication machineries of chromosomes and plasmid differ in their relative content of DNA polymerase delta. In addition, we obtained evidence through the use of phenylbutyl deoxyguanosine, an inhibitor of DNA polymerase alpha, that the structure of DNA polymerase alpha holoenzyme for chromosome replication is significantly different from that for plasmid replication.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Huebsch D., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H., Bravo R. Cloning and sequence of the human nuclear protein cyclin: homology with DNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews M. T., Brown D. D. Transient activation of oocyte 5S RNA genes in Xenopus embryos by raising the level of the trans-acting factor TFIIIA. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90640-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg C. A., Gall J. G. Microinjected Tetrahymena rDNA ends are not recognized as telomeres in Xenopus eggs. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):691–698. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Frank R., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H. Cyclin/PCNA is the auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase-delta. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):515–517. doi: 10.1038/326515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Macdonald-Bravo H. Changes in the nuclear distribution of cyclin (PCNA) but not its synthesis depend on DNA replication. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):655–661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03679.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Macdonald-Bravo H. Existence of two populations of cyclin/proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle: association with DNA replication sites. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1549–1554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R. Synthesis of the nuclear protein cyclin (PCNA) and its relationship with DNA replication. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Apr;163(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S. J., Reeder R. H. Fate of amplified nucleoli in Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Biol. 1982 Jun;91(2):458–467. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes J. J. Differential inhibitors of DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):628–634. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes J. J., Downey K. M., Black V. L., So A. G. A new mammalian DNA polymerase with 3' to 5' exonuclease activity: DNA polymerase delta. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2817–2823. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes J. J. Structural and functional properties of DNA polymerase delta from rabbit bone marrow. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984 Apr;62(1):13–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00230073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Bravo R., Larsen P. M., Fey S. J. Cyclin: a nuclear protein whose level correlates directly with the proliferative state of normal as well as transformed cells. Leuk Res. 1984;8(2):143–157. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(84)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Celis A. Cell cycle-dependent variations in the distribution of the nuclear protein cyclin proliferating cell nuclear antigen in cultured cells: subdivision of S phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3262–3266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Madsen P., Celis A., Nielsen H. V., Gesser B. Cyclin (PCNA, auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase delta) is a central component of the pathway(s) leading to DNA replication and cell division. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 10;220(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80865-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Madsen P. Increased nuclear cyclin/PCNA antigen staining of non S-phase transformed human amnion cells engaged in nucleotide excision DNA repair. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase J. W., Dawid I. B. Biogenesis of mitochondria during Xenopus laevis development. Dev Biol. 1972 Apr;27(4):504–518. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B. Evidence for the mitochondrial origin of frog egg cytoplasmic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):269–276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker R. S., Yamaguchi M., Possenti R., Bradley M. K., DePamphilis M. L. In vitro initiation of DNA replication in simian virus 40 chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10863–10872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresler S. L., Frattini M. G. DNA replication and UV-induced DNA repair synthesis in human fibroblasts are much less sensitive than DNA polymerase alpha to inhibition by butylphenyl-deoxyguanosine triphosphate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7093–7102. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eki T., Murakami Y., Enomoto T., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. Characterization of DNA replication at a restrictive temperature in a mouse DNA temperature-sensitive mutant, tsFT20 strain, containing heat-labile DNA polymerase alpha activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8888–8893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Birnstiel M. L., Speight V. A. The replication of purified DNA introduced into living egg cytoplasm. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 18;174(2):614–628. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. A., Byrnes J. J., Miller M. R. Identification of DNA polymerase delta in CV-1 cells: studies implicating both DNA polymerase delta and DNA polymerase alpha in DNA replication. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6817–6824. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Laskey R. A. Regulated replication of DNA microinjected into eggs of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):761–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines P. J., Benbow R. M. Initiation of replication at specific origins in DNA molecules microinjected into unfertilized eggs of the frog Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourcade D., Dressler D., Wolfson J. The amplification of ribosomal RNA genes involves a rolling circle intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2926–2930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami S., Taguchi T., Ohashi M., Oguro M., Nagano H., Mano Y. Aphidicolin prevents mitotic cell division by interfering with the activity of DNA polymerase-alpha. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):458–460. doi: 10.1038/275458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Snyder M., Chang L. M., Davis R. W., Campbell J. L. Isolation of the gene encoding yeast DNA polymerase I. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Miller M. R., Hammond R. A., Mercer W. E. A microinjected monoclonal antibody against human DNA polymerase-alpha inhibits DNA replication in human, hamster, and mouse cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10802–10807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiserman H. B., Benbow R. M. Characterization of a stable, major DNA polymerase alpha species devoid of DNA primase activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10249–10265. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan N. N., Wright G. E., Dudycz L. W., Brown N. C. Butylphenyl dGTP: a selective and potent inhibitor of mammalian DNA polymerase alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3695–3706. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg A. DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Vanderlaan M., Dolbeare F., Gray J., Tan E. M. Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)/cyclin during the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Sep;166(1):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Kearsey S. E., Mechali M., Dingwall C., Mills A. D., Dilworth S. M., Kleinschmidt J. Chromosome replication in early Xenopus embryos. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:657–663. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. Y., Tan C. K., Downey K. M., So A. G. Further studies on calf thymus DNA polymerase delta purified to homogeneity by a new procedure. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 24;23(9):1906–1913. doi: 10.1021/bi00304a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. Y., Toomey N. L. Human placental DNA polymerase delta: identification of a 170-kilodalton polypeptide by activity staining and immunoblotting. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 24;26(4):1076–1085. doi: 10.1021/bi00378a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. Y., Toomey N. L., Wright G. E. Differential inhibition of human placental DNA polymerases delta and alpha by BuPdGTP and BuAdATP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8623–8630. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen P., Celis J. E. S-phase patterns of cyclin (PCNA) antigen staining resemble topographical patterns of DNA synthesis. A role for cyclin in DNA replication? FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 25;193(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Bernstein R. M., Franza B. R., Jr, Garrels J. I. Identity of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cyclin. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):374–376. doi: 10.1038/309374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Moriuchi T., Koji T., Nakane P. K. Molecular cloning of cDNA coding for rat proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)/cyclin. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):637–642. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04802.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. R., Seighman C., Ulrich R. G. Inhibition of DNA replication and DNA polymerase alpha activity by monoclonal anti-(DNA polymerase alpha) immunoglobulin G and F(ab) fragments. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7440–7445. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. R., Ulrich R. G., Wang T. S., Korn D. Monoclonal antibodies against human DNA polymerase-alpha inhibit DNA replication in permeabilized human cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):134–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi K., Fritzler M. J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to a nuclear antigen in proliferating cells. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2228–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. S., Sullivan K., Tan E. M., Prystowsky M. B. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen/cyclin is an interleukin 2-responsive gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8447–8450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méchali M., Kearsey S. Lack of specific sequence requirement for DNA replication in Xenopus eggs compared with high sequence specificity in yeast. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Kurki P., Celis J. E., Nakamura R. M., Tan E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to a nuclear protein (PCNA/cyclin) associated with DNA replication. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Feb;168(2):475–486. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Ogata Y., Nakamura R. M., Tan E. M. Purification and N-terminal amino acid sequence of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)/cyclin and development of ELISA for anti-PCNA antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2623–2627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Ogata Y., Takasaki Y., Tan E. M. Epitopes on proliferating cell nuclear antigen recognized by human lupus autoantibody and murine monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):2942–2946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Kostura M., Marshak D. R., Mathews M. B., Stillman B. The cell-cycle regulated proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):471–475. doi: 10.1038/326471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Tan C. K., Kostura M., Mathews M. B., So A. G., Downey K. M., Stillman B. Functional identity of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and a DNA polymerase-delta auxiliary protein. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):517–520. doi: 10.1038/326517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Transformation of frog embryos with a rabbit beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5051–5055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadaie M. R., Mathews M. B. Immunochemical and biochemical analysis of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Apr;163(2):423–433. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. K., Morris C. F., Alberts B. M. Efficient in vitro replication of double-stranded DNA templates by a purified T4 bacteriophage replication system. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4290–4293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanker L. H., Vanderlaan M., Juarez-Salinas H. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascites fluid by hydroxylapatite chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Jan 21;76(1):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki Y., Deng J. S., Tan E. M. A nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation and blast transformation. J Exp Med. 1981 Dec 1;154(6):1899–1909. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.6.1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. K., Castillo C., So A. G., Downey K. M. An auxiliary protein for DNA polymerase-delta from fetal calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12310–12316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. K., Sullivan K., Li X. Y., Tan E. M., Downey K. M., So A. G. Autoantibody to the proliferating cell nuclear antigen neutralizes the activity of the auxiliary protein for DNA polymerase delta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9299–9308. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Chan E. K., Sullivan K. F., Rubin R. L. Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs): diagnostically specific immune markers and clues toward the understanding of systemic autoimmunity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 May;47(2):121–141. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Ogata K., Takasaki Y. PCNA/cyclin: a lupus antigen connected with DNA replication. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1987 Jun;14 (Suppl 13):89–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Hu S. Z., Wang T. S., Korn D. Preparation and preliminary characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8386–8390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiébaud C. H., Fischberg M. DNA content in the genus Xenopus. Chromosoma. 1977 Feb 3;59(3):253–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00292781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W., Dumont J. N., Sega M. W. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. 3. Optimum incubation conditions. J Exp Zool. 1973 Jun;184(3):321–333. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401840305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright G. E., Dudycz L. W. Synthesis and characterization of N2-(p-n-butylphenyl)-2'-deoxyguanosine and its 5'-triphosphate and their inhibition of HeLa DNA polymerase alpha. J Med Chem. 1984 Feb;27(2):175–181. doi: 10.1021/jm00368a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. Effects of aphidicolin and/or 2',3'-dideoxythymidine on DNA repair induced in HeLa cells by four types of DNA-damaging agents. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10412–10417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]