Abstract
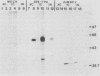
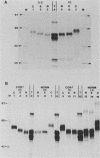
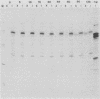
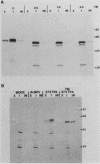
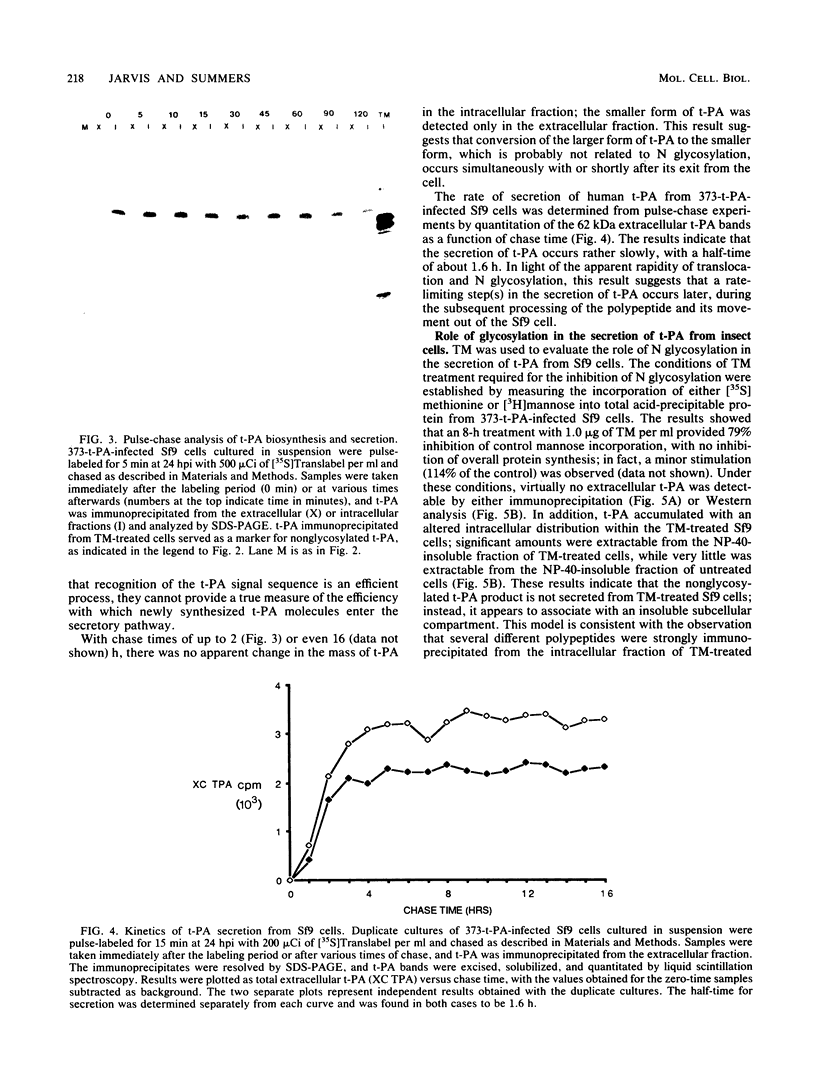
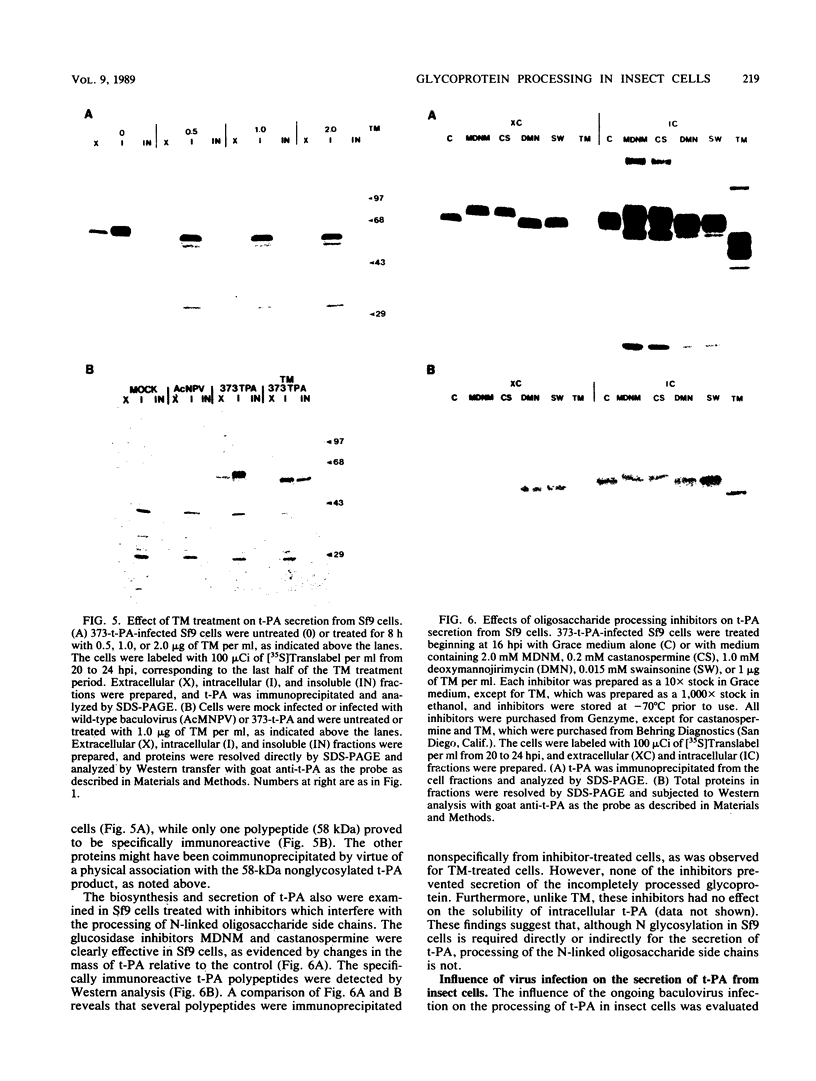
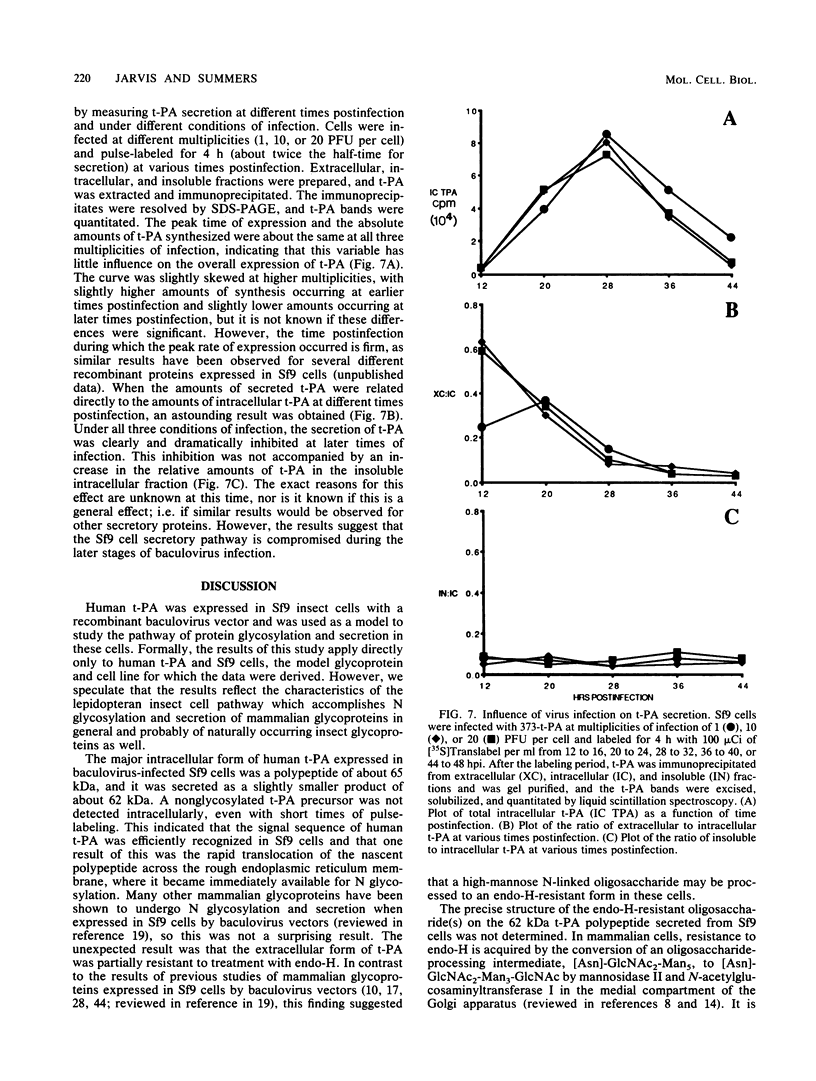
Cell lines established from the lepidopteran insect Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm; Sf9) are used routinely as hosts for the expression of foreign proteins by recombinant baculovirus vectors. We have examined the pathway of protein glycosylation and secretion in these cells, using human tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) as a model. t-PA expressed in Sf9 cells was both N glycosylated and secreted. At least a subset of the N-linked oligosaccharides in extracellular t-PA was resistant to endo-beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminidase H, which removes immature, high-mannose-type oligosaccharides. This refutes the general conclusion from previous studies that Sf9 cells cannot process immature N-linked oligosaccharides to an endo-beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminidase H-resistant form. A nonglycosylated t-PA precursor was not detected in Sf9 cells, even with very short pulse-labeling times. This suggests that the mammalian signal sequence of t-PA is efficiently recognized in Sf9 cells and that it can mediate rapid translocation across the membrane of the rough endoplasmic reticulum, where cotranslational N glycosylation takes place. However, t-PA was secreted rather slowly, with a half-time of about 1.6 h. Thus, a rate-limiting step(s) in secretion occurs subsequent to translocation and N glycosylation of the t-PA polypeptide. Treatment of Sf9 cells with tunicamycin, but not with inhibitors of oligosaccharide processing, prevented the appearance of t-PA in the extracellular medium. This suggests that N glycosylation per se, but not processing of the N-linked oligosaccharides, is required directly or indirectly in baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells for the secretion of t-PA. Finally, the relative efficiency of secretion decreased dramatically with time of infection, suggesting that the Sf9 host cell secretory pathway is compromised during the later stages of baculovirus infection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bole D. G., Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters T. D., Hughes R. C. Isolation and characterization of mosquito cell membrane glycoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters T. D., Hughes R. C., Vischer P. Steps in the biosynthesis of mosquito cell membrane glycoproteins and the effects of tunicamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):672–686. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton C. A., Volkman L. E. Effect of tunicamycin on the structural proteins and infectivity of budded Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):214–218. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. Inhibitors of the biosynthesis and processing of N-linked oligosaccharide chains. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:497–534. