Abstract
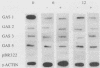
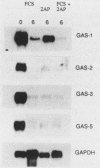
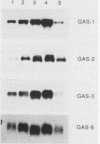
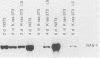
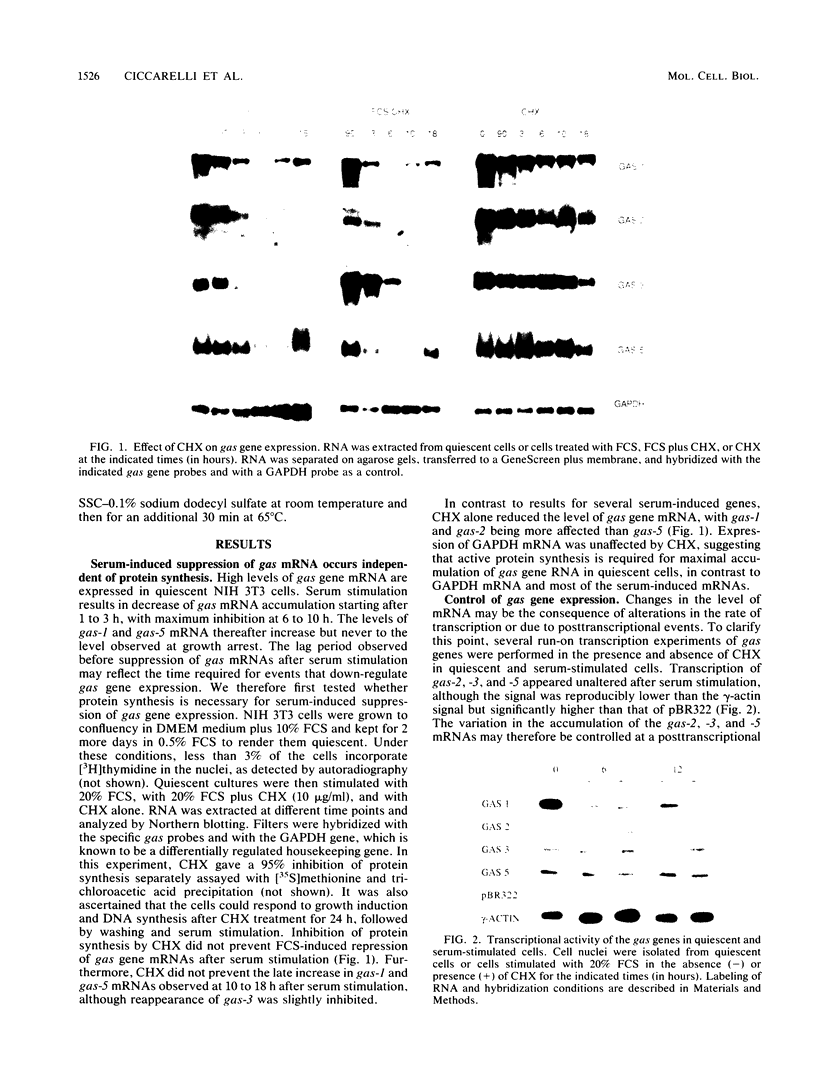
The suppression of growth arrest-specific (gas) gene expression by serum appeared to be independent of protein synthesis, but expression in resting cells was sensitive to 2-aminopurine, an inhibitor of intracellular protein kinases. Although accumulation of gas gene mRNA was reduced by serum, nuclear transcription of the gas-2, -3, and -5 genes was observed in serum-stimulated cells, indicating that posttranscriptional events may regulate mRNA levels. Growth induction by serum, on the other hand, led to suppression of transcription of the gas-1 gene. Cell cycle regulation and the serum response of gas-1 were lost in ras-transformed cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armelin H. A., Armelin M. C., Kelly K., Stewart T., Leder P., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D. Functional role for c-myc in mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):655–660. doi: 10.1038/310655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard P. A., Yannoni Y., Simmons D. L., Erikson R. L. Rapid repression of quiescence-specific gene expression by epidermal growth factor, insulin, and pp60v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1371–1375. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. mRNA decay: finding the right targets. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Regulation of c-myc mRNA stability in vitro by a labile destabilizer with an essential nucleic acid component. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1996–2006. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bédard P. A., Balk S. D., Gunther H. S., Morisi A., Erikson R. L. Repression of quiescence-specific polypeptides in chicken heart mesenchymal cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1450–1458. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:881–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Reffel A. C., Stiles C. D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Curran T. fra-1: a serum-inducible, cellular immediate-early gene that encodes a fos-related antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2063–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. W., Sager R. Suppression of tumorigenicity in hybrids of normal and oncogene-transformed CHEF cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2062–2066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F. Polypeptide growth factors: roles in normal and abnormal cell growth. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:443–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirtz A. M., Calabretta B. A c-myb antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits normal human hematopoiesis in vitro. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.2461588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. F., Cavenee W. K. Tumor suppressors: recessive mutations that lead to cancer. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):173–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R., Schwab G., Wickstrom E., Loke S. L., Pluznik D. H., Watt R., Neckers L. M. A c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits entry into S phase but not progress from G0 to G1. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):445–449. doi: 10.1038/328445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Hyland J. K., Watt R., Rosenberg M., Baserga R. Microinjected c-myc as a competence factor. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1313–1315. doi: 10.1126/science.4001943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knabbe C., Lippman M. E., Wakefield L. M., Flanders K. C., Kasid A., Derynck R., Dickson R. B. Evidence that transforming growth factor-beta is a hormonally regulated negative growth factor in human breast cancer cells. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohase M., Henriksen-DeStefano D., May L. T., Vilcek J., Sehgal P. B. Induction of beta 2-interferon by tumor necrosis factor: a homeostatic mechanism in the control of cell proliferation. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90780-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. L., Kikuchi T., Pledger W. J., Tamm I. Interferon inhibits the establishment of competence in Go/S-phase transition. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):356–359. doi: 10.1126/science.3726533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Growth-related changes in specific mRNAs of cultured mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Wilder E. L. Control of proliferin gene expression in serum-stimulated mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2080–2086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B., Dubrow R., Hamlin J. L., Kletzien R. F. Animal cell cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:715–750. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor beta. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:107–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., King R. M., Philipson L. Genes specifically expressed at growth arrest of mammalian cells. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):787–793. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino V., Bandyopadhyay S. TGF beta inhibits Go/S-phase transition in primary fibroblasts. Loss of response to the antigrowth effect of TGF beta is observed after immortalization. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):569–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino V., Drozdoff V., McKinney M. D., Zeitz L., Fleissner E. Potentiation of growth factor activity by exogenous c-myc expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8167–8171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino V., Drozdoff V., Zeitz L., Fleissner E. Increased radiation-induced transformation in C3H/10T1/2 cells after transfer of an exogenous c-myc gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4131–4134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Peptide growth factors are multifunctional. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):217–219. doi: 10.1038/332217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. A 57,000-mol-wt protein uniquely present in nonproliferating cells and senescent human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):545–551. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. Contact-inhibition-induced quiescent state is marked by intense nuclear expression of statin. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Oct;133(1):151–157. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Lin S. L. Disappearance of statin, a protein marker for non-proliferating and senescent cells, following serum-stimulated cell cycle entry. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Nov;167(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. Rapid disappearance of statin, a nonproliferating and senescent cell-specific protein, upon reentering the process of cell cycling. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1695–1701. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2538922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Toschi L., Ryseck R. P., Schuermann M., Müller R., Bravo R. The product of a novel growth factor activated gene, fos B, interacts with JUN proteins enhancing their DNA binding activity. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):805–813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03441.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Keller A., Whittemore L. A., Maniatis T. 2-Aminopurine selectively inhibits the induction of beta-interferon, c-fos, and c-myc gene expression. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):210–213. doi: 10.1126/science.3281258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]