Abstract
We generated a collection of ssrA-based C-terminal protein degradation tags with different degradation strengths. The steady-state fluorescence levels of different enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (eYFP) tag variants in a Synechocystis sp. indicated a tunable range from 1% to 50% of untagged eYFP.
TEXT
The development of cyanobacteria as platforms for bioenergy production has been hampered by the lack of available synthetic biology parts to predictively control gene transcription, translation, and the overall activity of desired pathways without compromising essential cell functions. Attempts to develop and thoroughly characterize the performance of different genetic modules in the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 (Synechocystis 6803) were only recently initiated (1). Despite these initial efforts, the majority of available synthetic parts originated from Escherichia coli and may therefore not function to their intended potential in a photosynthetic host (2). Thus, the development of a synthetic biology toolbox for cyanobacteria is crucial for use of their metabolic capacities for the production of value-added chemicals.
One key factor in controlling biological activities is the turnover rate of proteins. The SsrA-ClpX C-terminal tagging system represents an effective tool for targeted protein degradation in E. coli. In the native form, stalled proteins are cotranslationally tagged with a short peptide sequence encoded by the ssrA RNA before being released from the ribosome. This peptide tag is bound by the SspB and ClpX proteins, which associate with other proteases to degrade the tagged protein in an ATP-dependent manner. Cyanobacteria possess a comparable protein recycling system that recognizes the E. coli ClpX signaling sequence (1). In the current study, we generated various cyanobacterial and E. coli degradation tags and assayed their performance by fusing them to the reporter protein enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (eYFP) in Synechocystis 6803.
Identification and analysis of cyanobacterial degradation tags.
ssrA tag sequences were determined for 71 sequenced cyanobacterial genomes (see Table S1 in the supplemental material) (3). The ssrA sequences were identified using the ARAGORN program (4), and the consensus sequence was determined using ClustalX (5). The functional conserved motifs were similar to those previously identified in E. coli (6), with an N-terminal ANNIV motif and a C-terminal I/VAA motif (Fig. 1). The consensus sequence was used to generate tags with a broad range of degradation strengths.
Fig 1.

Consensus sequence of SsrA tags in cyanobacteria. The Synechocystis 6803 tag sequence is shown below. Spaces represent no consensus residue, and dashes represent the lack of a residue.
Construction of plasmids.
The degradation tags (Fig. 2) were cloned as C-terminal fusions to eYFP into the conjugation plasmid pPMQAK1 for expression in trans (1). Two BsaI restriction sites allowed scarless insertion of different tag sequences via the Golden Gate method (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material) (7).
Fig 2.
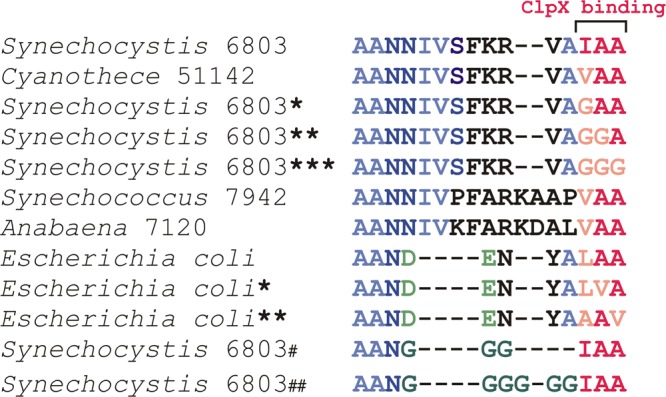
Overview of different native and modified SsrA tag sequences. *, amino acid substitution from the native tag sequence; #, tag sequence truncations and amino acid substitution.
Growth and culture conditions.
Plasmids were constructed in the XL1-Blue E. coli strain, and transformants were grown on LB agar plates with 40 μg/ml kanamycin at 37°C. Synechocystis 6803 isolates were maintained on BG-11 (8) agar plates and cultivated in liquid BG-11 supplemented with 10 μg/ml kanamycin at a light intensity of 30 μE m−2 s−1 at 30°C. Conjugative transfer of plasmids from E. coli cells to Synechocystis 6803 cells was performed as previously described (9), using pRL443 as a helper plasmid (10).
Fluorescence assay.
The different eYFP tag variants were assayed by measuring eYFP fluorescence with a Synergy Mx plate reader (Biotek Instruments) with excitation at 513 nm and emission at 532 nm. Twenty-milliliter cultures were inoculated at an optical density at 730 nm (OD730) of 0.1, supplemented with 2 mM isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), and grown for 48 h. For degradation studies, 150 μg/ml chloramphenicol was added 1 h prior to the time course experiment. Aliquots of 150 μl of the cell suspension were added to 96-well plates and grown until the OD730 reached 1.0, measured using a μQuant plate reader (Biotek Instruments). The fluorescence signal was calculated per cell.
