Abstract
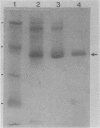
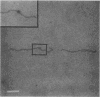
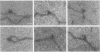
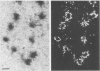
We have used a high-resolution analytical electron microscopic technique, electron spectroscopic imaging, to study the in vitro interaction between the transcription factor IIIA (TFIIIA) and 5S ribosomal gene DNA. The images and analytical measurements support our proposal that the helix axis is bent by the protein into a hairpin-shaped configuration.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazett-Jones D. P., Locklear L., Rattner J. B. Electron spectroscopic imaging of DNA. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1988 Apr;99(1):48–58. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(88)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazett-Jones D. P. Phosphorus imaging of the 7-S ribonucleoprotein particle. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1988 Apr;99(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(88)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Gurdon J. B. Cloned single repeating units of 5S DNA direct accurate transcription of 5S RNA when injected into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2849–2853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairall L., Rhodes D., Klug A. Mapping of the sites of protection on a 5 S RNA gene by the Xenopus transcription factor IIIA. A model for the interaction. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):577–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90278-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M. DNA sequence-directed nucleosome reconstitution on 5S RNA genes of Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1612–1622. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu C. W. Cooperative model for the binding of Xenopus transcription factor A to the 5S RNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2142–2145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Wegnez M. Isolation of a 7S particle from Xenopus laevis oocytes: a 5S RNA-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):241–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds W. F., Gottesfeld J. M. 5S rRNA gene transcription factor IIIA alters the helical configuration of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1862–1866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. Structural analysis of a triple complex between the histone octamer, a Xenopus gene for 5S RNA and transcription factor IIIA. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3473–3482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuey D. J., Parker C. S. Bending of promoter DNA on binding of heat shock transcription factor. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):459–461. doi: 10.1038/323459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Jackson I. J., Brown D. D. Domains of the positive transcription factor specific for the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes through a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex without disrupting it. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Heggeler B., Wahli W. Visualization of RNA polymerase II ternary transcription complexes formed in vitro on a Xenopus laevis vitellogenin gene. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2269–2273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03925.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]