Abstract
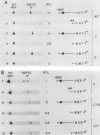
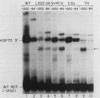
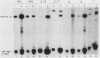
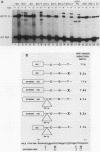
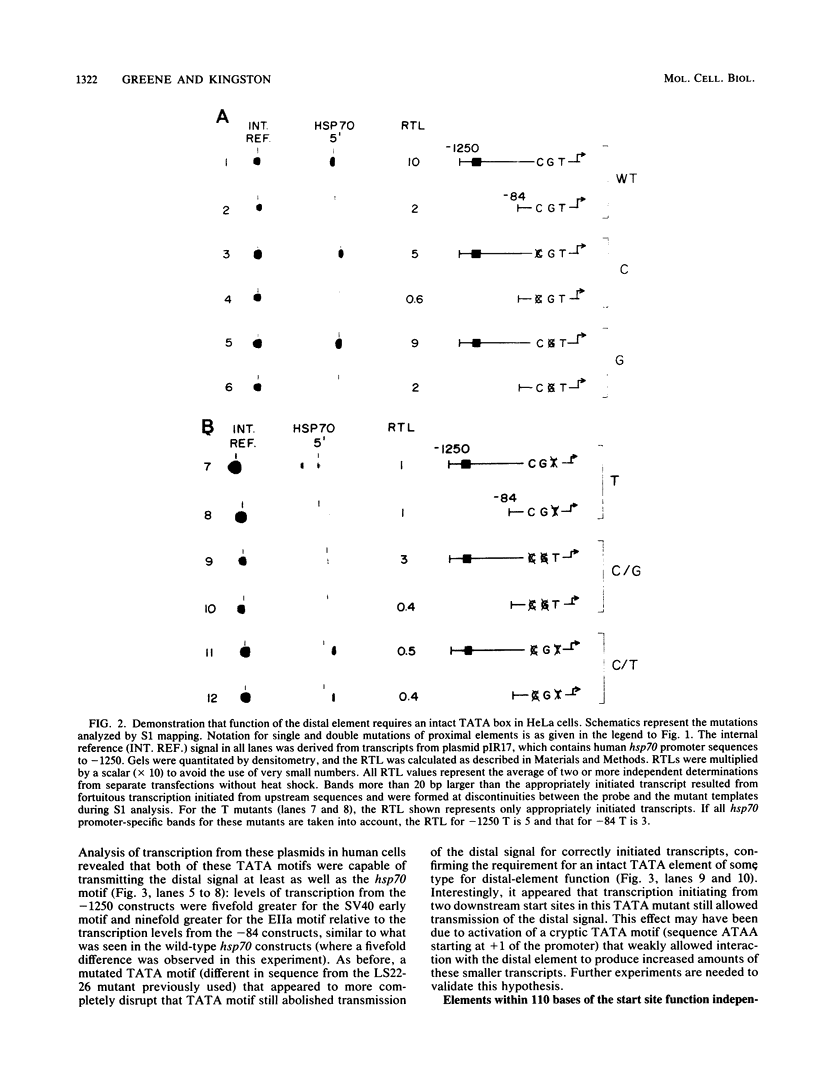
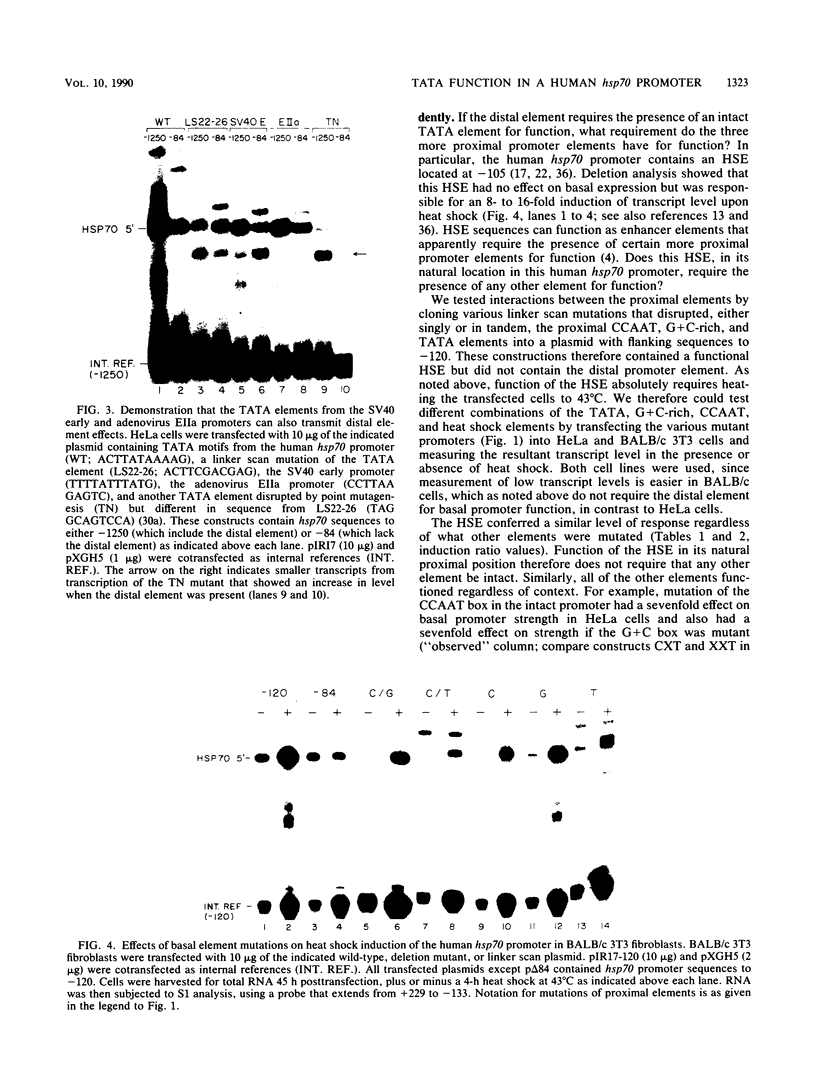
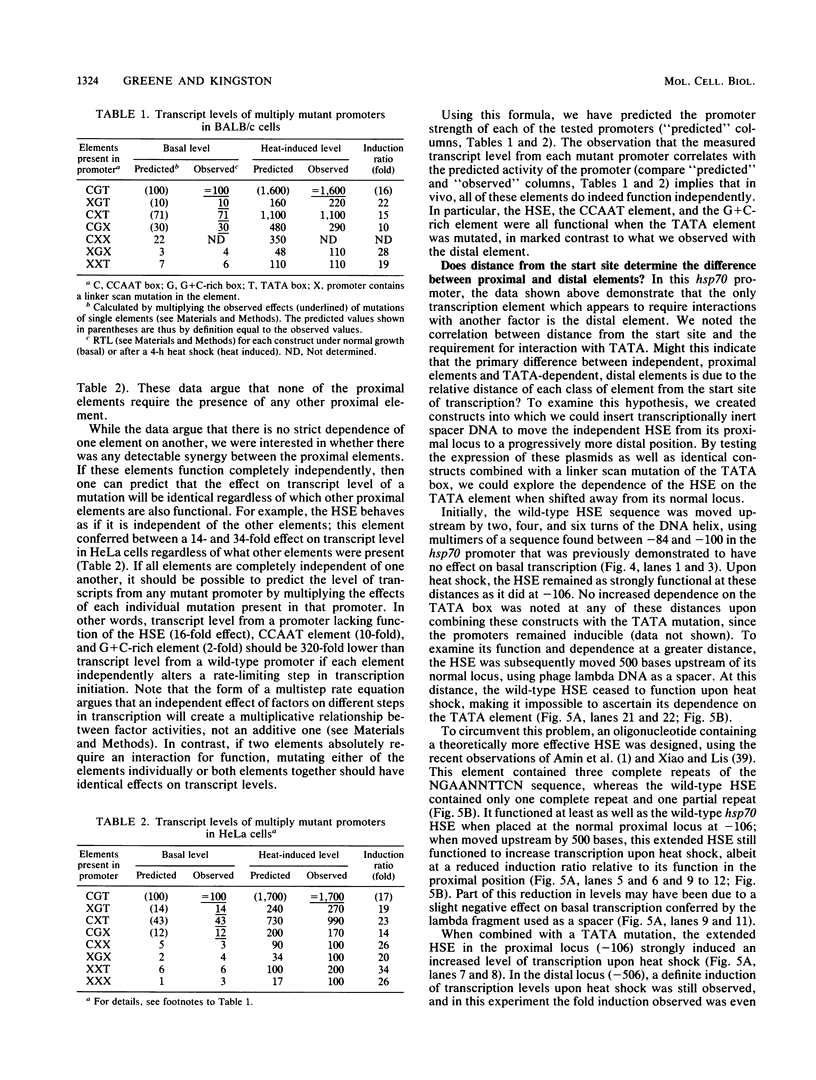
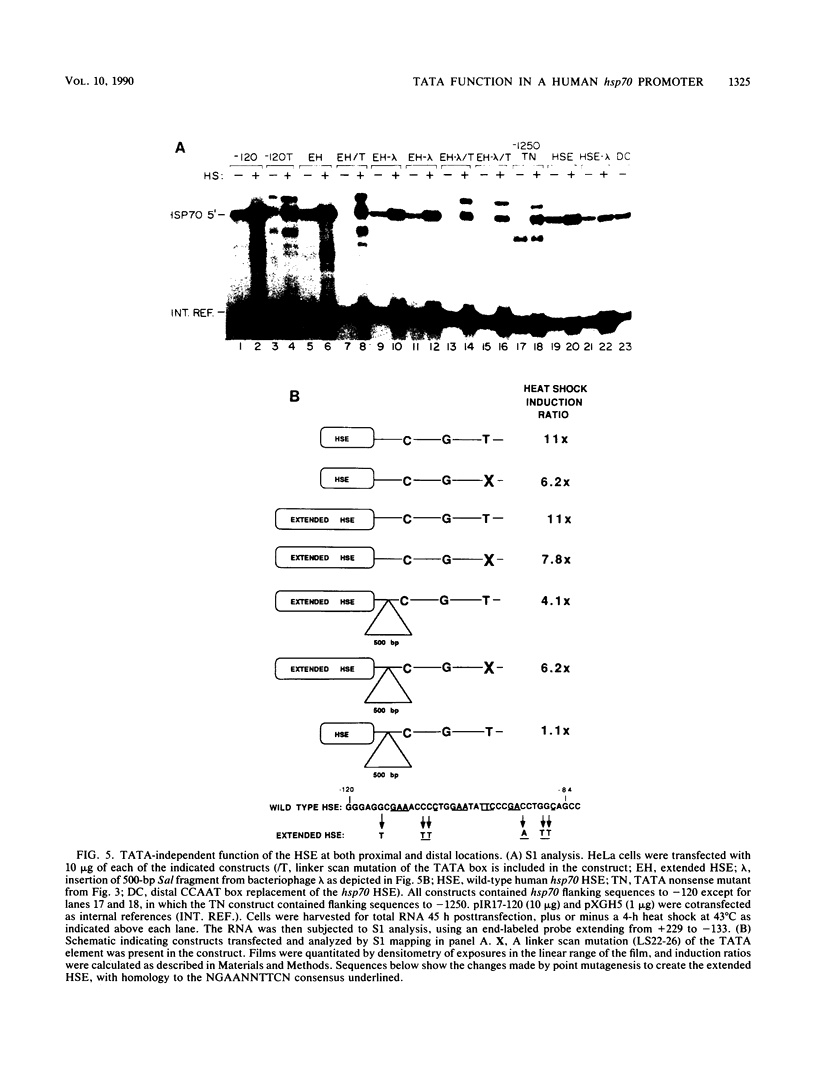
We have characterized the interactions between the TATA element and other sequence elements of a human heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) promoter by a mutational approach. Expression of a distal element of this promoter requires an intact TATA element in human cell lines. The hsp70 TATA element can be functionally replaced for this interaction by TATA elements from the simian virus 40 early and adenovirus EIIa promoters. The TATA element in this promoter therefore both determines the appropriate start site and determines strength by allowing function of the distal element. In contrast, three proximal upstream elements necessary for basal and heat-regulated transcription have no requirement either for a TATA element or for any other proximal element. The behavior of promoters multiply mutant in these proximal elements implies that these elements function independently. We examined the interaction between the heat shock element (HSE) and the TATA element as the distance between the two factor-binding sites was increased. It was necessary to create a mutant HSE with an extended consensus sequence in order for the HSE to function at a distance. Moving this extended HSE 500 bases upstream did not increase its dependence on the TATA element, suggesting that the TATA independence of this element is intrinsic to its function and is not determined by distance from the promoter.