Abstract
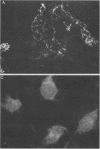
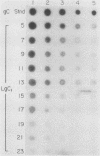
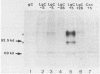
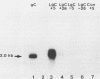
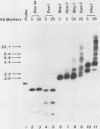
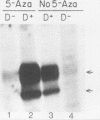
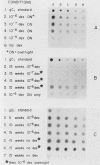
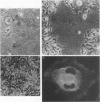
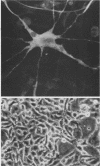
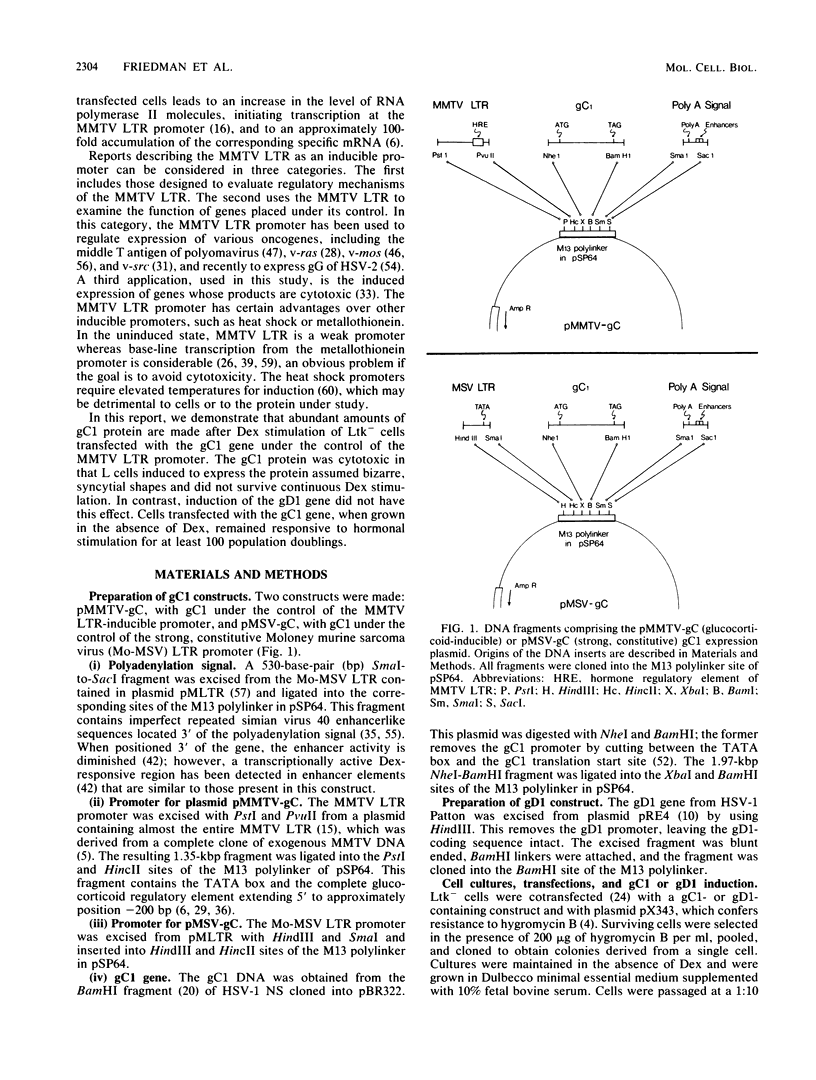
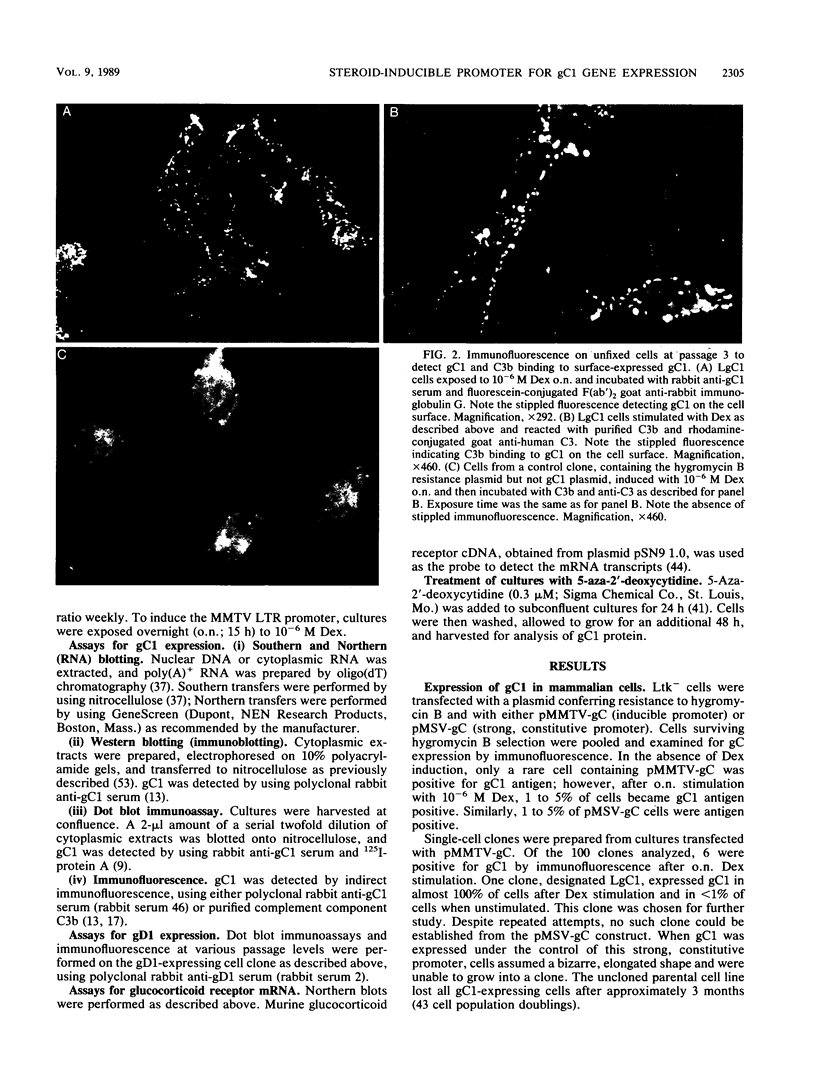
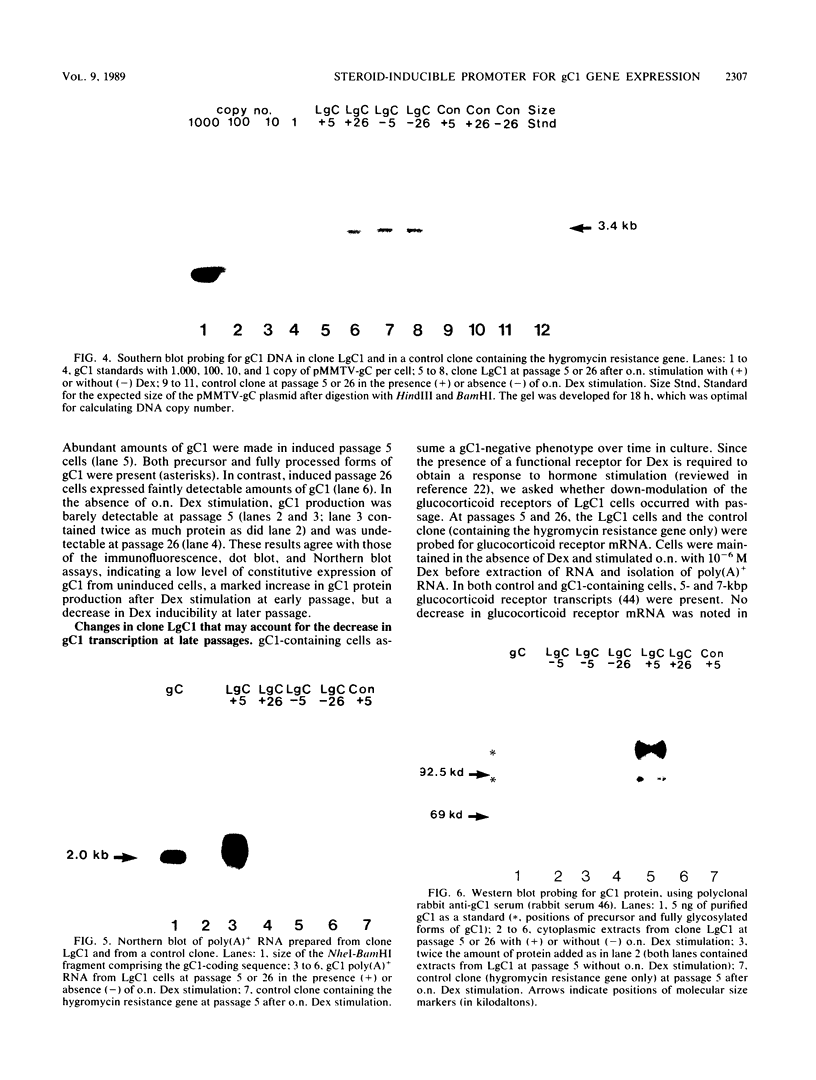
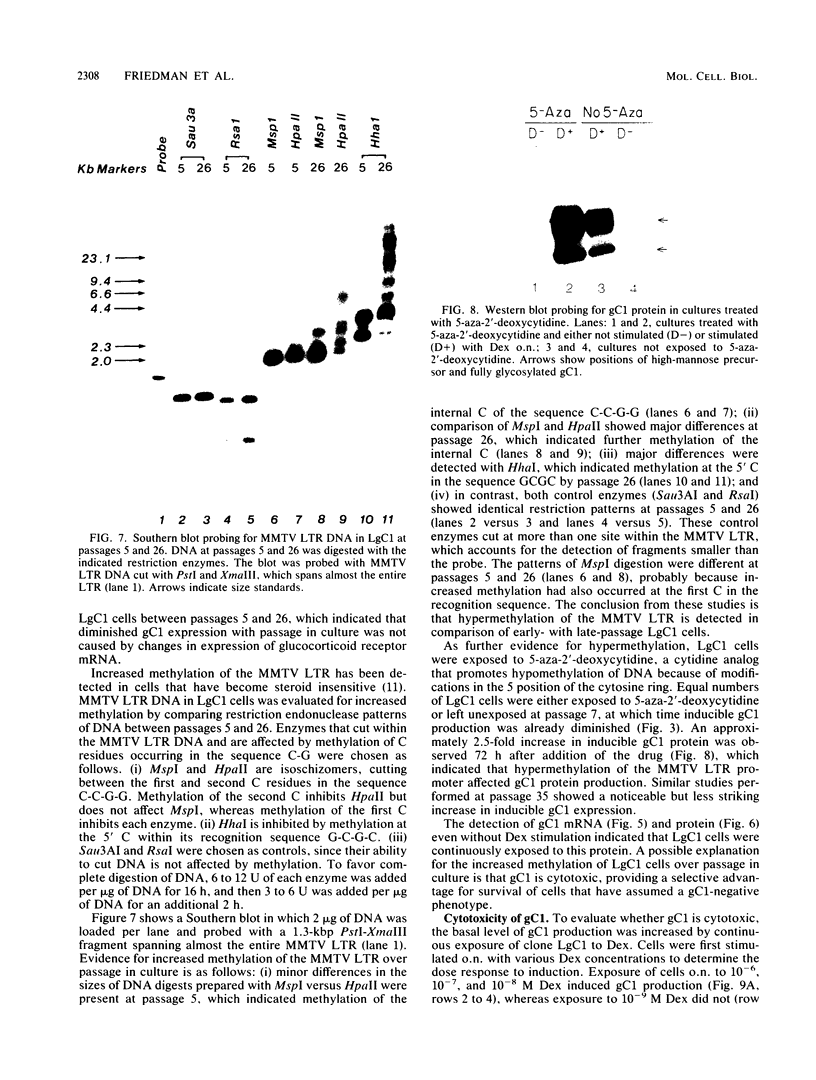
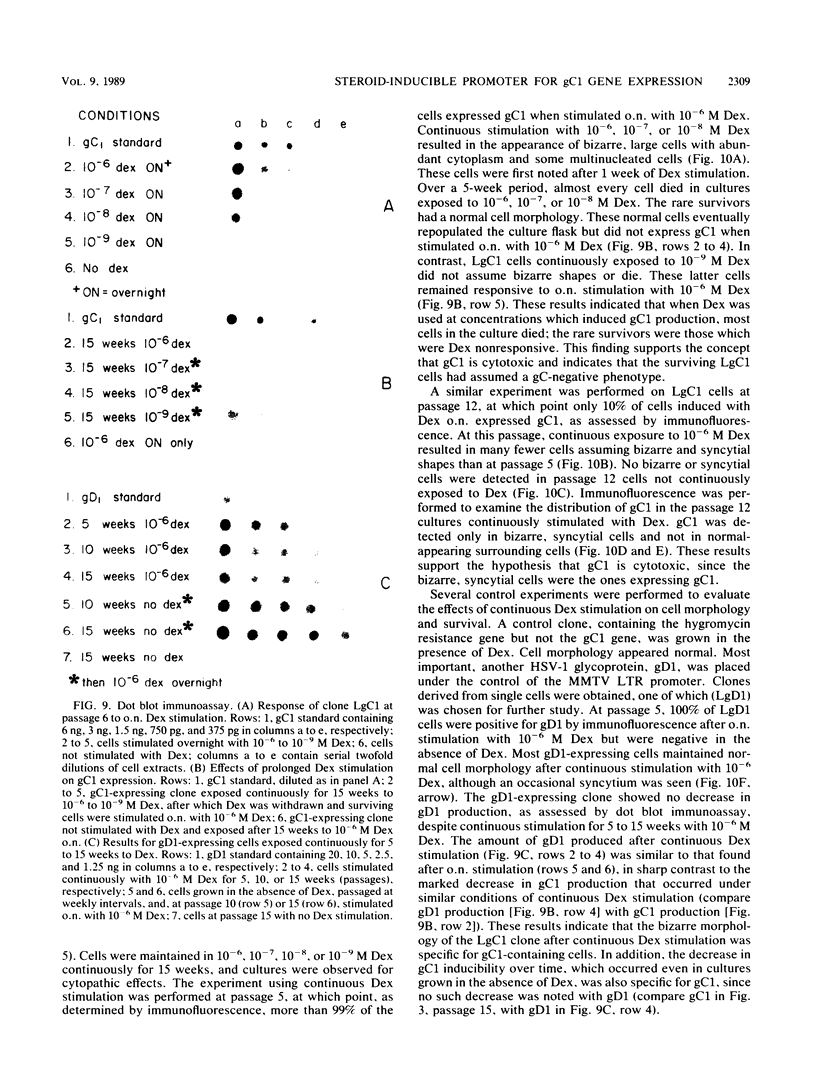
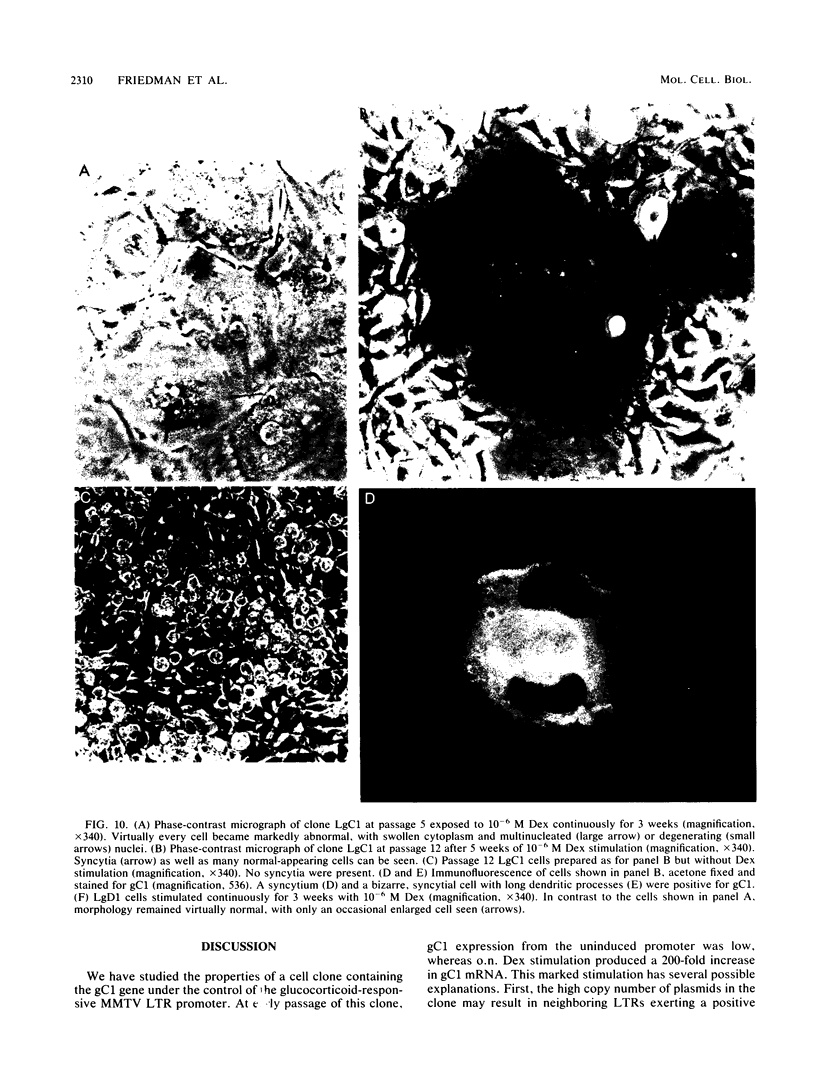
Abundant expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein gC (gC1) in transfected mammalian cells has not previously been achieved, possibly because gC1 protein is toxic to cells. To approach this problem, the gC1 coding sequence was placed under the control of the weak but inducible glucocorticoid-responsive promoter from the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) long terminal repeat (LTR). As controls to evaluate for gC1 cytotoxicity, the MMTV LTR promoter was used to express glycoprotein gD1, and a strong, constitutive promoter from the Moloney murine sarcoma virus LTR was used to express gC1. L cells were transfected with these constructs, and a clone expressing gC1 from the inducible MMTV LTR promoter was analyzed. In the absence of glucocorticoid (dexamethasone) stimulation, only a low level of gC1 mRNA expression was detected; after overnight stimulation with dexamethasone, transcription increased approximately 200-fold. Abundant gC1 protein that was functionally active in that it bound complement component C3b, was produced. From passages 5 through 26 (70 cell population doublings), the gC1-producing clone became less responsive to overnight dexamethasone stimulation. The block to gC1 expression occurred at the level of transcription and was associated with hypermethylation of the MMTV LTR DNA. Treatment of the clone with 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine partially reversed the block in gC1 protein production. Late-passage cells assumed a gC1-negative phenotype that appeared to offer a selective growth