Abstract
In recent years, microRNAs (miRNA) have emerged as important posttranscriptional regulators of gene expression in a wide variety of biological pathways. Since the discovery of the liver-specific miRNA-122 (miR-122) and its critical role in hepatic function, numerous additional miRNAs have been implicated in lipid metabolism. It is now apparent that lipid homeostasis is governed in part by an intricate web of miRNA activity. miRNAs are thought to confer robustness against environmental changes, such as diet modifications. Therefore, naturally occurring genetic variation that perturbs miRNA expression and/or function is likely to contribute to interindividual variability in lipid phenotypes. Although the field is still in its infancy, this review describes the growing evidence for miRNA-related genetic variation as etiological factors in lipid disorders. Specific examples, including a variant in a miRNA transcriptional control element that leads to dyslipidemia as well as a variant in a miRNA target site that modulates the effect of diet on plasma lipid levels, are discussed. Finally, the utility of recent systems genetics approaches to uncover hidden miRNA-related genetic associations with lipid disorders are considered, thereby illuminating the needles in the genetic haystack.
Keywords: gene regulation, dyslipidemia, mutation
Hepatic miRNAs and lipid homeostasis
Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a diverse class of regulatory molecules involved in the control of gene expression (1). Different subtypes of ncRNA mediate pre-, co-, and posttranscriptional regulatory processes. For instance, long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) facilitates chromatin remodeling, small nuclear RNA (snRNA) mediates splicing, and cytoplasmic microRNA (miRNA) destabilizes RNA and/or inhibits protein translation. Although mammalian miRNAs were not discovered until a decade ago (2), they have rapidly emerged as important posttranscriptional regulators of gene expression in a wide variety of biological pathways (3). Moreover, miRNAs have been demonstrated to be i) stable plasma biomarkers of physiological status (4, 5), ii) novel intercellular signaling molecules (6), iii) etiological factors in complex diseases (7), and iv) promising therapeutic targets (8, 9).
In 2002, miR-122 was found to be the most abundant miRNA in the liver, accounting for greater than 70% of all hepatic miRNA expression (2). More recent, high-throughput small RNA sequencing (smRNA-seq) studies have confirmed this finding and, notably, have not detected miR-122 in any other cell type (10). Circulating levels of miR-122 have been identified as a clinically relevant biomarker of liver injury (11, 12), cirrhosis (13), necroinflammation (14), and hyperlipidemia (15). In 2005, miR-122 was also shown to directly promote the replication of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) (16). Subsequently, it was demonstrated that inhibition of miR-122 by a locked nucleic acid (LNA) antisense oligonucleotide diminishes HCV viremia in chimpanzees (17). The anti-miR-122 LNA molecule (known as Miravirsen) has since advanced to phase II human clinical trials for hepatitis C treatment, and it appears to induce a potent antiviral effect in the absence of evident liver or cardiac toxicities (18).
miR-122 was also the first miRNA identified as a regulator of lipid metabolism (19). In 2006, antisense oligonucleotide-mediated inhibition of miR-122 (ASO-miR-122) in mice reduced plasma cholesterol levels, decreased hepatic lipid synthesis, and enhanced hepatic fatty acid oxidation (19). Moreover, the ASO-miR-122 was also able to reverse the effects of diet-induced obesity by reducing hepatic steatosis. Consistent with these findings, Miravirsen (anti-miR-122 LNA) has been shown to reduce plasma cholesterol levels in humans as well (18). Recently, miR-122 was also demonstrated to be a critical regulator of hepatic circadian rhythm (20), inflammation (21), fibrosis (22), and lipoprotein secretion (22); as such, it is a very important component of liver function and lipid homeostasis.
In the last few years, numerous studies have demonstrated that physiological and pathological changes in lipid metabolism are associated with altered hepatic and circulating miRNA profiles (5, 15, 23–33). For example, Cheung et al. found that the expression levels of 46 hepatic miRNAs are significantly altered in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) compared with normolipidemic individuals (26). Moreover, they demonstrated that many miRNAs, including miR-145, miR-27b, miR-30d, and miR-34a, are more significantly altered in NASH than miR-122. Very recently, several of these miRNAs, such as miR-27b (28) and miR-34a (34), and a growing number of others, including miR-125a, miR-33, miR-370, miR-378, miR-613, and miR-758, have been directly implicated in the regulation of lipid synthesis, transport, storage, and metabolism. Given these findings, which have been summarized in several recent review articles (35–41), it is apparent that the activity of numerous miRNAs contributes to lipid homeostasis.
