Abstract
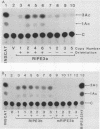
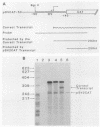
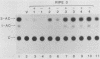
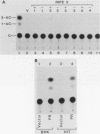
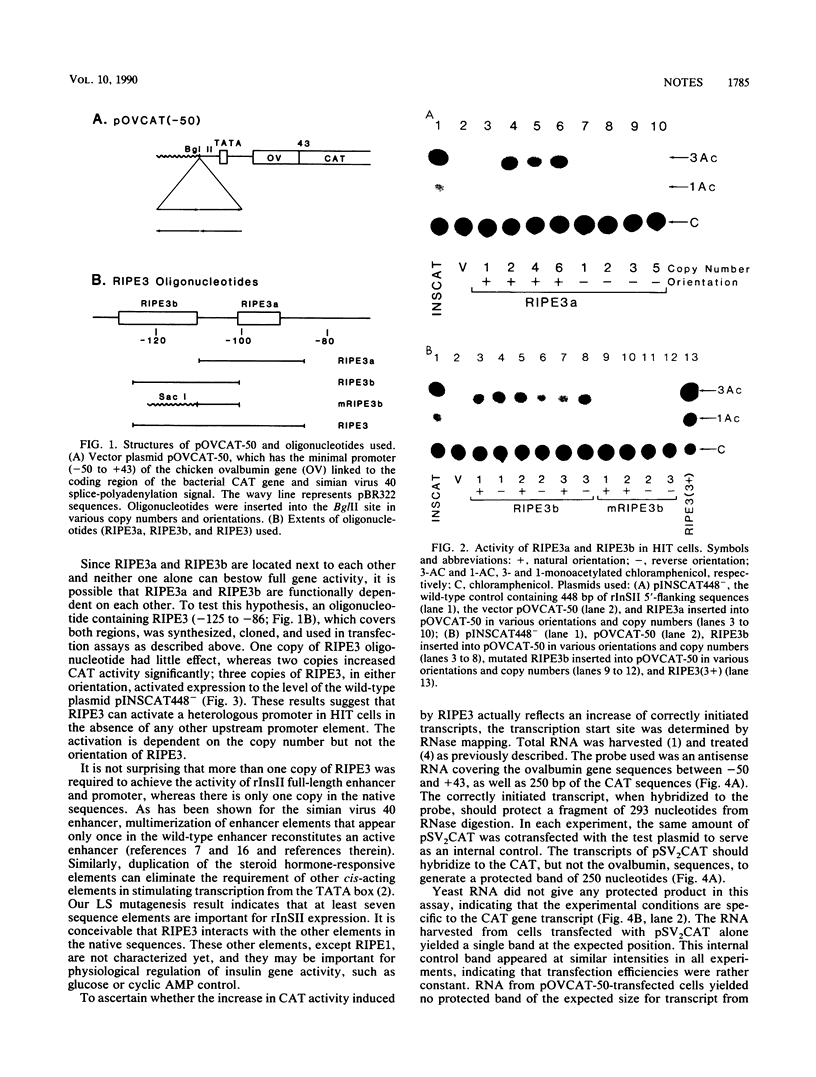
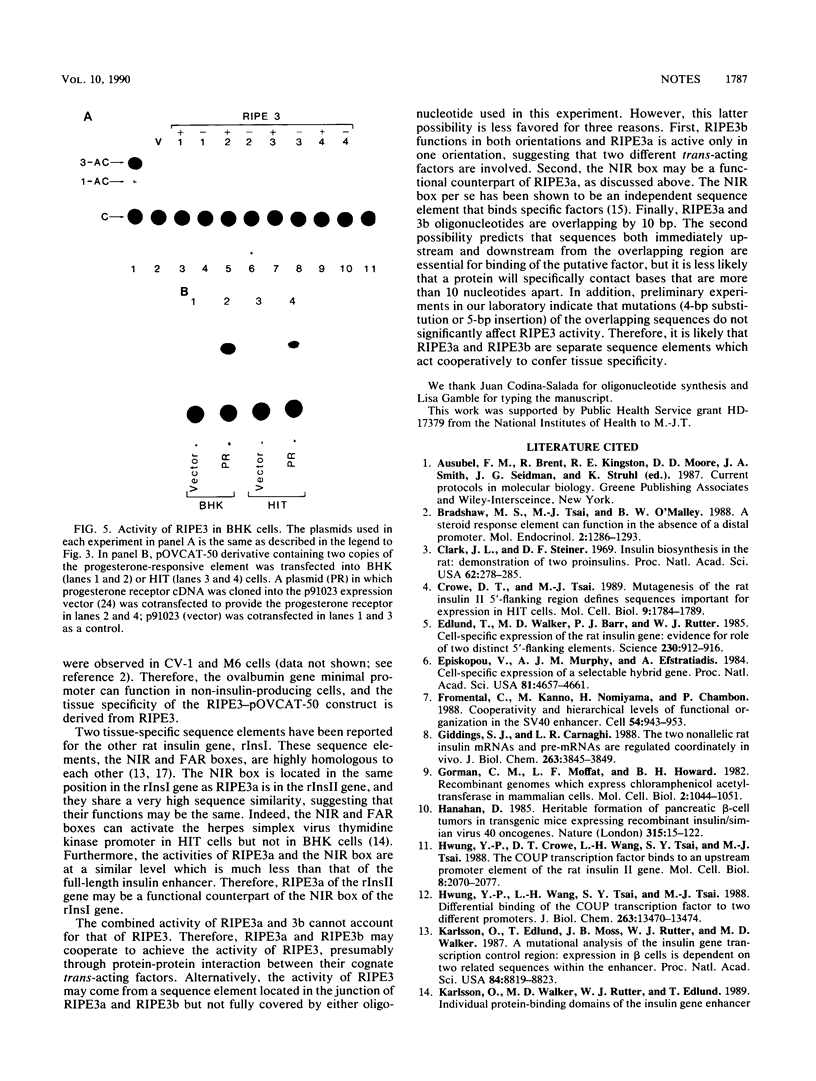
The 5'-flanking region of the rat insulin II gene (-448 to +50) is sufficient for tissue-specific expression. To further determine the tissue-specific cis-acting element(s), important sequences defined by linker-scanning mutagenesis were placed upstream of a heterologous promoter and transfected into insulin-producing and -nonproducing cells. Rat insulin promoter element 3 (RIPE3), which spans from -125 to -86, was shown to confer beta-cell-specific expression in either orientation. However, two subregions of RIPE3, RIPE3a and RIPE3b (defined by linker-scanning mutations), displayed only marginal activities. These results suggest that the two subregions cooperate to confer tissue specificity, presumably via their cognate binding factors.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradshaw M. S., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. A steroid response element can function in the absence of a distal promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1286–1293. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. L., Steiner D. F. Insulin biosynthesis in the rat: demonstration of two proinsulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):278–285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe D. T., Tsai M. J. Mutagenesis of the rat insulin II 5'-flanking region defines sequences important for expression in HIT cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1784–1789. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Episkopou V., Murphy A. J., Efstratiadis A. Cell-specified expression of a selectable hybrid gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4657–4661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Carnaghi L. R. The two nonallelic rat insulin mRNAs and pre-mRNAs are regulated coordinately in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3845–3849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwung Y. P., Crowe D. T., Wang L. H., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J. The COUP transcription factor binds to an upstream promoter element of the rat insulin II gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2070–2077. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwung Y. P., Wang L. H., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J. Differential binding of the chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter (COUP) transcription factor to two different promoters. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13470–13474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Edlund T., Moss J. B., Rutter W. J., Walker M. D. A mutational analysis of the insulin gene transcription control region: expression in beta cells is dependent on two related sequences within the enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8819–8823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss L. G., Moss J. B., Rutter W. J. Systematic binding analysis of the insulin gene transcription control region: insulin and immunoglobulin enhancers utilize similar transactivators. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2620–2627. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Karlsson O., Edlund T. A beta-cell-specific protein binds to the two major regulatory sequences of the insulin gene enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4228–4231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastorcic M., Wang H., Elbrecht A., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Control of transcription initiation in vitro requires binding of a transcription factor to the distal promoter of the ovalbumin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2784–2791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagami I., Tsai S. Y., Wang H., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Identification of two factors required for transcription of the ovalbumin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4259–4267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santerre R. F., Cook R. A., Crisel R. M., Sharp J. D., Schmidt R. J., Williams D. C., Wilson C. P. Insulin synthesis in a clonal cell line of simian virus 40-transformed hamster pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4339–4343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. B., Schon E., Henderson A., Karathanasis S. K., Cate R., Zeitlin S., Chirgwin J., Efstratiadis A. RNA-mediated gene duplication: the rat preproinsulin I gene is a functional retroposon. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2090–2103. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Chan S. J., Welsh J. M., Kwok S. C. Structure and evolution of the insulin gene. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:463–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]