RT-PCR analysis.
Semiquantitative reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) analysis was performed on RNA samples isolated from cultures inoculated at an OD730 of 0.1 and supplemented with 2 mM IPTG and 10 μg/ml kanamycin after 48 h of growth at a light intensity of 30 μE m−2 s−1 at 30°C. RNA was isolated and quantified as previously described (11). A total of 1 μg DNase (Promega)-treated RNA was used for reverse transcription with Superscript II reverse transcriptase and random primers (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The absence of DNA contamination was tested using RNA as the template for the PCR. PCR was carried out at 94°C for 2 min, 94°C for 30 s, annealing temperatures of 58°C (16S rRNA) or 62°C (eyfp) for 20 s, extension at 72°C for 30 s, and a final extension time of 2 min at 72°C. A total of 23 cycles were run for 16S rRNA using the primer pairs F (5′-TGTAGCGGTGAAATGCGT-3′) and R (5′-AGGTTCTTCGCGTTGCAT-3′), and 26 cycles were conducted for eyfp using the primer pair F (5′-ACGTAAACGGCCACAAGTTCA-3′) and R (5′-TTGTAGTTGCCGTCGTCCTT-3′).
Fluorescence measurements.
Sequence analysis of 71 cyanobacterial genomes revealed that the majority of cyanobacterial species (80%), including Cyanothece sp. strain 51142, Anabaena sp. strain 7120, and Synechococcus sp. strain 7942, contain a hydrophobic Val-Ala-Ala motif at the C terminus of the SsrA tag (Fig. 1). In Synechocystis 6803 and E. coli, this Val residue is replaced by Ile and Leu, respectively (Fig. 1 and 2). We generated a collection of SsrA tags in Synechocystis 6803 by replacing one, two, or all three amino acids in this motif with a hydrophobic Gly residue to modify binding of ClpX to the C terminus (Fig. 2). The different SsrA tag variants were C-terminally fused to eYFP, and steady-state fluorescence of accumulated eYFP was determined at levels ranging from <1% to 50% of untagged eYFP (Fig. 3A). RT-PCR analysis showed that the corresponding eyfp transcripts were present in near-equal amounts in all Synechocystis 6803 eYFP variants (Fig. 3B). The Synechocystis 6803 eYFP tags with single and double substitutions showed fluorescence signals not significantly different from that of wild type, whereas the triple substitution considerably compromised the performance of the tag (Fig. 3A). These results are in agreement with those of previous studies in E. coli, which showed that targeted replacement of Ala residues at the C terminus weakens ClpX binding and reduces degradation efficiency (12). Two additional degradation tags with either three or six Gly repeats replacing the less-conserved central part of the SsrA tag were also tested, and they revealed steady-state fluorescence levels of about 40% and 50% compared to that of untagged eYFP (Fig. 2 and 3A).
Fig 3.
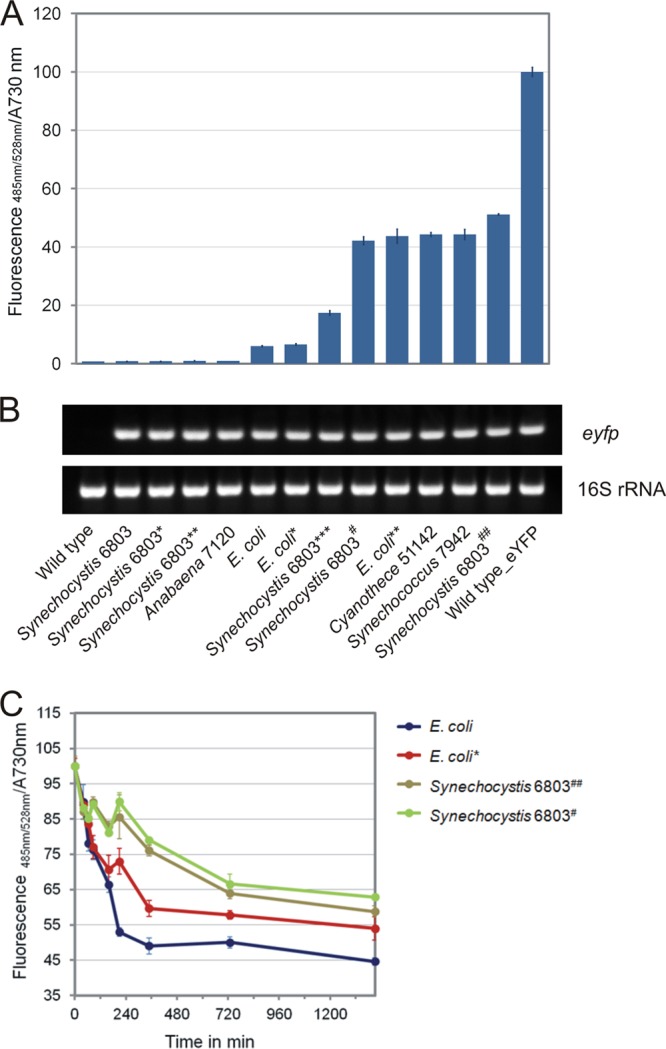
(A and B) Steady-state fluorescence (A) and transcript level measurements (B) of different eYFP constructs expressed in Synechocystis 6803. 16S rRNA was used as a loading control. (C) Stability of different SsrA-eYFP variants in Synechocystis 6803 after addition of chloramphenicol.