Genetic variation in the miRNA regulome and lipid-related disorders
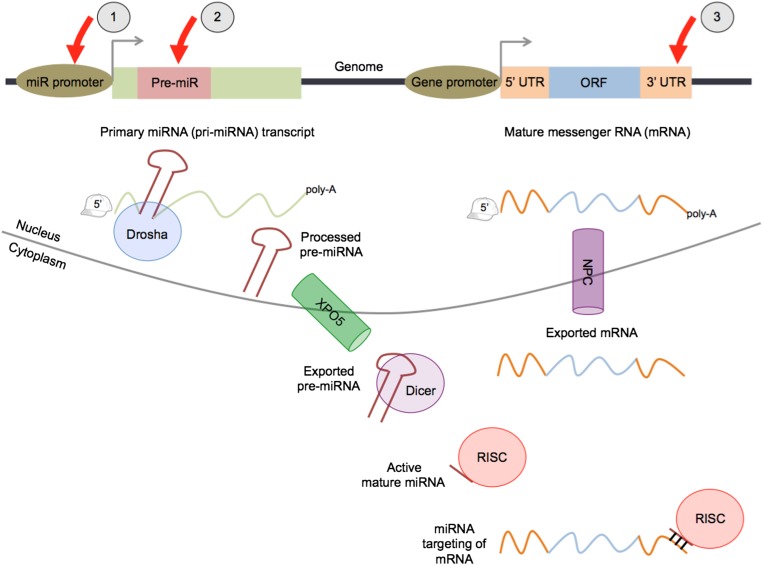
miRNA loci are transcribed predominantly by RNA Polymerase II (42), which yields primary transcripts (pri-miRNA) that range from a few kilobases to a few hundred kilobases in length (43). Pri-miRNAs harbor one or more hairpin-like secondary structures, termed precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNA), which are cleaved and shuttled to the cytoplasm, where they are processed further into ∼22 bp double-stranded RNA duplexes (44). One of the strands, referred to as the mature miRNA, is loaded onto the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The miRNA guides and tethers the RISC to specific target sites within RNA molecules in order to regulate their stability and/or translation (3). The canonical pathway for miRNA biogenesis and targeting is shown in Fig. 1. The miRNA regulome is defined as the compendium of regulatory elements that either regulate miRNA expression (transcriptional control elements and pre-miRNAs) or are regulated by miRNA activity (RNA target sites). Genetic variation in the miRNA regulome can perturb miRNA expression and/or function, potentially contributing to a wide variety of lipid-related phenotypes (45–47).
Fig. 1.
microRNA biogenesis and targeting. The canonical pathway for miRNA maturation and targeting activity is shown. Red arrows indicate components of the miRNA regulome: 1) transcriptional control elements within miRNA promoter regions, 2) miRNA precursors (pre-miRNAs), and 3) miRNA target sites that are located predominantly within 3′ UTRs. Both pri-miRNAs and mRNAs are generally 5′-capped and polyadenylated. XPO5, exportin 5; NPC, nuclear pore complex.
Genetic variation in miRNA transcriptional control elements
Transcriptional control elements can be classified as either proximal (i.e., promoter) or distal (i.e., long-range regulatory elements; LRE). Both classes of elements recruit transcriptional factor (TF) complexes that enhance or silence the expression of one or more genes (48). Genetic mutations within these elements can alter the binding affinity for one or more TFs, and the resulting effect on transcription could directly influence lipid metabolic pathways. For example, several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in the core promoter region of the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene have been shown to abolish binding of the transcription factor Sp1 (49–53), which leads to familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). As another example, a very recent study demonstrated that the minor allele of the SNP rs12740374, located within an LRE at the 1p13 locus, dramatically increases the binding affinity for the transcription factor CEBPA, which in turn alters the hepatic expression of the gene sortilin 1 (SORT1), leading to impaired lipoprotein metabolism (54, 55).
Until recently, attempts to map disease-associated genetic variants to miRNA transcriptional control elements have been severely hindered by poor annotation of miRNA promoters and LREs. Conventional methods for the identification of a gene promoter, such as 5′ rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5′-RACE), require access to the full-length primary transcript of the gene. However, the primary transcripts of miRNAs are often too rapidly processed and degraded, which renders these traditional approaches less reliable for miRNA promoter identification (56). In the last few years, several conceptual and technological advances in the field of epigenomics have allowed for the detection of miRNA promoter regions by analyzing chromatin structure (57, 58). Active promoters are characterized by a nucleosome-free site (open chromatin) that is flanked by regions enriched for specific chromatin marks, including histone H3 lysine 27 mono-acetylation (H3K27ac), histone H3 lysine 4 tri-methylation (H3K4me3), and histone H3 lysine 79 di-methylation (H3K79me2). In the last few years, the application of epigenome-wide chromatin profiling strategies has led to a comprehensive set of annotations for mammalian miRNA promoters (42).
Largely due to the relatively recent annotation of miRNA promoters, disease-causing variants in miRNA transcriptional control elements have not yet been extensively investigated. However, one illustrative example is that of a functional SNP (rs57095329) in the promoter of miR-146a that confers significant risk for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (59). The rs57095329 minor allele reduces the binding affinity for the transcriptional activator Ets1, which in turn reduces miR-146a expression (59). SLE is associated with dyslipoproteinemia (60, 61), including increased LDL oxidation (oxLDL) and atherosclerotic foam cell formation (60). Interestingly, miR-146a was recently shown to inhibit oxLDL-induced lipid accumulation by repressing toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-dependent signaling pathways in macrophages (62). Furthermore, viral administration of miR-146a to lupus-prone mice was found to inhibit the progression of SLE (63). Therefore, the overexpression of miR-146a may represent a novel preventative and/or therapeutic strategy for immune-related lipid disorders.
Genetic variation in miRNA target sites
Bona fide miRNA target sites are distributed across the entire transcriptome (64, 65) in noncoding RNAs, 5′-untranslated regions (UTR), open reading frames (ORF), and 3′-UTRs. The 3′-UTR sites are thought to be the most prevalent and functionally efficacious (3). Numerous algorithms have been developed for large-scale miRNA target prediction within 3′-UTRs (66). One of the most widely used in silico methods is TargetScan, which predicts target sites for a miRNA by searching for ∼7 nucleotide segments that perfectly complement the “seed” region (nucleotides 2 through 8 at the 5′-end) of the miRNA (67). Predicted “seed-match” sites are then scored according to five other sequence features that have been shown to contribute to target site efficacy (68). Genetic variation in predicted miRNA target sites has been demonstrated to have widespread effects on miRNA-mediated gene regulation (69). Although the contribution of allele-specific miRNA targeting to lipid phenotypic variation in the human population is not yet fully understood, recent findings summarized below strongly suggest that it is an area with substantive implications for the pharmacogenetics of lipid disorders.
Numerous candidate gene association studies have identified SNPs within annotated 3′-UTRs that may be associated with lipid-related phenotypes (70–77). One interesting 2008 study of plasma cholesterol levels in ∼10,000 Caucasians and ∼3,500 African Americans found significant population-specific interaction effects between dietary fatty acid intake and two SNPs (rs6008259 and rs3892755) in the 3′-UTR of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARA) (77). PPARA is a lipid-activated TF that regulates the expression of many genes involved in hepatic lipid metabolism (78). Although the authors did not explicitly discuss the possibility of a miRNA-related mechanistic link, a simple search of the TargetScan database (http://targetscan.org) suggests that rs3892755 is located within a predicted target site for miR-1204. Also, because association does not imply causation, it is entirely possible that one or both of rs6008259 and rs3892755 tags a haplotype block that contains the true functional variant(s). Therefore, in these types of cases, more detailed genetic and molecular experiments are necessary to determine whether the mechanism underlying the observed association is related to miRNA targeting.
In more recent candidate gene association studies of lipid-related phenotypes, miRNA-mediated mechanistic links have been explicitly tested. For instance, in 2011, Richardson et al. identified a significant association between a SNP (rs8887) in the 3′-UTR of perilipin 4 (PLIN4) and adiposity in two cohorts composed of several thousand Caucasian individuals (70). They further demonstrated that the rs8887 minor allele is associated with reduced levels of PLIN4 expression in adipose. Through an in silico target prediction strategy, they found that the rs8887 minor allele creates a putative target site for an adipose-expressed miRNA, miR-522. They then provided experimental support for this prediction by establishing with in vitro reporter gene assays that miR-522 targets the PLIN4 3′-UTR only in the presence of the rs8887 minor allele. Taking their findings together, the authors proposed that differential miR-522 targeting activity underlies the genetic association of the PLIN4 locus with adiposity (70). It remains unclear why the reduction of PLIN4, which is thought to be involved in the biogenesis of lipid droplets, would lead to increased adiposity (79). Nonetheless, the authors’ interesting findings strongly motivate further investigation into the function of PLIN4 and other closely related protein family members.
