Abstract
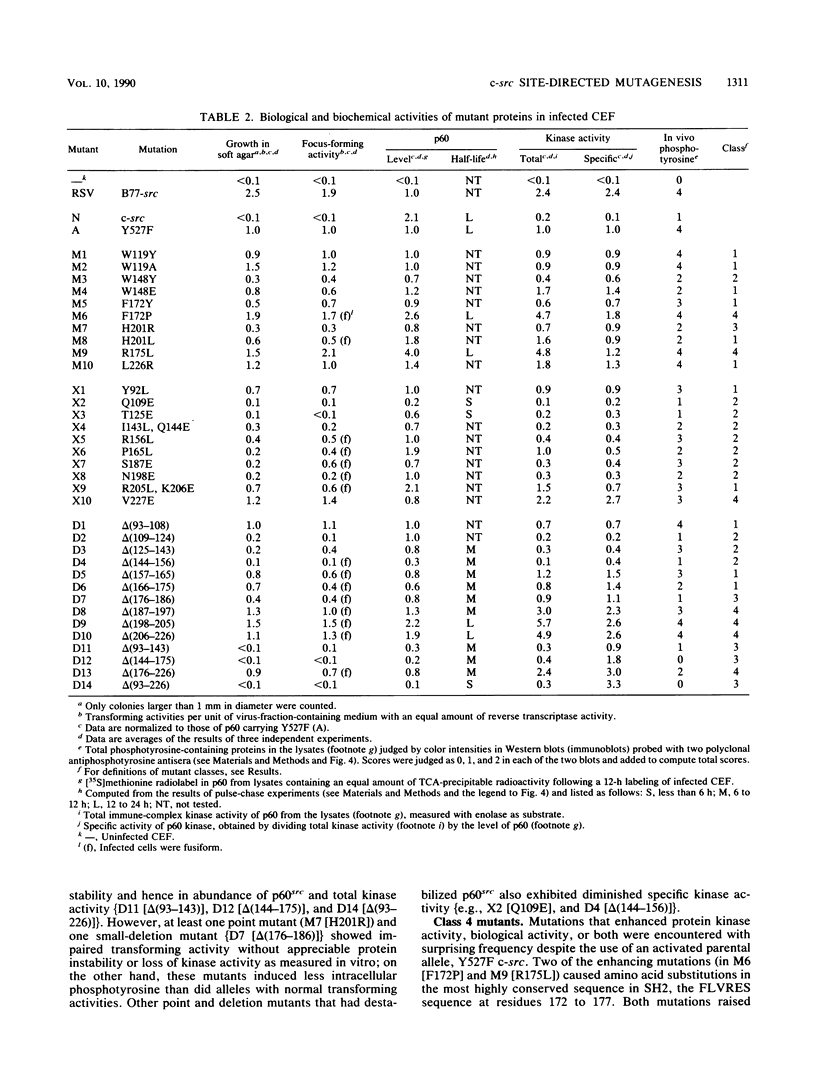
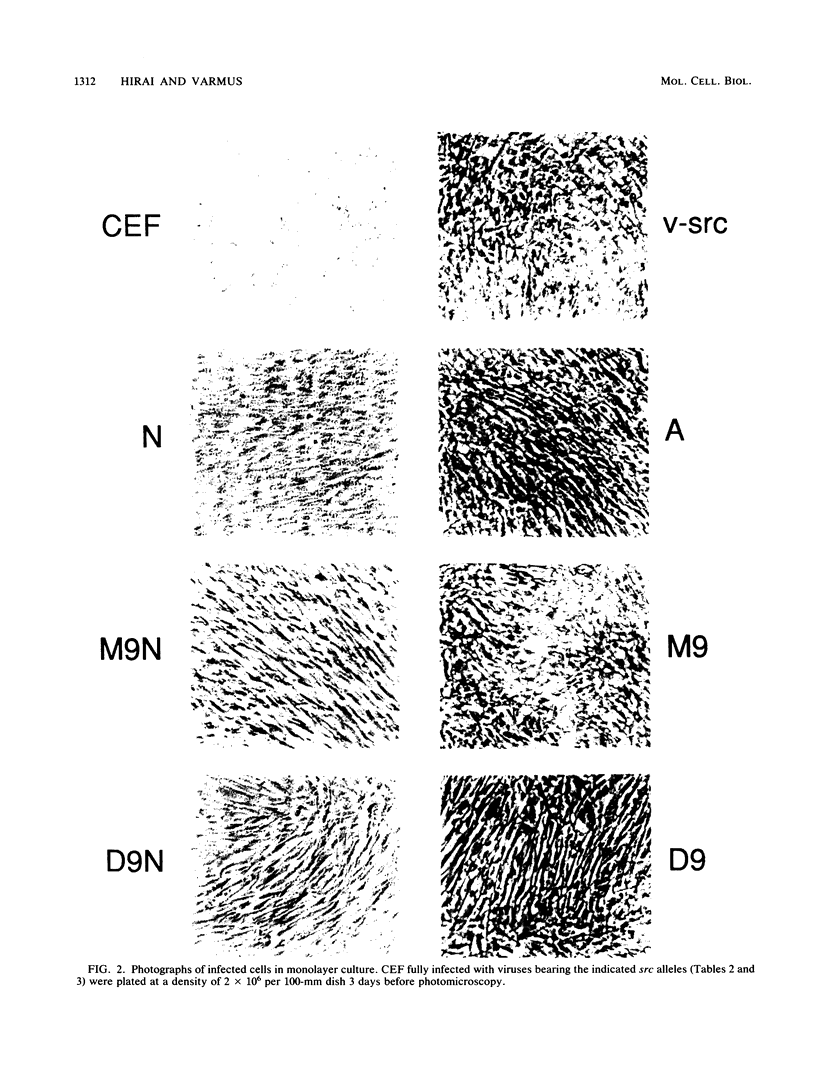
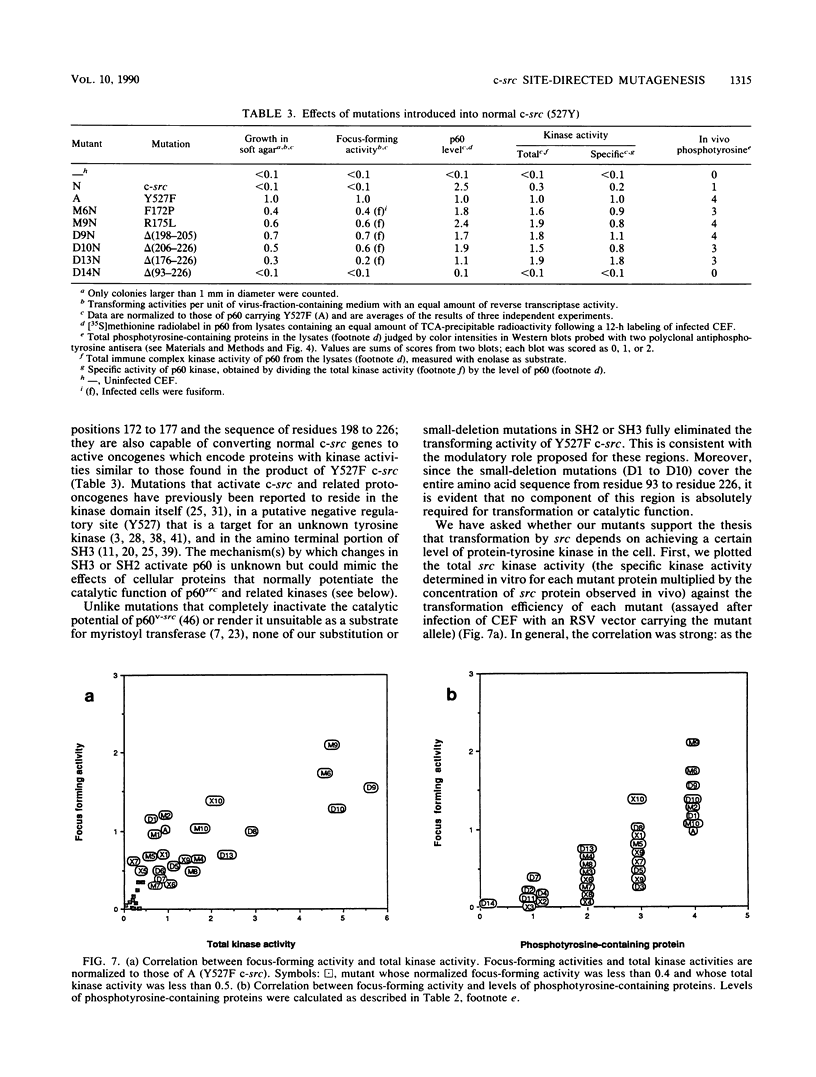
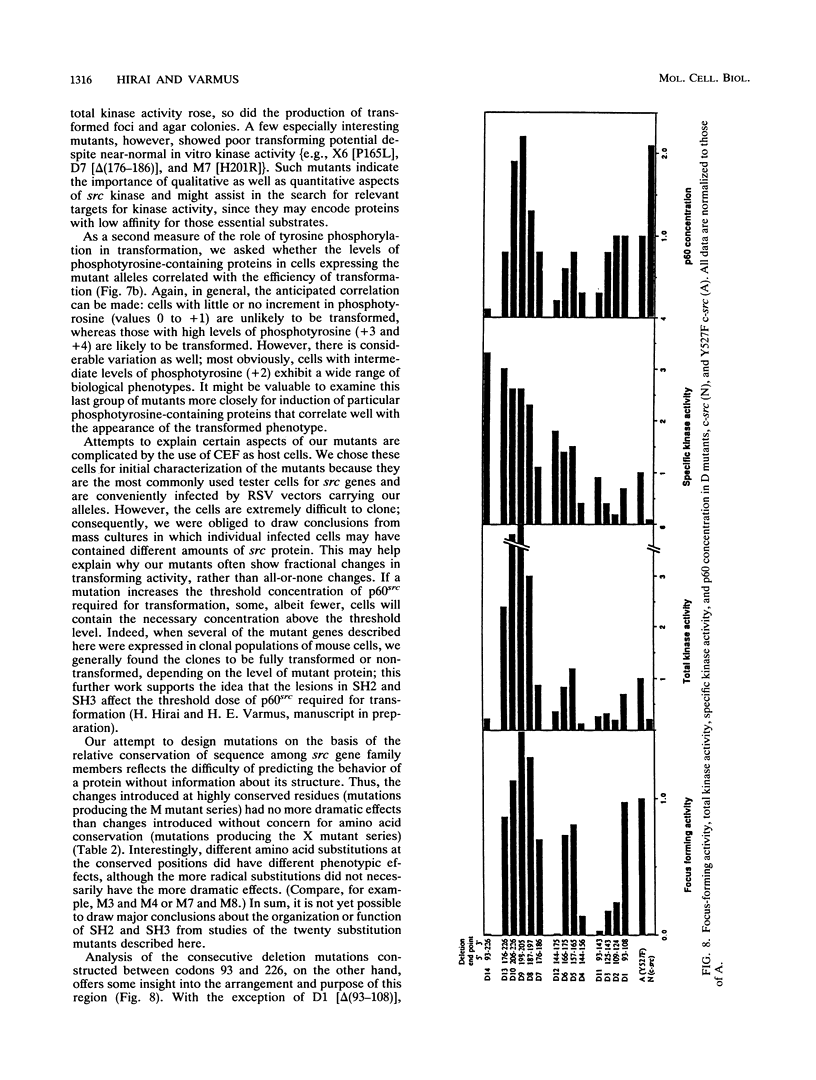
The products of the viral and cellular src genes, p60v-src and p60c-src, appear to be composed of multiple functional domains. Highly conserved regions called src homology 2 and 3 (SH2 and SH3), comprising amino acid residues 88 to 250, are believed to modulate the protein-tyrosine kinase activity present in the carboxy-terminal halves of the src proteins. To explore the functions of these regions more fully, we have made 34 site-directed mutations in a transformation-competent c-src gene encoding phenylalanine in place of tyrosine 527 (Y527F c-src). Twenty of the new mutations change only one or two amino acids, and the remainder delete small or large portions of the SH2-SH3 region. These mutant alleles have been incorporated into a replication-competent Rous sarcoma virus vector to examine the biochemical and biological properties of the mutant proteins after infection of chicken embryo fibroblasts. Four classes of mutant proteins were observed: class 1, mutants with only slight differences from the parental gene products; class 2, mutant proteins with diminished transforming and specific kinase activities; class 3, mutant proteins with normal or enhanced specific kinase activity but impaired biological activity, often as a consequence of instability; and class 4, mutant proteins with augmented biological and catalytic activities. In general, there was a strong correlation between total kinase activity (or amounts of intracellular phosphotyrosine-containing proteins) and transforming activity. Deletion mutations and some point mutations affecting residues 109 to 156 inhibited kinase and transforming functions, whereas deletions affecting residues 187 to 226 generally had positive effects on one or both of those functions, confirming that SH2-SH3 has complex regulatory properties. Five mutations that augmented the transforming and kinase activities of Y527F c-src [F172P, R175L, delta(198-205), delta(206-226), and delta(176-226)] conferred transformation competence on an otherwise normal c-src gene, indicating that mutations in SH2 (like previously described lesions in SH3, the kinase domain, and a carboxy-terminal inhibitory domain) can activate c-src.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brugge J. S., Darrow D. Analysis of the catalytic domain of phosphotransferase activity of two avian sarcoma virus-transforming proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4550–4557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D., Parsons J. T. Site-directed mutagenesis of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus: construction and characterization of a deletion mutant temperature sensitive for transformation. