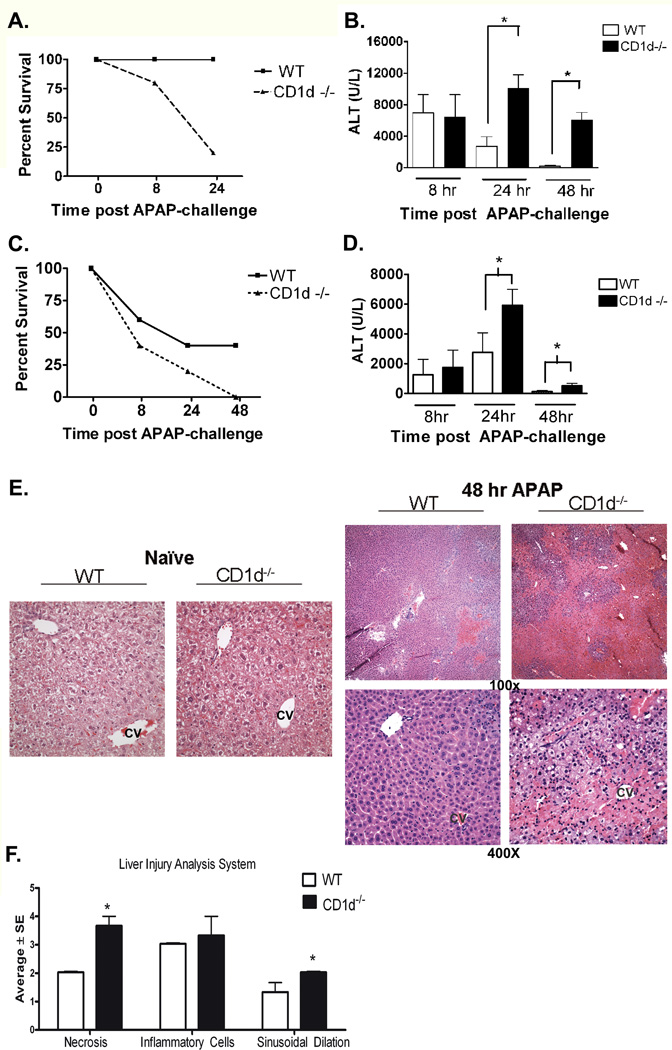
Figure 1. Increased susceptibility of CD1d−/− mice to AILI.
A) Decreased survival of female CD1d−/− mice compared to WT mice after APAP-challenge (385 mg/kg). B) Serum ALT levels, measured by using a colorimetric assay (Teco Diagnostics, Anaheim, CA), were increased in female CD1d−/− mice compared to WT mice at 24 h and 48 h post-APAP challenge (350 mg/kg ). C) Decreased survival of male CD1d−/− mice compared to WT mice after APAP-challenge (235 mg/kg APAP). D) Increased serum ALT levels in male CD1d−/− mice compared to WT mice at 24 h and 4 8h post-APAP challenge (230 mg/kg APAP). E) Photomicrograph (100× and 400X final magnification) of H&E-stained liver sections from female WT and CD1d−/− mice following 48 h APAP. CV, central vein. F) Necrosis, inflammatory infiltration and sinusoidal dilation scores from WT and CD1d−/− mice following 48 h APAP. The individual necrosis (A) and cellular infiltration (B) sinusoidal dilation (C) scores from each mouse strain (3 mice per group) were determined. Results in panel A-D represent mean ± SEM of 10 mice per group. Results in panel F represent average ± SE of 3 mice per group. *p < 0.05 versus WT mice. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments.