Abstract
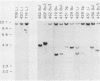
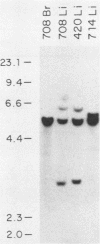
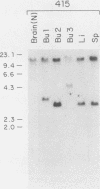
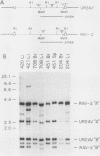
We have examined avian leukosis virus-induced B-cell lymphomas for multiple, stage-specific oncogene activations. Three targets for viral integration were identified: c-myb, c-myc, and a newly identified locus termed c-bic. The c-myb and c-myc genes were associated with different lymphoma phenotypes. The c-bic locus was a target for integration in one class of lymphomas, usually in conjunction with c-myc activation. The data indicate that c-myc and c-bic may act synergistically during lymphomagenesis and that c-bic is involved in late stages of tumor progression.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Harris A. W., Pinkert C. A., Corcoran L. M., Alexander W. S., Cory S., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):533–538. doi: 10.1038/318533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba T. W., Humphries E. H. Formation of a transformed follicle is necessary but not sufficient for development of an avian leukosis virus-induced lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):213–216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach W. R., Keath E. J., Cole M. D. A mouse c-myc retrovirus transforms established fibroblast lines in vitro and induces monocyte-macrophage tumors in vivo. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):276–283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.276-283.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewert D. L., de Boer G. F. Avian lymphoid leukosis: mechanisms of lymphomagenesis. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1988;32:37–55. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-039232-2.50006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Orientation and position of avian leukosis virus DNA relative to the cellular oncogene c-myc in B-lymphoma tumors of highly susceptible 15I5 X 7(2) chickens. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):742–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.742-746.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Fadly A. M., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. On the mechanism of retrovirus-induced avian lymphoid leukosis: deletion and integration of the proviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3418–3422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow M. M., Hayward W. S. 5' long terminal repeats of myc-associated proviruses appear structurally intact but are functionally impaired in tumors induced by avian leukosis viruses. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2489–2498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2489-2498.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., von Weizsaecker F., Grieser S., Coll J., Stehelin D., Patschinsky T., Bister K., Bechade C., Calothy G., Leutz A. v-mil induces autocrine growth and enhanced tumorigenicity in v-myc-transformed avian macrophages. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanter M. R., Smith R. E., Hayward W. S. Rapid induction of B-cell lymphomas: insertional activation of c-myb by avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1423–1432. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1423-1432.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucenski M. L., Gilbert D. J., Taylor B. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Common sites of viral integration in lymphomas arising in AKXD recombinant inbred mouse strains. Oncogene Res. 1987;2(1):33–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Hayward W. S., Robinson H. L., Fang J., Astrin S. M. Avian leukosis virus-induced tumors have common proviral integration sites and synthesize discrete new RNAs: oncogenesis by promoter insertion. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P., Wolf C., Enrietto P. J., Cooper G. M. A retroviral myc gene induces preneoplastic transformation of lymphocytes in a bursal transplantation assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):222–226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P., Leder A., Kuo A., Stewart T., Leder P. Lymphohematopoietic and other malignant neoplasms occurring spontaneously in transgenic mice carrying and expressing MTV/myc fusion genes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;132:9–16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71562-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Multiple arrangements of viral DNA and an activated host oncogene in bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):209–214. doi: 10.1038/295209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Courtneidge S. A., Crittenden L. B., Fadly A. M., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Analysis of avian leukosis virus DNA and RNA in bursal tumours: viral gene expression is not required for maintenance of the tumor state. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud C. A., Anquez V., Dahan A., Weill J. C. A single rearrangement event generates most of the chicken immunoglobulin light chain diversity. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90142-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Gagnon G. C. Patterns of proviral insertion and deletion in avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.28-36.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Berns A. Proviral activation of the putative oncogene Pim-1 in MuLV induced T-cell lymphomas. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1793–1798. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Neckameyer W. S., Hayward W. S., Smith R. E. Genetic determinants of neoplastic diseases induced by a subgroup F avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1203–1212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1203-1212.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Smith R. E., Hayward W. S. Mechanisms of oncogenesis by subgroup F avian leukosis viruses. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.1-8.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Pattengale P. K., Leder P. Spontaneous mammary adenocarcinomas in transgenic mice that carry and express MTV/myc fusion genes. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift R. A., Boerkoel C., Ridgway A., Fujita D. J., Dodgson J. B., Kung H. J. B-lymphoma induction by reticuloendotheliosis virus: characterization of a mutated chicken syncytial virus provirus involved in c-myc activation. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2084–2090. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2084-2090.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Humphries E. H., Carlson L. M., Chen C. L., Neiman P. E. The effect of alterations in myc gene expression on B cell development in the bursa of Fabricius. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):371–381. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90633-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Lohse M. A. Concerted DNA rearrangements in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced thymomas: a potential synergistic relationship in oncogenesis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.258-267.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weill J. C., Leibowitch M., Reynaud C. A. Questioning the role of the embryonic bursa in the molecular differentiation of B lymphocytes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1987;135:111–124. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71851-9_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]