Abstract
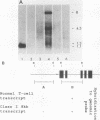
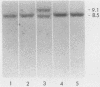
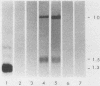
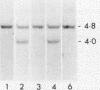
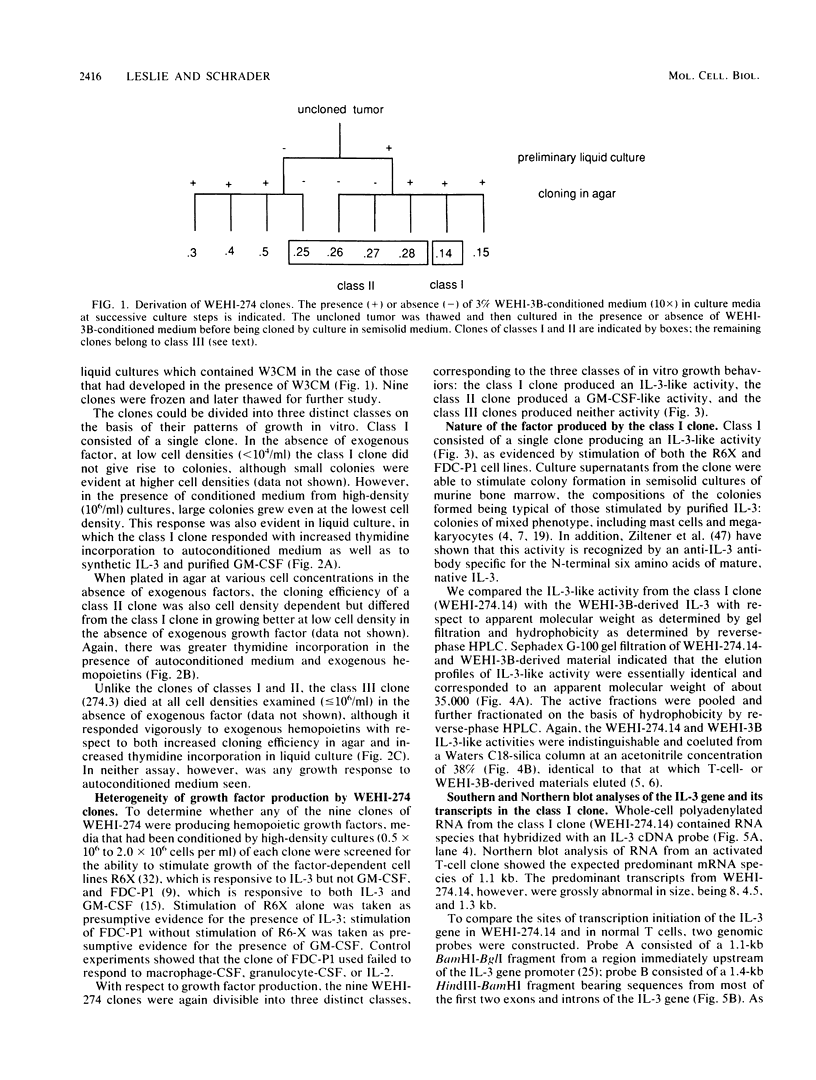
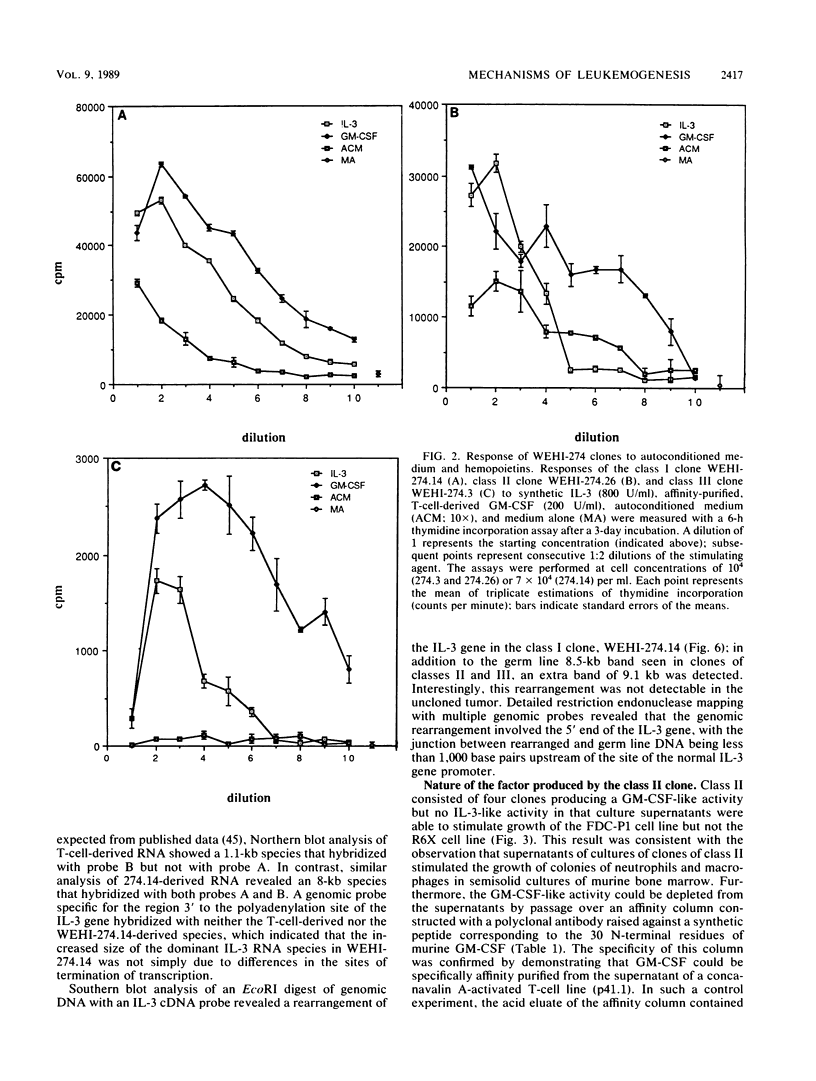
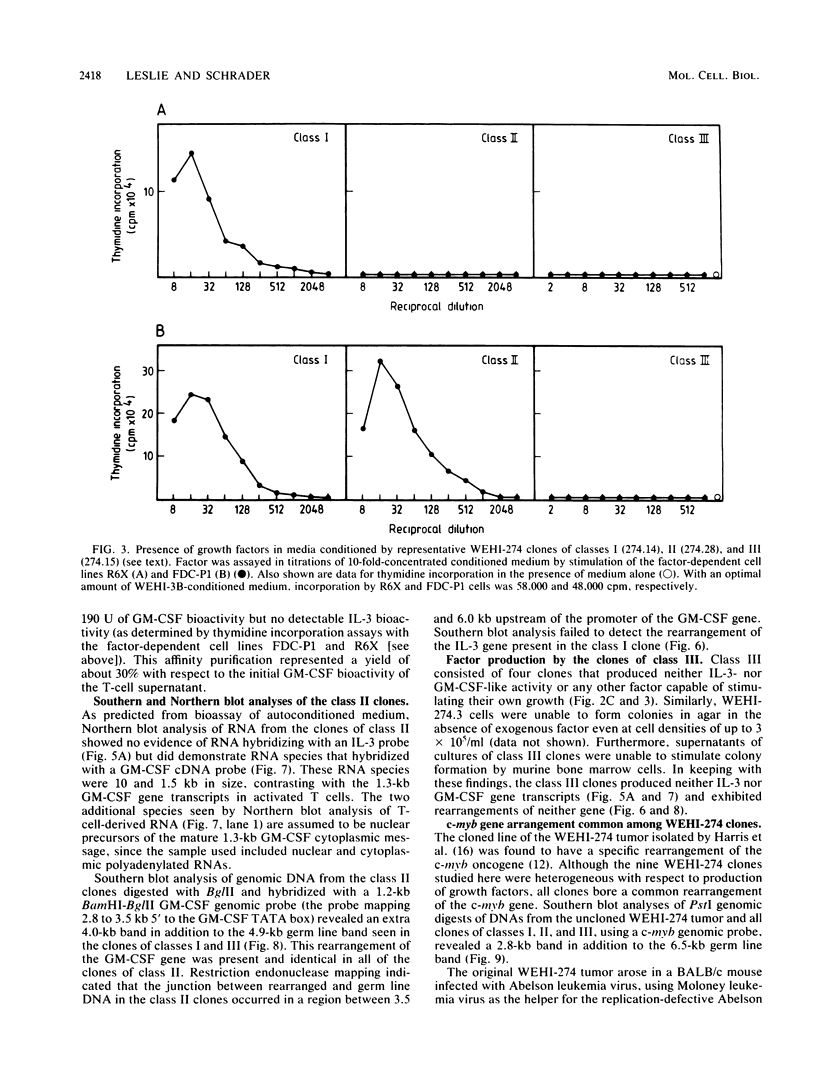
Cell lines were isolated from an in vivo-passaged myelomonocytic leukemia, WEHI-274, that arose in a mouse infected with the Abelson leukemia virus-Moloney leukemia virus complex. Clones were isolated in vitro in the presence or absence of a source of a hemopoietic growth factor, interleukin-3 (IL-3), and were divisible into three distinct classes. All three classes were leukemogenic in vivo. In vitro, the class I clone grew slowly at low cell density but responded with an increased growth rate to IL-3, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and autoconditioned medium. Supernatants of these cultures contained a factor with the biological, biochemical, and antigenic properties of IL-3. Class II clones grew better in vitro at low cell densities than did the class I clone and also responded with an increased growth rate to IL-3, GM-CSF, and autoconditional medium but produced GM-CSF rather than IL-3. In contrast, class III clones died in vitro at all cell densities unless exogenous IL-3 or GM-CSF was added. Moreover, they produced no autostimulatory factors. In the class I and class II clones, one allele of the respective IL-3 or GM-CSF gene is rearranged, and in each case, grossly abnormal RNA transcripts of the rearranged gene are present. Neither rearrangements nor abnormal RNA transcripts of the IL-3 or GM-CSF gene were detected in the class III clones. All three classes exhibited a common rearrangement of the c-myb gene, which suggested that all were derived from the one ancestral cell. These experiments demonstrate that two distinct and independent autostimulatory events were involved in the progression of a single disease.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adkins B., Leutz A., Graf T. Autocrine growth induced by src-related oncogenes in transformed chicken myeloid cells. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Hayman M. J., Graf T. Myeloblasts transformed by the avian acute leukemia virus E26 are hormone-dependent for growth and for the expression of a putative myb-containing protein, p135 E26. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1069–1073. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Kent S. B., Schrader J. W. Purification to apparent homogeneity of a factor stimulating the growth of multiple lineages of hemopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7488–7494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Schrader J. W. P cell-stimulating factor: biochemical characterization of a new T cell-derived factor. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1941–1947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Thomas W. R., Schrader J. W. Characterization of hemopoietic growth factors from T cells and the myelomonocytic leukemia WEHI-3B. Exp Hematol. 