None of the aforementioned genetic associations, which were based on candidate gene studies, have yet been confirmed by unbiased genome-wide association studies (GWAS). In the past few years, GWAS have been conducted for hundreds of complex diseases and traits (80). Several bioinformatic strategies have been developed to map GWAS-derived disease-associated variants, as well as SNPs in strong linkage disequilibrium (LD), onto predicted miRNA target sites (81–86). A very recent approach uncovered 87 such SNPs (84). To date, only one of these, rs13702, has been validated by follow-up genetic and molecular studies (87). Specifically, Richardson et al. performed a large-scale genetic association study in more than 25,000 individuals from the Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology (CHARGE) and confirmed previous reports that the lipoprotein lipase (LPL) 3′ UTR SNP rs13702 is associated with plasma lipid levels (87). They also demonstrated that this association is significantly modulated by dietary intake of poly-unsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), providing evidence for gene-by-diet interaction. To identify the molecular basis for the observed genetic association/interaction, they first performed an in silico screen for miRNA target sites and predicted an allele-specific target site for a widely expressed miRNA, miR-410. They then determined, via in vitro reporter gene assays, that miR-410 targets only the rs13702 major allele and that the rs13702 minor allele abrogates miR-410-mediated repression of LPL (87). This seminal study represents the best evidence to date for a miRNA-mediated mechanism underlying a GWAS-derived complex trait genetic association.
Systems genetics analysis of miRNA expression: implications for lipid-related traits
Recently, Gamazon et al. carried out a large-scale study to identify genetic loci associated with miRNA expression (miRNA expression quantitative trait loci; miR-eQTL) in the lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCL) from 53 individuals of European ancestry (HapMap CEU) and 54 individuals of African ancestry (HapMap YRI) (88). They found that in the CEU and YRI samples, 1,792 and 1,390 SNPs, respectively, were modestly associated (P < 10−6) with the expression levels of 131 and 154 miRNAs, respectively. Furthermore, they reported that 21 of these miR-eQTLs were previously associated with several complex traits/diseases in GWAS (88). One of these is the SNP rs3846662, which is strongly associated with the LCL expression levels of miR-221 (P = 1.1 × 10−7) and miR-222 (P = 3.5 × 10−8), and also significantly associated with total plasma cholesterol (P = 3.0 × 10−19). In support of this result, another recent study found that miR-221 and miR-222 are among the most significantly downregulated hepatic miRNAs in baboons with high LDL-C that were fed a high-cholesterol/high-fat diet (27). These interesting findings highlight the utility of systems genetics approaches to generate miRNA-related mechanistic hypotheses for genetic loci associated with lipid-related traits/disorders. Moreover, the power to detect miR-eQTLs associated with disease will only increase as studies such as the one by Gamazon et al. are performed in larger cohorts across broader sets of cell types.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Jeanette Baran-Gale and Dr. Kasey Vickers for their helpful suggestions regarding the manuscript.
Footnotes
Abbreviations:
- LRE
- long-range regulatory element
- miRNA (miR)
- microRNA
- miR-122
- miRNA-122
- pre-miRNA
- miRNA precursor
- pri-miRNA
- primary miRNA
- ORF
- open reading frame
- RISC
- RNA-induced silencing complex
- SNP
- single nucleotide polymorphism
- TF
- transcriptional factor
- UTR
- untranslated region
This work was supported in part by National Institutes of Health (NIDDK) Grants R00-DK-091318-02 and P30-DK-056350.
