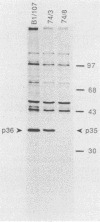
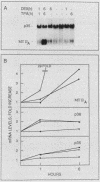
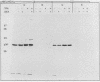
Abstract
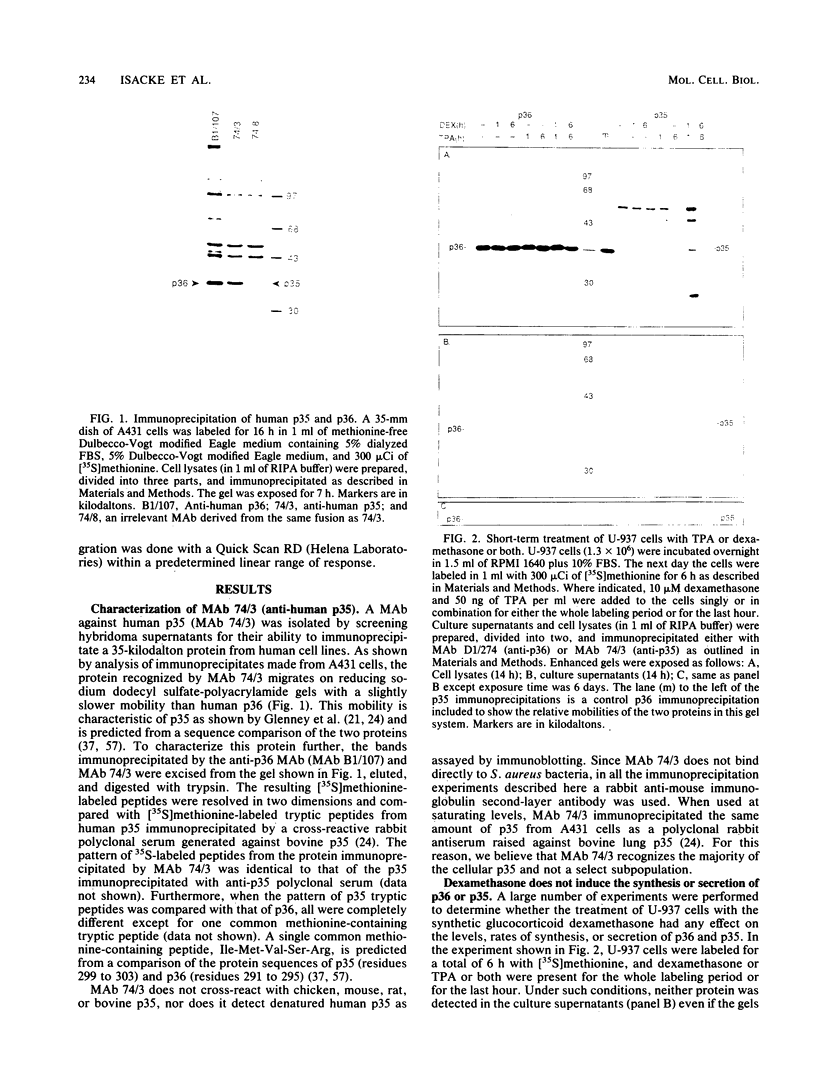
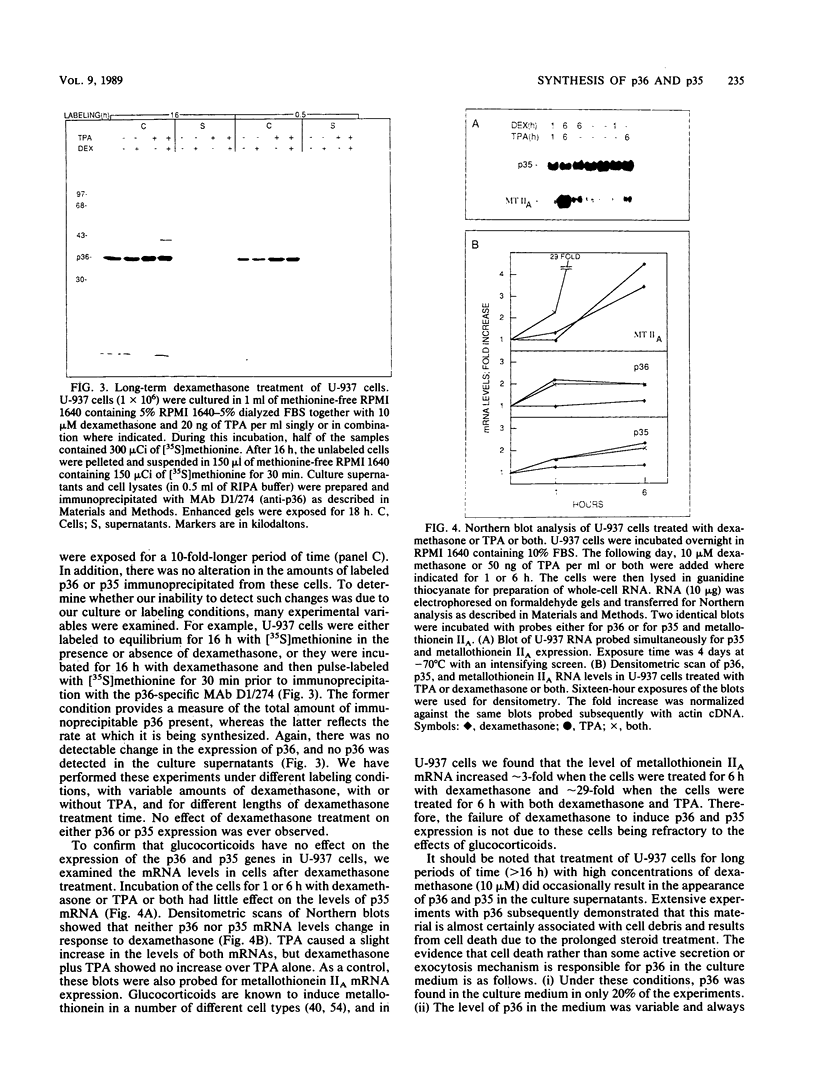
p36 and p35 are distinct but related proteins that share many structural and biochemical features which were first identified as major substrates for protein-tyrosine kinases. Subsequently, both proteins have been shown to be Ca2+-, phospholipid-, and F-actin-binding proteins that underlie the plasma membrane and are associated with the cortical cytoskeleton. Recent reports have claimed that these proteins function as lipocortins, i.e., phospholipase A2 inhibitors that mediate the anti-inflammatory action of glucocorticoids. To investigate this possibility and to learn more about the functions of p36 and p35, we used human-specific anti-p36 and anti-p35 monoclonal antibodies to determine whether the expression or secretion of either protein was inducible by dexamethasone in the human U-937 myeloid cell line and in other human cell types. Additionally, we examined the levels of mRNA for both proteins. No effect of dexamethasone was observed on p36 or p35 expression at either the mRNA or protein level, nor were these proteins secreted under any of the culture conditions investigated. However, it was observed that in these cells the rate of synthesis and accumulation of both proteins was increased when the U-937 cells were induced to differentiate in culture to adherent macrophagelike cells. This offers a model system with which to study the control of p36 and p35 expression.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beemon K., Hunter T. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus src gene products synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):551–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.551-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Flower R. J., Parente L., Persico P. Macrocortin: a polypeptide causing the anti-phospholipase effect of glucocorticoids. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):147–149. doi: 10.1038/287147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brönnegård M., Andersson O., Edwall D., Lund J., Norstedt G., Carstedt-Duke J. Human calpactin II (lipocortin I) messenger ribonucleic acid is not induced by glucocorticoids. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Aug;2(8):732–739. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-8-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C., Howlett A. R., Martin G. S., Bissell M. J. The tyrosine phosphorylation substrate p36 is developmentally regulated in embryonic avian limb and is induced in cell culture. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):2017–2024. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirino G., Flower R. J., Browning J. L., Sinclair L. K., Pepinsky R. B. Recombinant human lipocortin 1 inhibits thromboxane release from guinea-pig isolated perfused lung. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):270–272. doi: 10.1038/328270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Identification and characterization of cellular targets for tyrosine protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1108–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Similarities and differences between the effects of epidermal growth factor and Rous sarcoma virus. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):878–883. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson F. F., Dennis E. A., Powell M., Glenney J. R., Jr Inhibition of phospholipase A2 by "lipocortins" and calpactins. An effect of binding to substrate phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1698–1705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. K., Misono K. S., Lukas T. J., Mroczkowski B., Cohen S. A calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase isolated from normal tissue. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13784–13792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drust D. S., Creutz C. E. Aggregation of chromaffin granules by calpactin at micromolar levels of calcium. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):88–91. doi: 10.1038/331088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Cook R., Miller G. J., Erikson R. L. The same normal cell protein is phosphorylated after transformation by avian sarcoma viruses with unrelated transforming genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;1(1):43–50. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., Cohen S. Isolation of a calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase from A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2636–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Blackwell G. J. Anti-inflammatory steroids induce biosynthesis of a phospholipase A2 inhibitor which prevents prostaglandin generation. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):456–459. doi: 10.1038/278456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J. Common domain structure of Ca2+ and lipid-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 14;203(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81445-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Weber K. Identity of p36K phosphorylated upon Rous sarcoma virus transformation with a protein purified from brush borders; calcium-dependent binding to non-erythroid spectrin and F-actin. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):227–233. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giugni T. D., James L. C., Haigler H. T. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of specific proteins in permeabilized human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15081–15090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B. F. Amino-terminal sequence of p36 and associated p10: identification of the site of tyrosine phosphorylation and homology with S-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7884–7888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B., Powell M. A. Calpactins: two distinct Ca++-regulated phospholipid- and actin-binding proteins isolated from lung and placenta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):503–511. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. Phospholipid-dependent Ca2+ binding by the 36-kDa tyrosine kinase substrate (calpactin) and its 33-kDa core. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7247–7252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. Two related but distinct forms of the Mr 36,000 tyrosine kinase substrate (calpactin) that interact with phospholipid and actin in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4258–4262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. The 46,000-dalton tyrosine protein kinase substrate is widespread, whereas the 36,000-dalton substrate is only expressed at high levels in certain rodent tissues. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):487–497. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Woodgett J. R., Isacke C. M., Hunter T. The protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 is also a substrate for protein kinase C in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2738–2744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Edelman G. M. The 34 kd pp60src substrate is located at the inner face of the plasma membrane. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Schlaepfer D. D., Burgess W. H. Characterization of lipocortin I and an immunologically unrelated 33-kDa protein as epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase substrates and phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6921–6930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K. Homology probing: identification of cDNA clones encoding members of the protein-serine kinase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):388–392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Hoffman T., Hirata F. Differentiation of a histiocytic lymphoma cell line by lipomodulin, a phospholipase inhibitory protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90342-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Matsuda K., Notsu Y., Hattori T., del Carmine R. Phosphorylation at a tyrosine residue of lipomodulin in mitogen-stimulated murine thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4717–4721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Notsu Y., Iwata M., Parente L., DiRosa M., Flower R. J. Identification of several species of phospholipase inhibitory protein(s) by radioimmunoassay for lipomodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91588-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Schiffmann E., Venkatasubramanian K., Salomon D., Axelrod J. A phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein in rabbit neutrophils induced by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2533–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., McGray P., Mattaliano R. J., Burne C., Chow E. P., Sinclair L. K., Pepinsky R. B. Purification and characterization of proteolytic fragments of lipocortin I that inhibit phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7639–7645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Burne C., Frey A., Hession C., McGray P., Sinclair L. K., Chow E. P. Two human 35 kd inhibitors of phospholipase A2 are related to substrates of pp60v-src and of the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90736-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacke C. M., Sauvage C. A., Hyman R., Lesley J., Schulte R., Trowbridge I. S. Identification and characterization of the human Pgp-1 glycoprotein. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(5):326–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00398797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacke C. M., Trowbridge I. S., Hunter T. Modulation of p36 phosphorylation in human cells: studies using anti-p36 monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2745–2751. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Andersen R. D., Slater E., Smith K., Herschman H. R. Metallothionein mRNA induction in HeLa cells in response to zinc or dexamethasone is a primary induction response. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):295–297. doi: 10.1038/286295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes: molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3165–3173. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., Saris C. J., Hunter T., Hicks L. J., Noonan D. J., Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B. F. Primary structure of bovine calpactin I heavy chain (p36), a major cellular substrate for retroviral protein-tyrosine kinases: homology with the human phospholipase A2 inhibitor lipocortin. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4497–4503. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. W., Tsou A. P., Chan H., Thomas J., Petrie K., Eugui E. M., Allison A. C. Glucocorticoids selectively inhibit the transcription of the interleukin 1 beta gene and decrease the stability of interleukin 1 beta mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Henning-Chubb C., Huberman E., Verma I. M. c-fos expression is neither sufficient nor obligatory for differentiation of monomyelocytes to macrophages. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. F., Siegel M. I. The appearance of phospholipase activity in the human macrophage-like cell line U937 during dimethyl sulfoxide induced differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Immunofluorescent localization of a 39,000-dalton substrate of tyrosine protein kinases to the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1601–1609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Forsbeck K., Gidlund M., Sundström C., Tötterman T., Sällström J., Venge P. Surface characteristics of the U-937 human histiocytic lymphoma cell line: specific changes during inducible morphologic and functional differentiation in vitro. Haematol Blood Transfus. 1981;26:215–221. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67984-1_35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Valentine-Braun K. A., Johnson L. K., Severson D. L., Hollenberg M. D. Evaluation of the antiinflammatory and phospholipase-inhibitory activity of calpactin II/lipocortin I. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1347–1352. doi: 10.1172/JCI113737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Sinclair L. K., Browning J. L., Mattaliano R. J., Smart J. E., Chow E. P., Falbel T., Ribolini A., Garwin J. L., Wallner B. P. Purification and partial sequence analysis of a 37-kDa protein that inhibits phospholipase A2 activity from rat peritoneal exudates. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4239–4246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell M. A., Glenney J. R. Regulation of calpactin I phospholipid binding by calpactin I light-chain binding and phosphorylation by p60v-src. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):321–328. doi: 10.1042/bj2470321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Carter V. C., Moss P., Dehazya P., Schliwa M., Martin G. S. Membrane association of a 36,000-dalton substrate for tyrosine phosphorylation in chicken embryo fibroblasts transformed by avian sarcoma viruses. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1601–1611. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: a cellular substrate for transformation-specific protein phosphorylation contains phosphotyrosine. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: effects of src gene expression on the synthesis and phosphorylation of cellular polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5212–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Heguy A., Karin M. Structural and functional analysis of the human metallothionein-IA gene: differential induction by metal ions and glucocorticoids. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90322-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Santoli D., Damsky C. Human promyelocytic leukemia cells in culture differentiate into macrophage-like cells when treated with a phorbol diester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2779–2783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Kristensen T., D'Eustachio P., Hicks L. J., Noonan D. J., Hunter T., Tack B. F. cDNA sequence and tissue distribution of the mRNA for bovine and murine p11, the S100-related light chain of the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I). J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10663–10671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Tack B. F., Kristensen T., Glenney J. R., Jr, Hunter T. The cDNA sequence for the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I heavy chain) reveals a multidomain protein with internal repeats. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates the phosphorylation of the calcium-dependent 35,000-dalton substrate in intact A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8233–8236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Haigler H. T. Characterization of Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding and phosphorylation of lipocortin I. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6931–6937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Beemon K., Hunter T. Comparison of the expression of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus in vitro and in vivo. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):957–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.957-971.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Cate R. L., Tizard R., Sinclair L. K., Foeller C., Chow E. P., Browing J. L., Ramachandran K. L. Cloning and expression of human lipocortin, a phospholipase A2 inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):77–81. doi: 10.1038/320077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zokas L., Glenney J. R., Jr The calpactin light chain is tightly linked to the cytoskeletal form of calpactin I: studies using monoclonal antibodies to calpactin subunits. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2111–2121. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]