advantage, which suggested that gC1 was cytotoxic. Several findings support this view: (i) some cells expressing gC1 after overnight stimulation with dexamethasone assumed bizarre, syncytial shapes; (ii) continuous stimulation with dexamethasone for 5 weeks resulted in death of most cells; (iii) cells transfected with gC1 under the control of the strong Moloney murine sarcoma virus promoter assumed bizarre shapes, and stable gC1-expressing clones could not be established; and (iv) cells induced to express gD1 retained a normal appearance after overnight stimulation or 15 weeks of continuous stimulation with dexamethasone. The inducible MMTV LTR promoter is useful for expressing gC1 and may have applications for expressing other cytotoxic proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
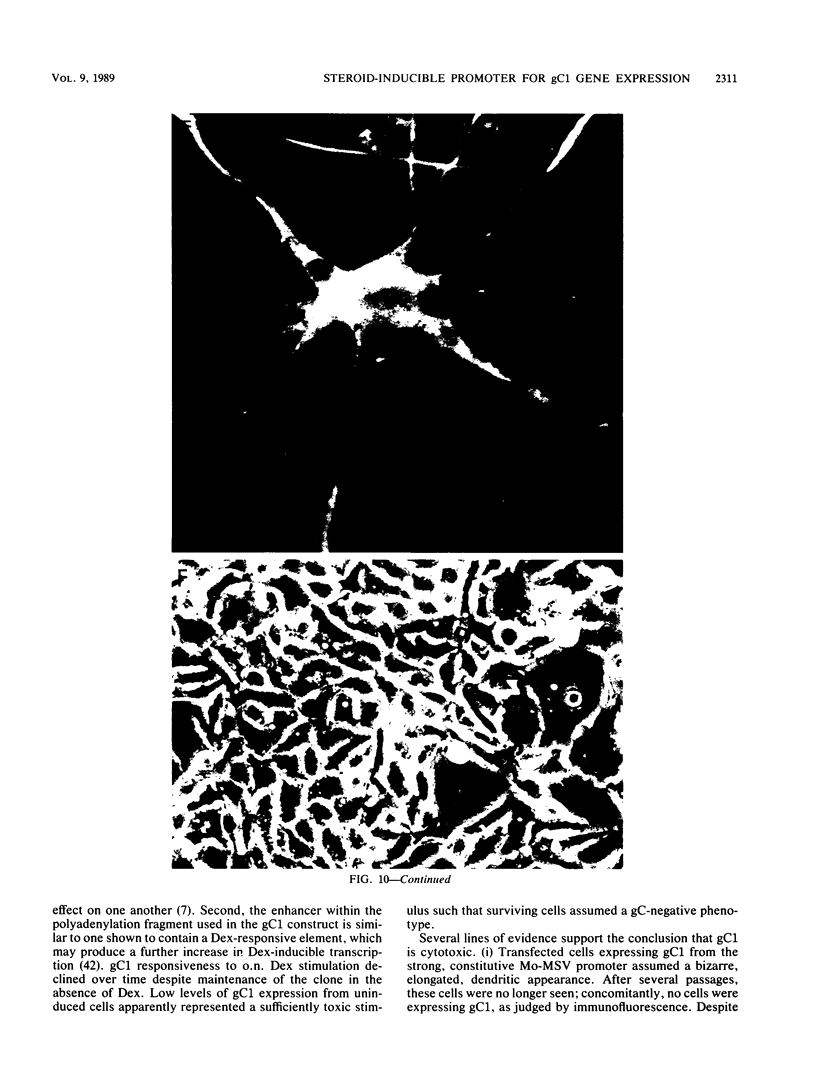
- Arsenakis M., Campadelli-Fiume G., Roizman B. Regulation of glycoprotein D synthesis: does alpha 4, the major regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus 1, regulate late genes both positively and negatively? J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):148–158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.148-158.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arsenakis M., Tomasi L. F., Speziali V., Roizman B., Campadelli-Fiume G. Expression and regulation of glycoprotein C gene of herpes simplex virus 1 resident in a clonal L-cell line. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):367–376. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.367-376.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. W., Dowbenko D., Lasky L. A., Simonsen C. C. Detection of antibodies to herpes simplex virus with a continuous cell line expressing cloned glycoprotein D. Science. 1983 Nov 4;222(4623):524–527. doi: 10.1126/science.6312563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochlinger K., Diggelmann H. Hygromycin B phosphotransferase as a selectable marker for DNA transfer experiments with higher eucaryotic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2929–2931. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Cloned mouse mammary tumor virus DNA is biologically active in transfected mouse cells and its expression is stimulated by glucocorticoid hormones. