Abstract
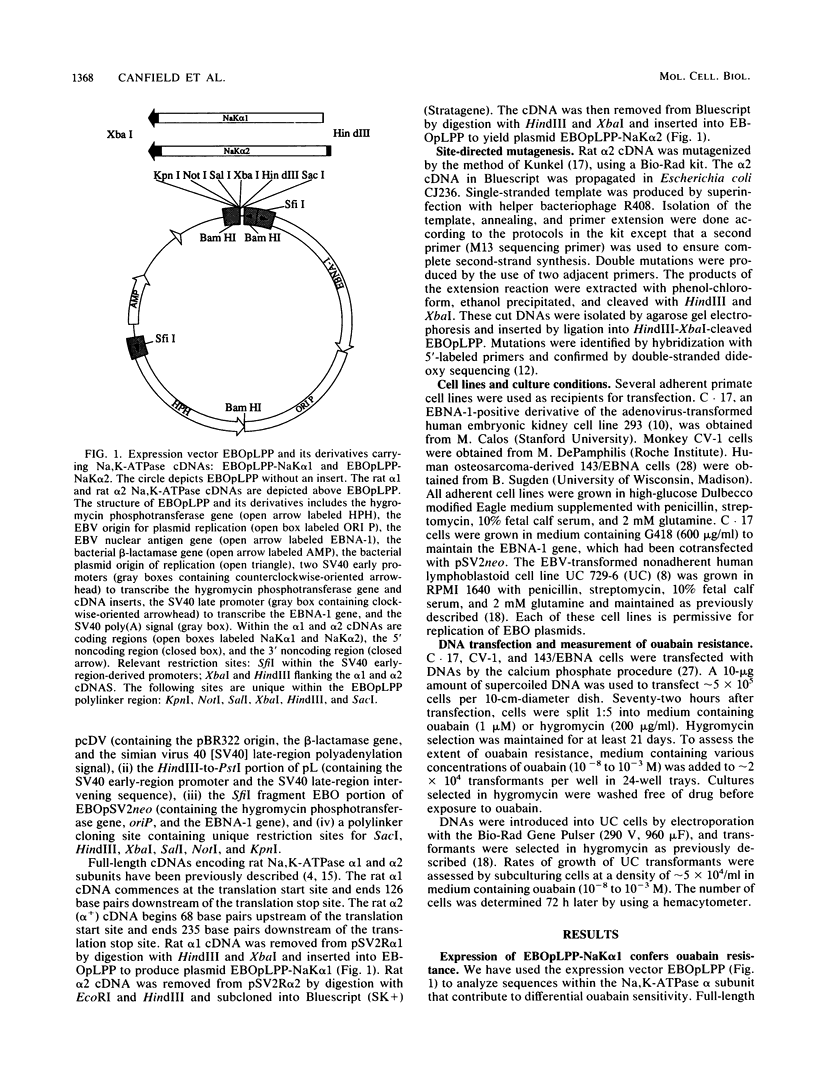
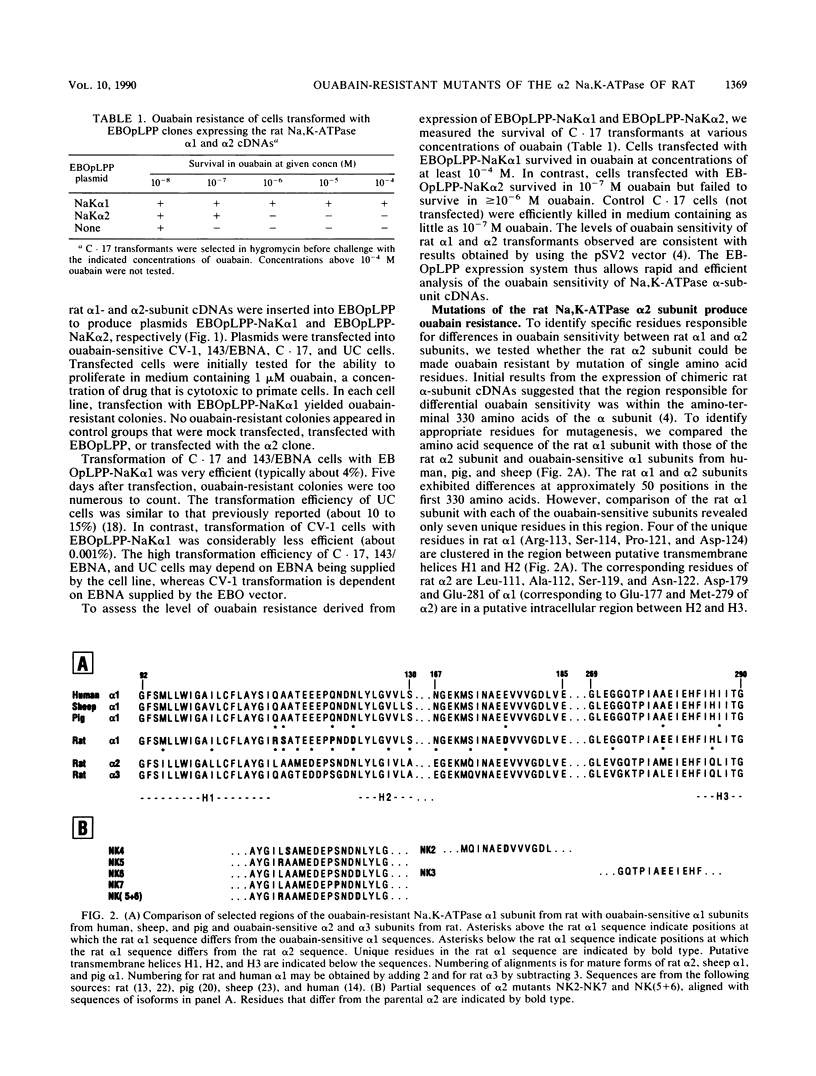
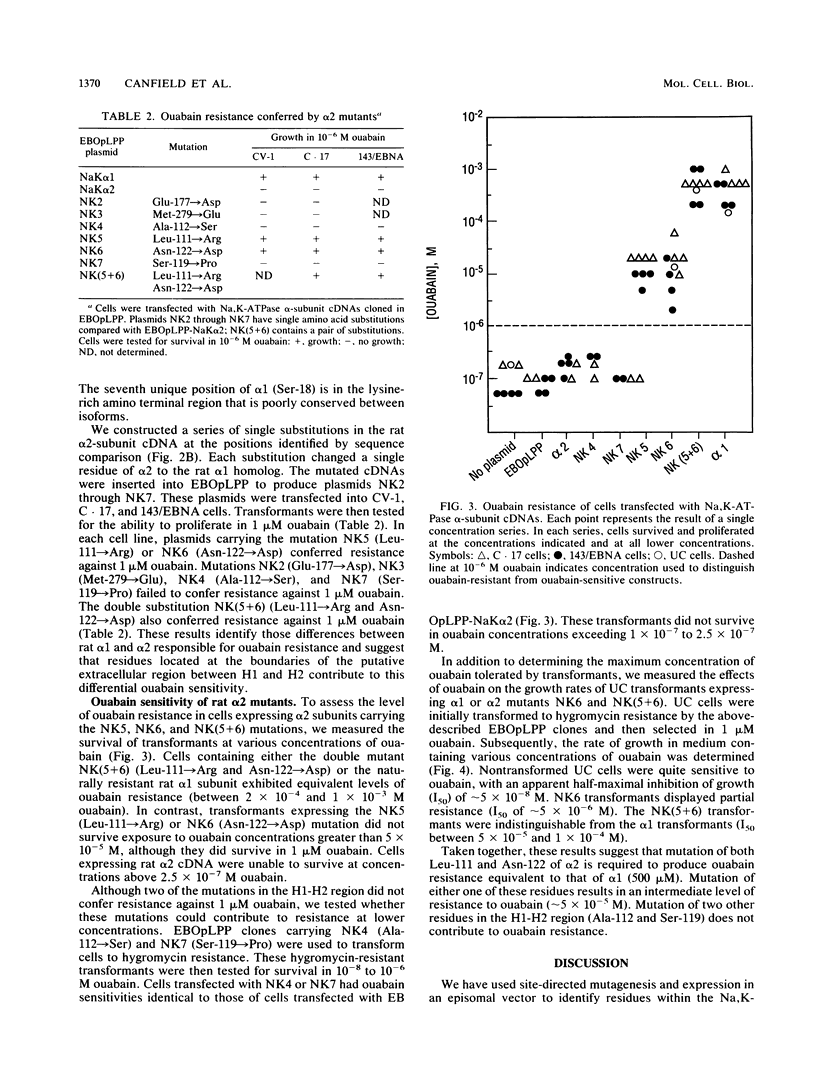
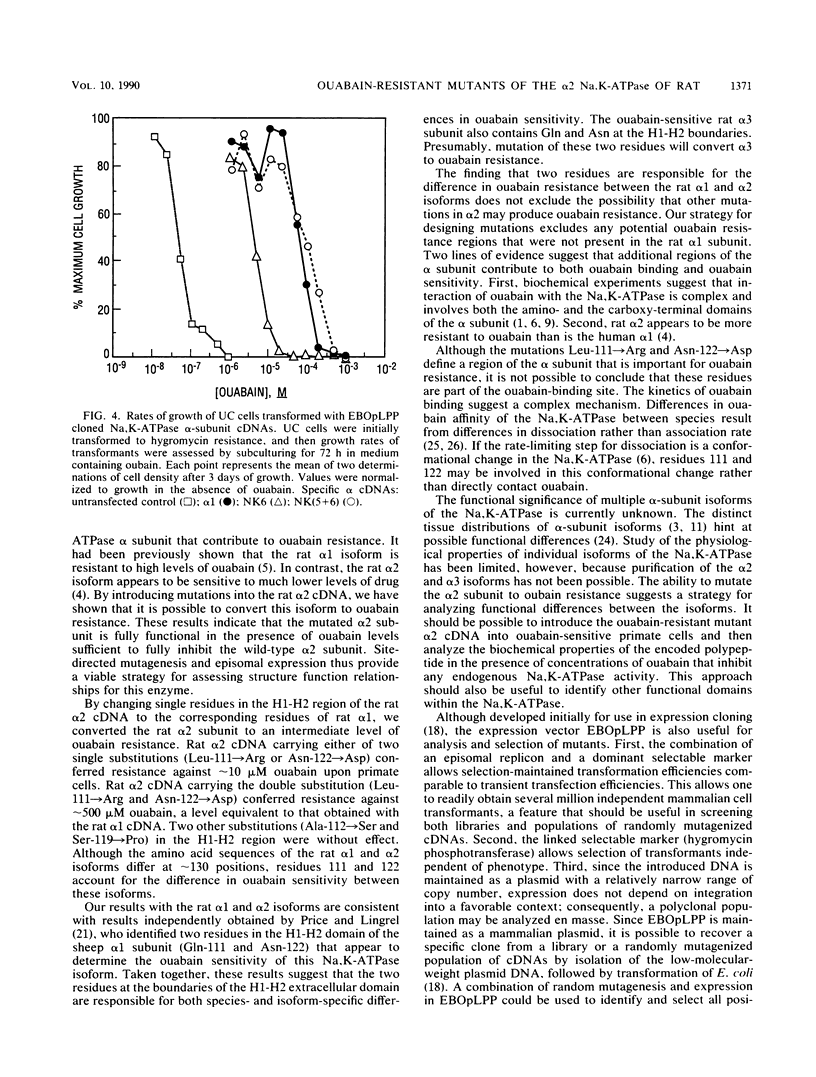
Site-directed mutagenesis was used to identify residues responsible for the greater than 1,000-fold difference in ouabain sensitivity between the rat Na,K-ATPase alpha 1 and alpha 2 isoforms. A series of mutagenized cDNAs was constructed that replaced residues of the rat alpha 2 subunit with the corresponding residues from the rat alpha 1 subunit. These cDNAs were cloned into a mammalian episomal expression vector (EBOpLPP) and expressed in ouabain-sensitive primate cells. Either of two single substitutions introduced into the rat alpha 2 subunit cDNA (Leu-111----Arg or Asn-122----Asp) conferred partial resistance (approximately 10 microM ouabain) upon transformed cells. This resistance was intermediate between the levels conferred by the rat alpha 1 cDNA (approximately 500 microM ouabain) and the rat alpha 2 cDNA (approximately 0.2 microM ouabain). A double substitution of the rat alpha 2 cDNA (Leu-111----Arg and Asn-122----Asp) conferred a resistance level equivalent to that obtained with rat alpha 1. These results demonstrate that the residues responsible for isoform-specific differences in ouabain sensitivity are located at the end of the H1-H2 extracellular domain. The combination of site-directed mutagenesis and episomal expression provides a useful system for the selection and analysis of mutants.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed K., Rohrer D. C., Fullerton D. S., Deffo T., Kitatsuji E., From A. H. Interaction of (Na+,K+)-ATPases and digitalis genins. A general model for inhibitory activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8092–8097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel J. R., Garetz S., Stone L., Levenson R. Differential expression of Na+,K+-ATPase alpha- and beta-subunit mRNAs in rat tissues and cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9030–9034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel J. R., Graw S., Housman D., Levenson R. Identification of a region within the Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit that contributes to differential ouabain sensitivity. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3744–3749. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel J. R., Schulz J., Zhou X. M., Kent R. B., Housman D., Cantley L., Levenson R. Expression of an ouabain-resistant Na,K-ATPase in CV-1 cells after transfection with a cDNA encoding the rat Na,K-ATPase alpha 1 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7726–7733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortes P. A. Anthroylouabain: a specific fluorescent probe for the cardiac glycoside receptor of the Na-K ATPase. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 8;16(3):531–540. doi: 10.1021/bi00622a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassy M. C., Handley H. H., Hagiwara H., Royston I. UC 729-6, a human lymphoblastoid B-cell line useful for generating antibody-secreting human-human hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6327–6331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeldner M. P., Hirth C. G., Rossi B., Ponzio G., Lazdunski M. Specific photoaffinity labeling of the digitalis binding site of the sodium and potassium ion activated adenosinetriphosphatase induced by energy transfer. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4685–4690. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara Y., Nikamoto A., Kojima T., Matsumoto A., Nakao M. Expression of sodium pump activities in BALB/c 3T3 cells transfected with cDNA encoding alpha 3-subunits of rat brain Na+,K+-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 26;238(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera V. L., Emanuel J. R., Ruiz-Opazo N., Levenson R., Nadal-Ginard B. Three differentially expressed Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit isoforms: structural and functional implications. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1855–1865. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Ohta T., Nojima H., Nagano K. Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of human Na,K-ATPase deduced from cDNA sequence. J Biochem. 1986 Aug;100(2):389–397. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent R. B., Emanuel J. R., Ben Neriah Y., Levenson R., Housman D. E. Ouabain resistance conferred by expression of the cDNA for a murine Na+, K+-ATPase alpha subunit. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):901–903. doi: 10.1126/science.3039660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent R. B., Fallows D. A., Geissler E., Glaser T., Emanuel J. R., Lalley P. A., Levenson R., Housman D. E. Genes encoding alpha and beta subunits of Na,K-ATPase are located on three different chromosomes in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5369–5373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolskee R. F., Kavathas P., Berg P. Epstein-Barr virus shuttle vector for stable episomal replication of cDNA expression libraries in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2837–2847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Modyanov N. N., Broude N. E., Petrukhin K. E., Grishin A. V., Arzamazova N. M., Aldanova N. A., Monastyrskaya G. S., Sverdlov E. D. Pig kidney Na+,K+-ATPase. Primary structure and spatial organization. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jun 9;201(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80616-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price E. M., Lingrel J. B. Structure-function relationships in the Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit: site-directed mutagenesis of glutamine-111 to arginine and asparagine-122 to aspartic acid generates a ouabain-resistant enzyme. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 1;27(22):8400–8408. doi: 10.1021/bi00422a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J., Lingrel J. B. Molecular cloning of three distinct forms of the Na+,K+-ATPase alpha-subunit from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8125–8132. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Schwartz A., Lingrel J. B. Amino-acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of the (Na+ + K+)ATPase deduced from a complementary DNA. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):691–695. doi: 10.1038/316691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Isozymes of the Na+/K+-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 9;988(2):185–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin T., Brody T. M. Rates of dissociation of enzyme-ouabain complexes and K 0.5 values in (Na + + K + ) adenosine triphosphatase from different species. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Jun 1;21(11):1553–1560. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90305-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallick E. T., Pitts B. J., Lane L. K., Schwartz A. A kinetic comparison of cardiac glycoside interactions with Na+,K+-ATPases from skeletal and cardiac muscle and from kidney. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jul;202(2):442–449. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