REFERENCES
- 1.Esteller M. 2011. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 12: 861–874 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lagos-Quintana M., Rauhut R., Yalcin A., Meyer J., Lendeckel W., Tuschl T. 2002. Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr. Biol. 12: 735–739 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bartel D. P. 2009. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 136: 215–233 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mitchell P. S., Parkin R. K., Kroh E. M., Fritz B. R., Wyman S. K., Pogosova-Agadjanyan E. L., Peterson A., Noteboom J., O'Briant K. C., Allen A., et al. 2008. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 105: 10513–10518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Karolina D. S., Tavintharan S., Armugam A., Sepramaniam S., Pek S. L., Wong M. T., Lim S. C., Sum C. F., Jeyaseelan K. 2012. Circulating miRNA profiles in patients with metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97: E2271–E2276 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vickers K. C., Remaley A. T. 2012. Lipid-based carriers of microRNAs and intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 23: 91–97 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Couzin J. 2008. MicroRNAs make big impression in disease after disease. Science. 319: 1782–1784 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.van Rooij E., Purcell A. L., Levin A. A. 2012. Developing microRNA therapeutics. Circ. Res. 110: 496–507 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jackson A. L., Levin A. A. 2012. Developing microRNA therapeutics: approaching the unique complexities. Nucleic Acid Ther. 22: 213–225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jopling C. 2012. Liver-specific microRNA-122: Biogenesis and function. RNA Biol. 9: 137–142 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Laterza O. F., Lim L., Garrett-Engele P. W., Vlasakova K., Muniappa N., Tanaka W. K., Johnson J. M., Sina J. F., Fare T. L., Sistare F. D., et al. 2009. Plasma MicroRNAs as sensitive and specific biomarkers of tissue injury. Clin. Chem. 55: 1977–1983 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ding X., Ding J., Ning J., Yi F., Chen J., Zhao D., Zheng J., Liang Z., Hu Z., Du Q. 2012. Circulating microRNA-122 as a potential biomarker for liver injury. Mol. Med. Report. 5: 1428–1432 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Waidmann O., Koberle V., Brunner F., Zeuzem S., Piiper A., Kronenberger B. 2012. Serum microRNA-122 predicts survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. PLoS ONE. 7: e45652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bihrer V., Friedrich-Rust M., Kronenberger B., Forestier N., Haupenthal J., Shi Y., Peveling-Oberhag J., Radeke H. H., Sarrazin C., Herrmann E., et al. 2011. Serum miR-122 as a biomarker of necroinflammation in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 106: 1663–1669 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gao W., He H. W., Wang Z. M., Zhao H., Lian X. Q., Wang Y. S., Zhu J., Yan J. J., Zhang D. G., Yang Z. J., et al. 2012. Plasma levels of lipometabolism-related miR-122 and miR-370 are increased in patients with hyperlipidemia and associated with coronary artery disease. Lipids Health Dis. 11: 55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jopling C. L., Yi M., Lancaster A. M., Lemon S. M., Sarnow P. 2005. Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific microRNA. Science. 309: 1577–1581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lanford R. E., Hildebrandt-Eriksen E. S., Petri A., Persson R., Lindow M., Munk M. E., Kauppinen S., Orum H. 2010. Therapeutic silencing of microRNA-122 in primates with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Science. 327: 198–201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lindow M., Kauppinen S. 2012. Discovering the first microRNA-targeted drug. J. Cell Biol. 199: 407–412 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Esau C., Davis S., Murray S. F., Yu X. X., Pandey S. K., Pear M., Watts L., Booten S. L., Graham M., McKay R., et al. 2006. miR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab. 3: 87–98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gatfield D., Le Martelot G., Vejnar C. E., Gerlach D., Schaad O., Fleury-Olela F., Ruskeepaa A. L., Oresic M., Esau C. C., Zdobnov E. M., et al. 2009. Integration of microRNA miR-122 in hepatic circadian gene expression. Genes Dev. 23: 1313–1326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hsu S. H., Wang B., Kota J., Yu J., Costinean S., Kutay H., Yu L., Bai S., La Perle K., Chivukula R. R., et al. 2012. Essential metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic functions of miR-122 in liver. J. Clin. Invest. 122: 2871–2883 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tsai W. C., Hsu S. D., Hsu C. S., Lai T. C., Chen S. J., Shen R., Huang Y., Chen H. C., Lee C. H., Tsai T. F., et al. 2012. MicroRNA-122 plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 122: 2884–2897 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhao E., Keller M. P., Rabaglia M. E., Oler A. T., Stapleton D. S., Schueler K. L., Neto E. C., Moon J. Y., Wang P., Wang I. M., et al. 2009. Obesity and genetics regulate microRNAs in islets, liver, and adipose of diabetic mice. Mamm. Genome. 20: 476–485 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hoekstra M., van der Sluis R. J., Kuiper J., Van Berkel T. J. 2012. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an altered hepatocyte microRNA profile in LDL receptor knockout mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 23: 622–628 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Masotti A., Alisi A. 2012. Integrated bioinformatics analysis of microRNA expression profiles for an in-depth understanding of pathogenic mechanisms in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 27: 187–188 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cheung O., Puri P., Eicken C., Contos M. J., Mirshahi F., Maher J. W., Kellum J. M., Min H., Luketic V. A., Sanyal A. J. 2008. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with altered hepatic microRNA expression. Hepatology. 48: 1810–1820 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Karere G. M., Glenn J. P., Vandeberg J. L., Cox L. A. 2012. Differential microRNA response to a high-cholesterol, high-fat diet in livers of low and high LDL-C baboons. BMC Genomics. 13: 320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vickers K. C., Shoucri B. M., Levin M. G., Wu H., Pearson D. S., Osei-Hwedieh D., Collins F. S., Remaley A. T., Sethupathy P. 2013. MicroRNA-27b is a regulatory hub in lipid metabolism and is altered in dyslipidemia. Hepatology. 57: 533–542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rayner K. J., Suarez Y., Davalos A., Parathath S., Fitzgerald M. L., Tamehiro N., Fisher E. A., Moore K. J., Fernandez-Hernando C. 2010. MiR-33 contributes to the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 328: 1570–1573 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Najafi-Shoushtari S. H., Kristo F., Li Y., Shioda T., Cohen D. E., Gerszten R. E., Naar A. M. 2010. MicroRNA-33 and the SREBP host genes cooperate to control cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 328: 1566–1569 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kaur K., Bhatia H., Datta M. 2011. MicroRNAs in hepatic pathophysiology in diabetes. World J. Diabetes. 2: 158–163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cermelli S., Ruggieri A., Marrero J. A., Ioannou G. N., Beretta L. 2011. Circulating microRNAs in patients with chronic hepatitis C and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE. 6: e23937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Alisi A., Da Sacco L., Bruscalupi G., Piemonte F., Panera N., De Vito R., Leoni S., Bottazzo G. F., Masotti A., Nobili V. 2011. Mirnome analysis reveals novel molecular determinants in the pathogenesis of diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Lab. Invest. 91: 283–293 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lee J., Kemper J. K. 2010. Controlling SIRT1 expression by microRNAs in health and metabolic disease. Aging (Albany NY). 2: 527–534 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rayner K. J., Fernandez-Hernando C., Moore K. J. 2012. MicroRNAs regulating lipid metabolism in atherogenesis. Thromb. Haemost. 107: 642–647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Moore K. J., Rayner K. J., Suarez Y., Fernandez-Hernando C. 2011. The role of microRNAs in cholesterol efflux and hepatic lipid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 31: 49–63 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fernandez-Hernando C., Suarez Y., Rayner K. J., Moore K. J. 2011. MicroRNAs in lipid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 22: 86–92 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sacco J., Adeli K. 2012. MicroRNAs: emerging roles in lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 23: 220–225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Moore K. J., Rayner K. J., Suarez Y., Fernandez-Hernando C. 2010. microRNAs and cholesterol metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 21: 699–706 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rotllan N., Fernandez-Hernando C. 2012. MicroRNA regulation of cholesterol metabolism. Cholesterol. 2012: 847849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rottiers V., Naar A. M. 2012. MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13: 239–250 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schanen B. C., Li X. 2011. Transcriptional regulation of mammalian miRNA genes. Genomics. 97: 1–6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Saini H. K., Enright A. J., Griffiths-Jones S. 2008. Annotation of mammalian primary microRNAs. BMC Genomics. 9: 564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kim V. N., Han J., Siomi M. C. 2009. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10: 126–139 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sethupathy P., Collins F. S. 2008. MicroRNA target site polymorphisms and human disease. Trends Genet. 24: 489–497 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Borel C., Antonarakis S. E. 2008. Functional genetic variation of human miRNAs and phenotypic consequences. Mamm. Genome. 19: 503–509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mishra P. J., Bertino J. R. 2009. MicroRNA polymorphisms: the future of pharmacogenomics, molecular epidemiology and individualized medicine. Pharmacogenomics. 10: 399–416 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Maston G. A., Evans S. K., Green M. R. 2006. Transcriptional regulatory elements in the human genome. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 7: 29–59 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Usifo E., Leigh S. E., Whittall R. A., Lench N., Taylor A., Yeats C., Orengo C. A., Martin A. C., Celli J., Humphries S. E. 2012. Low-density lipoprotein receptor gene familial hypercholesterolemia variant database: update and pathological assessment. Ann. Hum. Genet. 76: 387–401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Mozas P., Galetto R., Albajar M., Ros E., Pocovi M., Rodriguez-Rey J. C. 2002. A mutation (-49C>T) in the promoter of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene associated with familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 43: 13–18 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Koivisto U. M., Palvimo J. J., Janne O. A., Kontula K. 1994. A single-base substitution in the proximal Sp1 site of the human low density lipoprotein receptor promoter as a cause of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 91: 10526–10530 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sun X. M., Neuwirth C., Wade D. P., Knight B. L., Soutar A. K. 1995. A mutation (T-45C) in the promoter region of the low-density-lipoprotein (LDL)-receptor gene is associated with a mild clinical phenotype in a patient with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH). Hum. Mol. Genet. 4: 2125–2129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Smith A. J., Ahmed F., Nair D., Whittall R., Wang D., Taylor A., Norbury G., Humphries S. E. 2007. A functional mutation in the LDLR promoter (-139C>G) in a patient with familial hypercholesterolemia. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 15: 1186–1189 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Musunuru K., Strong A., Frank-Kamenetsky M., Lee N. E., Ahfeldt T., Sachs K. V., Li X., Li H., Kuperwasser N., Ruda V. M., et al. 2010. From noncoding variant to phenotype via SORT1 at the 1p13 cholesterol locus. Nature. 466: 714–719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Marian A. J. 2011. Genome-wide association studies complemented with mechanistic biological studies identify sortilin 1 as a novel regulator of cholesterol trafficking. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 13: 190–192 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lee Y., Kim M., Han J., Yeom K. H., Lee S., Baek S. H., Kim V. N. 2004. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 23: 4051–4060 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kouzarides T. 2007. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 128: 693–705 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Park P. J. 2009. ChIP-seq: advantages and challenges of a maturing technology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10: 669–680 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Luo X., Yang W., Ye D. Q., Cui H., Zhang Y., Hirankarn N., Qian X., Tang Y., Lau Y. L., de Vries N., et al. 2011. A functional variant in microRNA-146a promoter modulates its expression and confers disease risk for systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Genet. 7: e1002128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Borba E. F., Carvalho J. F., Bonfa E. 2006. Mechanisms of dyslipoproteinemias in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 13: 203–208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Chung C. P., Oeser A., Solus J., Avalos I., Gebretsadik T., Shintani A., Linton M. F., Fazio S., Stein C. M. 2007. Inflammatory mechanisms affecting the lipid profile in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 34: 1849–1854 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yang K., He Y. S., Wang X. Q., Lu L., Chen Q. J., Liu J., Sun Z., Shen W. F. 2011. MiR-146a inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced lipid accumulation and inflammatory response via targeting toll-like receptor 4. FEBS Lett. 585: 854–860 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Pan Y., Jia T., Zhang Y., Zhang K., Zhang R., Li J., Wang L. 2012. MS2 VLP-based delivery of microRNA-146a inhibits autoantibody production in lupus-prone mice. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 7: 5957–5967 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chi S. W., Zang J. B., Mele A., Darnell R. B. 2009. Argonaute HITS-CLIP decodes microRNA-mRNA interaction maps. Nature. 460: 479–486 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hafner M., Landthaler M., Burger L., Khorshid M., Hausser J., Berninger P., Rothballer A., Ascano M., Jr, Jungkamp A. C., Munschauer M., et al. 2010. Transcriptome-wide identification of RNA-binding protein and microRNA target sites by PAR-CLIP. Cell. 141: 129–141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yue D., Liu H., Huang Y. 2009. Survey of computational algorithms for microRNA target prediction. Curr. Genomics. 10: 478–492 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Lewis B. P., Burge C. B., Bartel D. P. 2005. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120: 15–20 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Grimson A., Farh K. K., Johnston W. K., Garrett-Engele P., Lim L. P., Bartel D. P. 2007. MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol. Cell. 27: 91–105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kim J., Bartel D. P. 2009. Allelic imbalance sequencing reveals that single-nucleotide polymorphisms frequently alter microRNA-directed repression. Nat. Biotechnol. 