Abstract
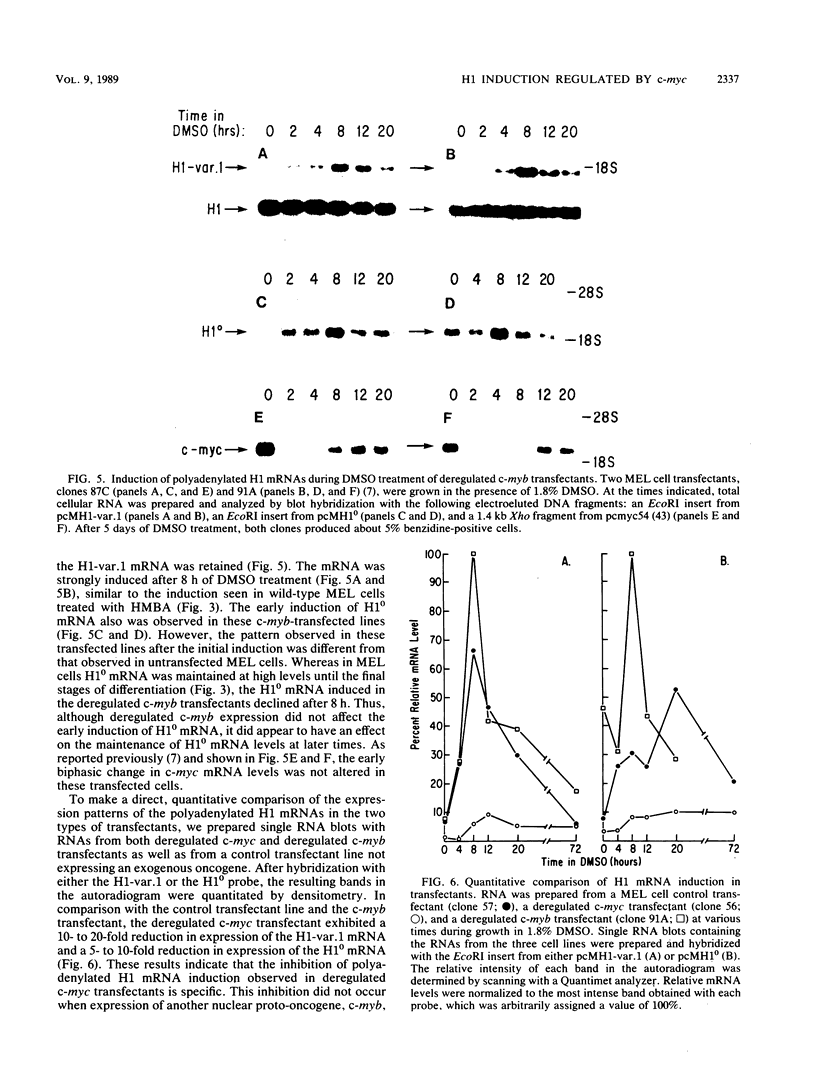
Chemically induced differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells is a multistep process involving a precommitment period in which exposure to inducer leads to cells that are irreversibly committed to terminal differentiation. Certain changes in the expression of cellular proto-oncogenes are an important feature of the precommitment phase. We have identified two H1 histone genes that are rapidly induced during this period. Unlike most histone genes, these two H1 genes encode polyadenylated mRNAs with long 3' untranslated regions. To investigate the relationship between induction of the H1 mRNAs and changes in proto-oncogene expression, we studied two independent series of mouse erythroleukemia cell lines that are inhibited from differentiating because of deregulated expression of transfected copies of c-myc or c-myb. The results showed that induction of the H1 mRNAs was negatively regulated by c-myc. The two H1 histone genes are among the first examples of specific cellular genes that are regulated by c-myc. The timing of their induction suggests that they may play an important role in achieving commitment to terminal differentiation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Nuclear location of the putative transforming protein of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):427–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Pfeifer S. O., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Identification of nuclear proteins encoded by viral and cellular myc oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):274–277. doi: 10.1038/306274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso A., Breuer B., Bouterfa H., Doenecke D. Early increase in histone H1(0) mRNA during differentiation of F9 cells to parietal endoderm. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3003–3008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03163.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoff S., Skoultchi A. I. X-linked control of hemoglobin production in somatic hybrids of mouse erythroleukemic cells and mouse lymphoma or bone marrow cells. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges K., Levenson R., Housman D., Cantley L. Calcium regulates the commitment of murine erythroleukemia cells to terminal erythroid differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):542–544. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. F., Kukowska-Latallo J. F., Westin E., Smith M., Prochownik E. V. Constitutive expression of a c-myb cDNA blocks Friend murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):884–892. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Cole M. D. Constitutive c-myc oncogene expression blocks mouse erythroleukaemia cell differentiation but not commitment. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):760–763. doi: 10.1038/320760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Anna J. A., Tobey R. A., Gurley L. R. Concentration-dependent effects of sodium butyrate in Chinese hamster cells: cell-cycle progression, inner-histone acetylation, histone H1 dephosphorylation, and induction of an H1-like protein. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2656–2671. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrovsky E., Kuehl W. M., Hollis G. F., Kirsch I. R., Bender T. P., Segal S. Expression of a transfected human c-myc oncogene inhibits differentiation of a mouse erythroleukaemia cell line. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):748–750. doi: 10.1038/322748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner P., Greiser-Wilke I., Moelling K. Nuclear localization and DNA binding of the transforming gene product of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):262–269. doi: 10.1038/296262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faletto D. L., Arrow A. S., Macara I. G. An early decrease in phosphatidylinositol turnover occurs on induction of Friend cell differentiation and precedes the decrease in c-myc expression. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faletto D. L., Macara I. G. The role of Ca2+ in dimethyl sulfoxide-induced differentiation of Friend erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4884–4889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Reuben R. C., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Effect of hexamethylene bisacetamide on the commitment to differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1977 Feb;37(2):440–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Scher W., Holland J. G., Sato T. Hemoglobin synthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: stimulation of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):378–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly S., Skoultchi A. I. Absolute rates of globin gene transcription and mRNA formation during differentiation of cultured mouse erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12167–12173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J., Geller R., Clarke B., Weeks V., Housman D. Commitment to erythroid differentiation by friend erythroleukemia cells: a stochastic analysis. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):221–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by v-myc and c-myc oncogenes: identification and localization in acute leukemia virus transformants and bursal lymphoma cell lines. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):789–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaddurah-Daouk R., Greene J. M., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Kingston R. E. Activation and repression of mammalian gene expression by the c-myc protein. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):347–357. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppel F., Allet B., Eisen H. Appearance of a chromatin protein during the erythroid differentiation of Friend virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):653–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Regulation of heat shock protein 70 gene expression by c-myc. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):280–282. doi: 10.1038/312280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume T. U., Takada S., Obinata M. Probability that the commitment of murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation is determined by the c-myc level. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):779–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90558-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Bella F., Zhong R., Heintz N. Cell type-specific expression of a human histone H1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2115–2118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Cheng G. H., Skoultchi A. I. Transfection of mouse erythroleukemia cells with myc sequences changes the rate of induced commitment to differentiate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6480–6484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Hatton K. S., Skoultchi A. I., Schildkraut C. L. c-myc mRNA levels in the cell cycle change in mouse erythroleukemia cells following inducer treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5323–5327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Skoultchi A. I. Expression of c-myc changes during differentiation of mouse erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):592–594. doi: 10.1038/310592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lannigan D. A., Knauf P. A. Decreased intracellular Na+ concentration is an early event in murine erythroleukemic cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7322–7324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennox R. W., Cohen L. H. The histone H1 complements of dividing and nondividing cells of the mouse. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):262–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennox R. W., Oshima R. G., Cohen L. H. The H1 histones and their interphase phosphorylated states in differentiated and undifferentiated cell lines derived from murine teratocarcinomas. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5183–5189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Erythroleukemic differentiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:419–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne H. B., Chabanas A. Kinetics of histone H10 accumulation and commitment to differentiation in murine erythroleukemia cells. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jun;152(2):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90646-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. The heterogeneity of histones. I. A quantitative analysis of calf histones in very long polyacrylamide gels. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):3972–3979. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pehrson J., Cole R. D. Histone H10 accumulates in growth-inhibited cultured cells. Nature. 1980 May 1;285(5759):43–44. doi: 10.1038/285043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Leder P. Nuclear localization and DNA binding properties of a protein expressed by human c-myc oncogene. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):718–721. doi: 10.1126/science.6463648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler C., Adolf G. R., Swetly P. Accumulation of histone H1(0) during chemically induced differentiation of murine neuroblastoma cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):329–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Kukowska J. Deregulated expression of c-myc by murine erythroleukaemia cells prevents differentiation. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):848–850. doi: 10.1038/322848a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay R. G., Ikeda K., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Changes in gene expression associated with induced differentiation of erythroleukemia: protooncogenes, globin genes, and cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6849–6853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Darnell J. E. Competition hybridization by "pre-saturation" of HeLa cell DNA. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):551–562. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Watt R., Marcu K. B. Translocation, breakage and truncated transcripts of c-myc oncogene in murine plasmacytomas. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):401–406. doi: 10.1038/303401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]