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Glucocorticoid regulation of mouse mammary tumor virus: identification of a short essential DNA region. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1423–1429. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Kühnel B. Distinct sequence elements involved in the glucocorticoid regulation of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Arsenakis M., Farabegoli F., Roizman B. Entry of herpes simplex virus 1 in BJ cells that constitutively express viral glycoprotein D is by endocytosis and results in degradation of the virus. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):159–167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.159-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Dietzschold B., Ponce de Leon M., Long D., Golub E., Varrichio A., Pereira L., Eisenberg R. J. Localization and synthesis of an antigenic determinant of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D that stimulates the production of neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):102–108. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.102-108.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Wilcox W. C., Sodora D. L., Long D., Levin J. Z., Eisenberg R. J. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D deletion mutants in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1932–1940. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1932-1940.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darbre P. D., King R. J. Progression to steroid insensitivity can occur irrespective of the presence of functional steroid receptors. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):521–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Ponce de Leon M., Friedman H. M., Fries L. F., Frank M. M., Hastings J. C., Cohen G. H. Complement component C3b binds directly to purified glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Microb Pathog. 1987 Dec;3(6):423–435. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis N., Keitges E., Gartler S. M., Rocchi M. High-frequency reactivation of X-linked genes in Chinese hamster X human hybrid cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 May;13(3):191–204. doi: 10.1007/BF01535202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasel N., Pearson K., Buetti E., Diggelmann H. The region of mouse mammary tumor virus DNA containing the long terminal repeat includes a long coding sequence and signals for hormonally regulated transcription. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):3–7. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01115.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firzlaff J. M., Diggelmann H. Dexamethasone increases the number of RNA polymerase II molecules transcribing integrated mouse mammary tumor virus DNA and flanking mouse sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1057–1062. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. M., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J., Seidel C. A., Cines D. B. Glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus 1 acts as a receptor for the C3b complement component on infected cells. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):633–635. doi: 10.1038/309633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. M., Glorioso J. C., Cohen G. H., Hastings J. C., Harris S. L., Eisenberg R. J. Binding of complement component C3b to glycoprotein gC of herpes simplex virus type 1: mapping of gC-binding sites and demonstration of conserved C3b binding in low-passage clinical isolates. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):470–475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.470-475.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries L. F., Friedman H. M., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J., Hammer C. H., Frank M. M. Glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus 1 is an inhibitor of the complement cascade. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1636–1641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Anti-glycoprotein D antibodies that permit adsorption but block infection by herpes simplex virus 1 prevent virion-cell fusion at the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5454–5458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring U. Genetics of glucocorticoid receptors. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Dec;48(2-3):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gompels U., Minson A. The properties and sequence of glycoprotein H of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1986 Sep;153(2):230–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslinger A., Karin M. Upstream promoter element of the human metallothionein-IIA gene can act like an enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8572–8576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Homa F. L., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. Herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C-negative mutants exhibit multiple phenotypes, including secretion of truncated glycoproteins. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):566–574. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.566-574.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. L., Ostrowski M. C., Berard D., Hager G. L. Glucocorticoid regulation of the Ha-MuSV p21 gene conferred by sequences from mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E., Kennedy N., Rahmsdorf U., Groner B. Hormone-responsive expression of an endogenous proviral gene of mouse mammary tumor virus after molecular cloning and gene transfer into cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2038–2042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N., van Ooyen A. J., Kennedy N., Herrlich P., Ponta H., Groner B. Subfragments of the large terminal repeat cause glucocorticoid-responsive expression of mouse mammary tumor virus and of an adjacent gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Hormonal regulation of the Rous sarcoma virus src gene via a heterologous promoter defines a threshold dose for cellular transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Taylor S. M., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J. Cell cycle-specific reactivation of an inactive X-chromosome locus by 5-azadeoxycytidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1215–1219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Brough D. E., Cleghon V. Introduction, stable integration, and controlled expression of a chimeric adenovirus gene whose product is toxic to the recipient human cell. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1354–1362. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Mulligan R., Berg P., Ringold G. Glucocorticoids regulate expression of dihydrofolate reductase cDNA in mouse mammary tumour virus chimaeric plasmids. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):228–232. doi: 10.1038/294228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson B., Khoury G., Vande Woude G., Gruss P. Activation of SV40 genome by 72-base pair tandem repeats of Moloney sarcoma virus. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):568–572. doi: 10.1038/295568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J., Varmus H. E. A small region of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat confers glucocorticoid hormone regulation on a linked heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5866–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manservigi R., Spear P. G., Buchan A. Cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus is promoted and suppressed by different viral glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Warren R., Palmiter R. D. The mouse metallothionein-I gene is transcriptionally regulated by cadmium following transfection into human or mouse cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNearney T. A., Odell C., Holers V. M., Spear P. G., Atkinson J. P. Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins gC-1 and gC-2 bind to the third component of complement and provide protection against complement-mediated neutralization of viral infectivity. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1525–1535. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Axelman J., Beggs A. H. Effect of ageing on reactivation of the human X-linked HPRT locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):93–96. doi: 10.1038/335093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Heber A., Schmid W., Danesch U., Posseckert G., Beato M., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the transcriptional enhancer of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble A. G., Lee G. T., Sprague R., Parish M. L., Spear P. G. Anti-gD monoclonal antibodies inhibit cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):218–224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90409-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrop J. P., Danielsen M., Ringold G. M. Analysis of glucocorticoid unresponsive cell variants using a mouse glucocorticoid receptor complementary DNA clone. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11064–11070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachl C., Burke R. L., Stuve L. L., Sanchez-Pescador L., Van Nest G., Masiarz F., Dina D. Expression of cell-associated and secreted forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein gB in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):315–325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.315-325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Ringold G. M. Use of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat to promote steroid-inducible expression of v-mos. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):420–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.420-430.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raptis L., Lamfrom H., Benjamin T. L. Regulation of cellular phenotype and expression of polyomavirus middle T antigen in rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2476–2486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal K. L., Smiley J. R., South S., Johnson D. C. Cells expressing herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gC but not gB, gD, or gE are recognized by murine virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2438–2447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2438-2447.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Morse L. S., Knipe D. M., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. II. Mapping of the major viral glycoproteins and of the genetic loci specifying the social behavior of infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):677–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.677-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorderet D. F., Keitges E. A., Dubois P. M., Gartler S. M. Inactivation and reactivation of sex-linked steroid sulfatase gene in murine cell culture. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Mar;14(2):113–121. doi: 10.1007/BF01534396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel-Dugan C., Ponce de Leon M., Friedman H. M., Fries L. F., Frank M. M., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J. C3b receptor activity on transfected cells expressing glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4027–4036. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4027-4036.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley M. L., Friedman H. M. Binding of complement component C3b to glycoprotein C is modulated by sialic acid on herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):857–861. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.857-861.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H. K., Courtney R. J. Inducible expression of herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein gene gG-2 in a mammalian cell line. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3668–3674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3668-3674.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Galleshaw J. A., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome of a murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. H., Seidman J. G. The expression of major histocompatibility antigens under metallothionein gene promoter control. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1999–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurm F. M., Gwinn K. A., Kingston R. E. Inducible overproduction of the mouse c-myc protein in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Hoorn F. A., Hulsebos E., Berns A. J., Bloemers H. P. Molecularly cloned c-mos(rat) is biologically active. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1313–1317. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Hoorn F. A., Müller V. Differential transformation of C3H10T1/2 cells by v-mos: sequential expression of transformation parameters. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2204–2211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]