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):683–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.683-691.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Esch F. S., Taylor S. S., Hunter T. Phosphorylation sites in enolase and lactate dehydrogenase utilized by tyrosine protein kinases in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7835–7841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. N-terminal deletions in Rous sarcoma virus p60src: effects on tyrosine kinase and biological activities and on recombination in tissue culture with the cellular src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2789–2795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Linker insertion-deletion mutagenesis of the v-src gene: isolation of host- and temperature-dependent mutants. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):542–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.542-554.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz W. M., Berger P., Wang J. Y. Deletion of an N-terminal regulatory domain of the c-abl tyrosine kinase activates its oncogenic potential. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):137–147. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03358.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Processing of p60v-src to its myristylated membrane-bound form. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2781–2788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Only membrane-associated RSV src proteins have amino-terminally bound lipid. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):161–163. doi: 10.1038/302161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkemeyer M. J., Bennett R. L., Gertler F. B., Hoffmann F. M. DNA sequence, structure, and tyrosine kinase activity of the Drosophila melanogaster Abelson proto-oncogene homolog. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):843–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann F. M., Fresco L. D., Hoffman-Falk H., Shilo B. Z. Nucleotide sequences of the Drosophila src and abl homologs: conservation and variability in the src family oncogenes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houts G. E., Miyagi M., Ellis C., Beard D., Beard J. W. Reverse transcriptase from avian myeloblastosis virus. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):517–522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.517-522.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P., Baltimore D. N-terminal mutations activate the leukemogenic potential of the myristoylated form of c-abl. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):449–456. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03397.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Hanafusa H. Cell transformation by the viral src oncogene. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:31–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Mayer B. J., Iba H., Laugier D., Poirier F., Calothy G., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Genetic analysis of p60v-src domains involved in the induction of different cell transformation parameters. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):840–848. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.840-848.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein lacking myristic acid phosphorylates known polypeptide substrates without inducing transformation. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. M., Mardon G., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. The first seven amino acids encoded by the v-src oncogene act as a myristylation signal: lysine 7 is a critical determinant. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2435–2441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating M. T., Williams L. T. Processing of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Biosynthetic and degradation studies using anti-receptor antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7932–7937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Yoshida M. Small deletion in src of Rous sarcoma virus modifying transformation phenotypes: identification of 207-nucleotide deletion and its smaller product with protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):985–992. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.985-992.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Iba H., Hanafusa H. Activation of the transforming potential of p60c-src by a single amino acid change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4228–4232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. A general method for saturation mutagenesis of cloned DNA fragments. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):242–247. doi: 10.1126/science.2990046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaye K. L., Eckstein F. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease Nci I cleavage by phosphorothioate groups and its application to oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9679–9698. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. An N-terminal peptide from p60src can direct myristylation and plasma membrane localization when fused to heterologous proteins. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):374–377. doi: 10.1038/314374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Fine structural mapping of a critical NH2-terminal region of p60src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1623–1627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts W. M., Reynolds A. B., Lansing T. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of pp60c-src transforming potential by mutations altering the structure of an amino terminal domain containing residues 90-95. Oncogene Res. 1988;3(4):343–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond V. W., Parsons J. T. Identification of an amino terminal domain required for the transforming activity of the Rous sarcoma virus src protein. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):400–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Vila J., Lansing T. J., Potts W. M., Weber M. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of the oncogenic potential of the avian cellular src protein by specific structural alteration of the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2359–2364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Stone J. C., Pawson T. A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Drees B., Kornberg T., Bishop J. M. The nucleotide sequence and the tissue-specific expression of Drosophila c-src. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. A mutation at the ATP-binding site of pp60v-src abolishes kinase activity, transformation, and tumorigenicity. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1772–1779. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEMIN H. M., RUBIN H. Characteristics of an assay for Rous sarcoma virus and Rous sarcoma cells in tissue culture. Virology. 1958 Dec;6(3):669–688. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten R. A., Jackson P., Baltimore D. The mouse type IV c-abl gene product is a nuclear protein, and activation of transforming ability is associated with cytoplasmic localization. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):669–678. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Quintrell N., Wyke J. Revertants of an ASV-transformed rat cell line have lost the complete provius or sustained mutations in src. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):28–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90525-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verderame M. F., Kaplan J. M., Varmus H. E. A mutation in v-src that removes a single conserved residue in the SH-2 domain of pp60v-src restricts transformation in a host-dependent manner. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):338–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.338-348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Deletions and insertions within an amino-terminal domain of pp60v-src inactivate transformation and modulate membrane stability. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):291–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.291-302.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke J. A., Stoker A. W. Genetic analysis of the form and function of the viral src oncogene product. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 20;907(1):47–69. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]