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G. Progress in unraveling pathways of Golgi traffic. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:447–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield C., Patel G., Clark S., Jones N., Waterfield M. D. Expression of the human EGF receptor with ligand-stimulatable kinase activity in insect cells using a baculovirus vector. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):139–146. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02793.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas I. G., Wabl M. Immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):387–389. doi: 10.1038/306387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Robbins P. W. Regulation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing. Oligosaccharide processing in Aedes albopictus mosquito cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2375–2382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukuruzinska M. A., Bergh M. L., Jackson B. J. Protein glycosylation in yeast. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:915–944. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda K., Hauser C., Rott R., Klenk H. D., Doerfler W. Expression of the influenza virus haemagglutinin in insect cells by a baculovirus vector. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1359–1365. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Bernard B. A., White S. L., Parent J. B. Function of the carbohydrate moieties of glycoproteins. J Cell Biochem. 1982;18(3):313–335. doi: 10.1002/jcb.1982.240180306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Holmes W. E., Kohr W. J., Harkins R. N., Vehar G. A., Ward C. A., Bennett W. F., Yelverton E., Seeburg P. H., Heyneker H. L. Cloning and expression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator cDNA in E. coli. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):214–221. doi: 10.1038/301214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennock G. D., Shoemaker C., Miller L. K. Strong and regulated expression of Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase in insect cells with a baculovirus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):399–406. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl G., Jörnvall H., Kok P., Wallén P. Porcine tissue plasminogen activator. Immunoaffinity purification, structural properties and glycosylation pattern. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80872-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl G., Källström M., Bergsdorf N., Wallén P., Jörnvall H. Tissue plasminogen activator: peptide analyses confirm an indirectly derived amino acid sequence, identify the active site serine residue, establish glycosylation sites, and localize variant differences. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3701–3707. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possee R. D. Cell-surface expression of influenza virus haemagglutinin in insect cells using a baculovirus vector. Virus Res. 1986 Jul;5(1):43–59. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan R. O., Anderson D. R., Grimes W. J., Law J. H. Arylphorin from Manduca sexta: carbohydrate structure and immunological studies. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Nov 15;243(1):115–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90779-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Fraser M. J., Summers M. D. Molecular Engineering of the Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Genome: Deletion Mutations Within the Polyhedrin Gene. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):584–593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.584-593.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. Analysis of baculovirus genomes with restriction endonucleases. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):517–527. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D., Fraser M. J. Production of human beta interferon in insect cells infected with a baculovirus expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2156–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel B. E. Coronary thrombolysis with tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA): emerging strategies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1986 Nov;8(5):1220–1225. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(86)80404-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Gómez C. M., Plummer T. H., Jr Deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycans by peptide:N-glycosidase F. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4665–4671. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. A comparison of the substrate specificities of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases from Streptomyces griseus and Diplococcus Pneumoniae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):455–462. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptomyces griseus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. L., Goodwin R. H., Tompkins G. J., McCawley P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro. 1977 Apr;13(4):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02615077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P., Bergsdorf N., Rånby M. Purification and identification of two structural variants of porcine tissue plasminogen activator by affinity adsorption on fibrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 24;719(2):318–328. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P., Pohl G., Bergsdorf N., Rånby M., Ny T., Jörnvall H. Purification and characterization of a melanoma cell plasminogen activator. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 16;132(3):681–686. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojchowski D. M., Orkin S. H., Sytkowski A. J. Active human erythropoietin expressed in insect cells using a baculovirus vector: a role for N-linked oligosaccharide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 8;910(3):224–232. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90114-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojchowski D. M., Parsons P., Nordin J. H., Kunkel J. G. Processing of pro-vitellogenin in insect fat body: a role for high-mannose oligosaccharide. Dev Biol. 1986 Aug;116(2):422–430. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]