1985 May;13(4):304–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. L., Metcalf D., Nicola N. A., Johnson G. R. Purification of a multipotential colony-stimulating factor from pokeweed mitogen-stimulated mouse spleen cell conditioned medium. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6579–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Garland J., Scott D., Scolnick E., Metcalf D. Growth of factor-dependent hemopoietic precursor cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):1036–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. C., Hapel A. J., Ymer S., Cohen D. R., Johnson R. M., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Molecular cloning of cDNA for murine interleukin-3. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):233–237. doi: 10.1038/307233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Cory S., Sobieszczuk P., Holtzman D., Adams J. M. Generation of altered transcripts by retroviral insertion within the c-myb gene in two murine monocytic leukemias. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2754–2763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2754-2763.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Metcalf D., Gough J., Grail D., Dunn A. R. Structure and expression of the mRNA for murine granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):645–653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., von Weizsaecker F., Grieser S., Coll J., Stehelin D., Patschinsky T., Bister K., Bechade C., Calothy G., Leutz A. v-mil induces autocrine growth and enhanced tumorigenicity in v-myc-transformed avian macrophages. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSU T. C. Chromosomal evolution in cell populations. Int Rev Cytol. 1961;12:69–161. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60539-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapel A. J., Warren H. S., Hume D. A. Different colony-stimulating factors are detected by the "interleukin-3"-dependent cell lines FDC-Pl and 32D cl-23. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):786–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. W., Reynolds E. C., Finch L. R. Effect of thymidine on the sensitivity of cultured mouse tumor cells to 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine. Cancer Res. 1979 Feb;39(2 Pt 1):538–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibanez C. E., Lipsick J. S. Structural and functional domains of the myb oncogene: requirements for nuclear transport, myeloid transformation, and colony formation. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1981–1988. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1981-1988.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Oroszlan S., Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Fitch F., Prystowsky M. B., Goldwasser E., Schrader J. W., Palaszynski E. Biologic properties of homogeneous interleukin 3. I. Demonstration of WEHI-3 growth factor activity, mast cell growth factor activity, p cell-stimulating factor activity, colony-stimulating factor activity, and histamine-producing cell-stimulating factor activity. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laker C., Stocking C., Bergholz U., Hess N., De Lamarter J. F., Ostertag W. Autocrine stimulation after transfer of the granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene and autonomous growth are distinct but interdependent steps in the oncogenic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8458–8462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. A., Metcalf D., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., Gonda T. J. Expression of a hemopoietic growth factor cDNA in a factor-dependent cell line results in autonomous growth and tumorigenicity. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Hapel A. J., Ihle J. N. Constitutive production of a unique lymphokine (IL 3) by the WEHI-3 cell line. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2393–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Moore M. A., Warner N. L. Colony formation in vitro by myelomonocytic leukemic cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Oct;43(4):983–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Structure of the chromosomal gene for murine interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):316–320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici M. G., Moscovici C. Isolation and characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant of avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1421–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Binding of the differentiation-inducer, granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor, to responsive but not unresponsive leukemic cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3765–3769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Hunter T. The ets sequence is required for induction of erythroblastosis in chickens by avian retrovirus E26. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):398–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.398-402.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci P. G., Lanfrancone L., Brathwaite M. D., Wolman S. R., Dalla-Favera R. Amplification of the c-myb oncogene in a case of human acute myelogenous leukemia. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1117–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.6585957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Beug H., Kornfeld S., Graf T. Transformation of both erythroid and myeloid cells by E26, an avian leukemia virus that contains the myb gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Moore M. A., Nilsson K. Lysozyme synthesis by established human and murine histiocytic lymphoma cell lines. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1528–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Clark-Lewis I., Crapper R. M., Wong G. W. P-cell stimulating factor: characterization, action on multiple lineages of bone-marrow-derived cells and role in oncogenesis. Immunol Rev. 1983;76:79–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Crapper R. M. Autogenous production of a hemopoietic growth factor, persisting-cell-stimulating factor, as a mechanism for transformation of bone marrow-derived cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6892–6896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Gardinier M. Expression of a proto-oncogene (proto-myb) in hemopoietic tissues of mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1206–1212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Morse H. C., 3rd, Potter M., Mushinski J. F. Two modes of c-myb activation in virus-induced mouse myeloid tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):380–392. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):745–747. doi: 10.1038/313745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Todaro G. J. Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 9;303(15):878–880. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010093031511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. B., Smith K. A. Interleukin-2 induction of T-cell G1 progression and c-myb expression. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):203–206. doi: 10.1126/science.3523754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Expression of the c-myb proto-oncogene during cellular proliferation. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):374–380. doi: 10.1038/319374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Mermod J. J., Vassalli P. Phagocytosis and inflammatory stimuli induce GM-CSF mRNA in macrophages through posttranscriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Gallo R. C., Arya S. K., Eva A., Souza L. M., Baluda M. A., Aaronson S. A., Wong-Staal F. Differential expression of the amv gene in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2194–2198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. M., Chung S. W., Nienhuis A. W. Retroviral transfer and expression of the interleukin-3 gene in hemopoietic cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):358–365. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S., Tucker W. Q., Sanderson C. J., Hapel A. J., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Constitutive synthesis of interleukin-3 by leukaemia cell line WEHI-3B is due to retroviral insertion near the gene. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):255–258. doi: 10.1038/317255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Lee F., Rennick D., Hall C., Arai N., Mosmann T., Nabel G., Cantor H., Arai K. Isolation and characterization of a mouse cDNA clone that expresses mast-cell growth-factor activity in monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1070–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. C., Griffin J. D. Autocrine secretion of GM-CSF in acute myeloblastic leukemia. Blood. 1986 Nov;68(5):1178–1181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziltener H. J., Clark-Lewis I., Fazekas de St Groth B., Hood L. E., Kent S. B., Schrader J. W. Antipeptide antibodies define the NH2-terminal structure of the pan-specific hemopoietin interleukin 3. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1105–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]