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin J., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Key features of heat shock regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3761–3769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Heat shock regulatory elements function as an inducible enhancer in the Xenopus hsp70 gene and when linked to a heterologous promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):753–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90789-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Hahn S., Ogden S., Schleif R. F. An operator at -280 base pairs that is required for repression of araBAD operon promoter: addition of DNA helical turns between the operator and promoter cyclically hinders repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5017–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene J. M., Larin Z., Taylor I. C., Prentice H., Gwinn K. A., Kingston R. E. Multiple basal elements of a human hsp70 promoter function differently in human and rodent cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3646–3655. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Green M. R. Analysis of the role of the transcription factor ATF in the assembly of a functional preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Carey M. F., Kakidani H., Roeder R. G. Mechanism of action of a yeast activator: direct effect of GAL4 derivatives on mammalian TFIID-promoter interactions. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):665–669. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaddurah-Daouk R., Greene J. M., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Kingston R. E. Activation and repression of mammalian gene expression by the c-myc protein. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):347–357. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Cowie A., Morimoto R. I., Gwinn K. A. Binding of polyomavirus large T antigen to the human hsp70 promoter is not required for trans activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3180–3190. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Carey M. F., Ptashne M., Green M. R. GAL4 derivatives function alone and synergistically with mammalian activators in vitro. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):659–664. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirault M. E., Southgate R., Delwart E. Regulation of heat-shock genes: a DNA sequence upstream of Drosophila hsp70 genes is essential for their induction in monkey cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1279–1285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D. Transcription factor Sp1 binds to and activates a human hsp70 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4099–4104. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D., Williams G. T., Morimoto R. I., Greene J., Kingston R. E., Tjian R. Two transcriptional activators, CCAAT-box-binding transcription factor and heat shock transcription factor, interact with a human hsp70 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1129–1138. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Jones S. D., Bond B., Yamamoto K. R. The immunoglobulin octanucleotide: independent activity and selective interaction with enhancers. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1498–1501. doi: 10.1126/science.3029871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Zhou Q., Berk A. J. Sp1 activates transcription without enhancing DNA-binding activity of the TATA box factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3299–3307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Howie K. B., Rowe M. E., Goodman H. M., Moore D. D. Human growth hormone as a reporter gene in regulation studies employing transient gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3173–3179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Fisch T. M., Benecke B. J., Nevins J. R., Heintz N. Definition of multiple, functionally distinct TATA elements, one of which is a target in the hsp70 promoter for E1A regulation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):723–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Constitutive and inducible Saccharomyces cerevisiae promoters: evidence for two distinct molecular mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3847–3853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Factor substitution in a human HSP70 gene promoter: TATA-dependent and TATA-independent interactions. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):165–175. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Maniatis T. Simian virus 40 enhancer increases number of RNA polymerase II molecules on linked DNA. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):73–75. doi: 10.1038/315072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T., McClanahan T. K., Morimoto R. I. E1a transactivation of the human HSP70 promoter is mediated through the basal transcriptional complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2574–2587. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Staudt L., Baltimore D. An octamer oligonucleotide upstream of a TATA motif is sufficient for lymphoid-specific promoter activity. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):174–178. doi: 10.1038/329174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Kingston R. E., Morimoto R. I. Human HSP70 promoter contains at least two distinct regulatory domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):629–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Williams G. T., Morimoto R. I. Detection of three protein binding sites in the serum-regulated promoter of the human gene encoding the 70-kDa heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2203–2207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B., Hunt C., Morimoto R. Structure and expression of the human gene encoding major heat shock protein HSP70. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):330–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Berk A. Constraints on spacing between transcription factor binding sites in a simple adenovirus promoter. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):403–411. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. Germline transformation used to define key features of heat-shock response elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.3125608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]