27: 472–477 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Richardson K., Louie-Gao Q., Arnett D. K., Parnell L. D., Lai C. Q., Davalos A., Fox C. S., Demissie S., Cupples L. A., Fernandez-Hernando C., et al. 2011. The PLIN4 variant rs8887 modulates obesity related phenotypes in humans through creation of a novel miR-522 seed site. PLoS ONE. 6: e17944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Sookoian S., Pirola C. J. 2012. PNPLA3, the triacylglycerol synthesis/hydrolysis/storage dilemma, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 18: 6018–6026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhang M., Zeng L., Wang Y. J., An Z. M., Ying B. W. 2012. Associations of fibroblast growth factor 21 gene 3′ untranslated region single-nucleotide polymorphisms with metabolic syndrome, obesity, and diabetes in a Han Chinese population. DNA Cell Biol. 31: 547–552 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Zhang J. J., Wang L. N., Feng Y., Zhi H., Ma G. S., Ye X. Z., Qian S. S., Wang B. 2012. Association study on the microRNA-1 target gene polymorphism and the risk of premature coronary artery disease [article in Chinese]. Zhonghua. Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 40: 386–391 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kurnaz O., Akadam-Teker A. B., Yilmaz-Aydogan H., Tekeli A., Isbir T. 2012. The LOX-1 3′UTR188CT polymorphism and coronary artery disease in Turkish patients. Mol. Biol. Rep. 39: 4351–4358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.van Greevenbroek M. M., Vermeulen V. M., Feskens E. J., Evelo C. T., Kruijshoop M., Hoebee B., van der Kallen C. J., de Bruin T. W. 2007. Genetic variation in thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) is associated with hypertriglyceridaemia and blood pressure in diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 24: 498–504 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Dammerman M., Sandkuijl L. A., Halaas J. L., Chung W., Breslow J. L. 1993. An apolipoprotein CIII haplotype protective against hypertriglyceridemia is specified by promoter and 3′ untranslated region polymorphisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 90: 4562–4566 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Volcik K. A., Nettleton J. A., Ballantyne C. M., Boerwinkle E. 2008. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor [alpha] genetic variation interacts with n-6 and long-chain n-3 fatty acid intake to affect total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol concentrations in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 87: 1926–1931 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.van Raalte D. H., Li M., Pritchard P. H., Wasan K. M. 2004. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-alpha: a pharmacological target with a promising future. Pharm. Res. 21: 1531–1538 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Smith C. E., Ordovas J. M. 2012. Update on perilipin polymorphisms and obesity. Nutr. Rev. 70: 611–621 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Hindorff L. A., Sethupathy P., Junkins H. A., Ramos E. M., Mehta J. P., Collins F. S., Manolio T. A. 2009. Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 106: 9362–9367 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Bruno A. E., Li L., Kalabus J. L., Pan Y., Yu A., Hu Z. 2012. miRdSNP: a database of disease-associated SNPs and microRNA target sites on 3′UTRs of human genes. BMC Genomics. 13: 44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Ziebarth J. D., Bhattacharya A., Chen A., Cui Y. 2012. PolymiRTS Database 2.0: linking polymorphisms in microRNA target sites with human diseases and complex traits. Nucleic Acids Res. 40: D216–D221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Thomas L. F., Saito T., Saetrom P. 2011. Inferring causative variants in microRNA target sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 39: e109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Richardson K., Lai C. Q., Parnell L. D., Lee Y. C., Ordovas J. M. 2011. A genome-wide survey for SNPs altering microRNA seed sites identifies functional candidates in GWAS. BMC Genomics. 12: 504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Li M. J., Wang P., Liu X., Lim E. L., Wang Z., Yeager M., Wong M. P., Sham P. C., Chanock S. J., Wang J. 2012. GWASdb: a database for human genetic variants identified by genome-wide association studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 40: D1047–D1054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Arnold M., Ellwanger D. C., Hartsperger M. L., Pfeufer A., Stumpflen V. 2012. Cis-acting polymorphisms affect complex traits through modifications of microRNA regulation pathways. PLoS ONE. 7: e36694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Richardson K., Nettleton J. A., Rotllan N., Tanaka T., Smith C. E., Lai C. Q., Parnell L. D., Lee Y. C., Lahti J., Lemaitre R. N., et al. 2013. Gain-of-function lipoprotein lipase variant rs13702 modulates lipid traits through disruption of a microRNA-410 seed site. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 92: 5–14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Gamazon E. R., Ziliak D., Im H. K., LaCroix B., Park D. S., Cox N. J., Huang R. S. 2012. Genetic architecture of microRNA expression: implications for the transcriptome and complex traits. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 90: 1046–1063 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]