In contrast, the native SsrA tag from Anabaena 7120 performed similarly to that of wild-type Synechocystis 6803, while the degradation tag sequences from Cyanothece 51142 and Synechococcus 7942 were less effective (Fig. 3A). Consistent with previous observations (1), we found that native and modified E. coli tags resulted in steady-state eYFP levels ranging from 5% to 42% of untagged eYFP. Degradation studies using different tag variants showed that the differences in steady-state fluorescence levels were due to variations in degradation efficiencies (Fig. 3C). Although the degradation tags generated in this study have only been tested using eYFP as the reporter protein, previous work utilizing SsrA tags in E. coli (13), with a similar fluorescent protein, have shown these tags to be widely applicable.
We have demonstrated the use of the native protein degradation machinery in Synechocystis 6803 to achieve targeted protein turnover at levels much higher than previously demonstrated with nonnative tags (1). Additionally, a variety of degradation tags were developed to fine-tune protein levels and protein turnover times. This technology allows the generation of more complex metabolic systems that have the potential to oscillate in step with circadian rhythms in cyanobacteria, similar to the metabolator in E. coli (14). This study contributes to the development of synthetic biology devices to effectively manipulate protein levels in a model cyanobacterial host.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank all members of the Pakrasi lab for collegial discussions.
This research was supported by funding from the Office of Science (BER), U.S. Department of Energy.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 8 February 2013
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03741-12.
REFERENCES
- 1. Huang HH, Camsund D, Lindblad P, Heidorn T. 2010. Design and characterization of molecular tools for a synthetic biology approach towards developing cyanobacterial biotechnology. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:2577–2593 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Ng WO, Pakrasi HB. 2001. DNA photolyase homologs are the major UV resistance factors in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Mol. Gen. Genet. 264:924–930 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Markowitz VM, Chen IM, Palaniappan K, Chu K, Szeto E, Grechkin Y, Ratner A, Jacob B, Huang J, Williams P, Huntemann M, Anderson I, Mavromatis K, Ivanova NN, Kyrpides NC. 2012. IMG: the Integrated Microbial Genomes database and comparative analysis system. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D115–D122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Laslett D, Canback B. 2004. ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:11–16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG. 2007. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Flynn JM, Levchenko I, Seidel M, Wickner SH, Sauer RT, Baker TA. 2001. Overlapping recognition determinants within the ssrA degradation tag allow modulation of proteolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98:10584–10589 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Engler C, Kandzia R, Marillonnet S. 2008. A one pot, one step, precision cloning method with high throughput capability. PLoS One 3:e3647 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Allen MM. 1968. Simple conditions for growth of unicellular blue-green algae on plates. J. Phycol. 4:1–4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Tsinoremas NF, Kutach AK, Strayer CA, Golden SS. 1994. Efficient gene transfer in Synechococcus sp. strains PCC 7942 and PCC 6301 by interspecies conjugation and chromosomal recombination. J. Bacteriol. 176:6764–6768 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Elhai J, Wolk CP. 1988. Conjugal transfer of DNA to cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol. 167:747–754 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Stockel J, Welsh EA, Liberton M, Kunnvakkam R, Aurora R, Pakrasi HB. 2008. Global transcriptomic analysis of Cyanothece 51142 reveals robust diurnal oscillation of central metabolic processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105:6156–6161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. McGinness KE, Baker TA, Sauer RT. 2006. Engineering controllable protein degradation. Mol. Cell 22:701–707 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Andersen JB, Sternberg C, Poulsen LK, Bjørn SP, Givskov M, Molin S. 1998. New unstable variants of green fluorescent protein for studies of transient gene expression in bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64:2240–2246 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Fung E, Wong WW, Suen JK, Bulter T, Lee S, Liao JC. 2005. A synthetic gene-metabolic oscillator. Nature 435:118–122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


