Abstract
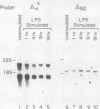
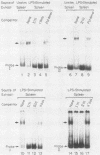
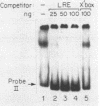
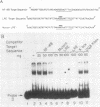
Class II (Ia) major histocompatibility complex molecules are cell surface proteins normally expressed by a limited subset of cells of the immune system. These molecules regulate the activation of T cells and are required for the presentation of antigens and the initiation of immune responses. The expression of Ia in B cells is determined by both the developmental stage of the B cell and by certain external stimuli. It has been demonstrated previously that treatment of B cells with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) results in increased surface expression of Ia protein. However, we have confirmed that LPS treatment results in a significant decrease in mRNA encoding the Ia proteins which persists for at least 18 h. Within the upstream regulatory region of A alpha k, an NF-kappa B-like binding site is present. We have identified an LPS-induced DNA-binding protein in extracts from athymic mice whose spleens consist predominantly of B cells. Binding activity is present in low levels in unstimulated spleen cells and is increased by LPS treatment. This protein binds to two sites in a regulatory region of the Ia A alpha k gene, one of which contains the NF-kappa B-like binding site. DNA fragments containing these sites cross-compete for protein binding. Analysis by DNase I footprinting identified a target binding sequence, named the LPS-responsive element. Although this target sequence contains an NF-kappa B-like binding site, competition with a mutant oligonucleotide demonstrated that bases critical for NF-kappa B binding are not required for binding of the LPS-inducible protein. Therefore, we hypothesized that this inducible protein represents a new mediator of LPS action, distinct from NF-kappa B, and may be one mechanism to account for the decrease in mRNA encoding the Ia proteins.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerblom I. E., Slater E. P., Beato M., Baxter J. D., Mellon P. L. Negative regulation by glucocorticoids through interference with a cAMP responsive enhancer. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):350–353. doi: 10.1126/science.2838908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Two transcription factors, NF-kappa B and H2TF1, interact with a single regulatory sequence in the class I major histocompatibility complex promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis A., Superti-Furga G., Busslinger M. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothby M., Gravallese E., Liou H. C., Glimcher L. H. A DNA binding protein regulated by IL-4 and by differentiation in B cells. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1559–1562. doi: 10.1126/science.3144043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothby M., Liou H. C., Glimcher L. H. Differences in DNA sequence specificity among MHC class II X box binding proteins. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):1005–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis G. J., Mizuguchi J., McMillan V., Finkelman F. D., Ohara J., Mond J. J. Comparison of the calcium requirement for the induction and maintenance of B cell class II molecule expression and for B cell proliferation stimulated by mitogens and purified growth factors. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4307–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Durand B., Marfing C., Le Meur M., Benoist C., Mathis D. Conserved major histocompatibility complex class II boxes--X and Y--are transcriptional control elements and specifically bind nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6249–6253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Fehling H. J., Koch W., Le Meur M., Gerlinger P., Benoist C., Mathis D. B-cell control region at the 5' end of a major histocompatibility complex class II gene: sequences and factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):3975–3987. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Bhattacharya A., Dorf M. E., Springer T. A. A single monoclonal anti-Ia antibody inhibits antigen-specific T cell proliferation controlled by distinct Ir genes mapping in different H-2 I subregions. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1409–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Malissen B. Analysis of the expression and function of class-II major histocompatibility complex-encoded molecules by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:281–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. The thyroid hormone receptor binds with opposite transcriptional effects to a common sequence motif in thyroid hormone and estrogen response elements. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goroff D. K., Stall A., Mond J. J., Finkelman F. D. In vitro and in vivo B lymphocyte-activating properties of monoclonal anti-delta antibodies. I. Determinants of B lymphocyte-activating properties. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2382–2392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halper J., Fu S. M., Wang C. Y., Winchester R., Kunkel H. G. Patterns of expression of human "Ia-like" antigens during the terminal stages of B cell development. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1480–1484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S. Footprinting DNA-protein complexes in situ following gel retardation assays using 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lac promoter complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7234–7238. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis L. A., Glimcher L. H., Paul W. E., Schwartz R. H. Magnitude of response of histocompatibility-restricted T-cell clones is a function of the product of the concentrations of antigen and Ia molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6019–6023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan V. M., Dennis G. J., Glimcher L. H., Finkelman F. D., Mond J. J. Corticosteroid induction of Ig+Ia- B cells in vitro is mediated via interaction with the glucocorticoid cytoplasmic receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2549–2555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Seghal E., Kung J., Finkelman F. D. Increased expression of I-region-associated antigen (Ia) on B cells after cross-linking of surface immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):881–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. G., Cambier J. C. Level of mIa expression on mitogen-stimulated murine B lymphocytes is dependent on position in cell cycle. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):626–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Bacterial endotoxins and host immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:293–450. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60802-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen H. T., Medford R. M., Nadal-Ginard B. Reversibility of muscle differentiation in the absence of commitment: analysis of a myogenic cell line temperature-sensitive for commitment. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noelle R. J., Kuziel W. A., Maliszewski C. R., McAdams E., Vitetta E. S., Tucker P. W. Regulation of the expression of multiple class II genes in murine B cells by B cell stimulatory factor-1 (BSF-1). J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1718–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noelle R., Krammer P. H., Ohara J., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. Increased expression of Ia antigens on resting B cells: an additional role for B-cell growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6149–6153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne T. F., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. 5' end of HMG CoA reductase gene contains sequences responsible for cholesterol-mediated inhibition of transcription. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):203–212. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polla B. S., Ohara J., Paul W. E., Nabavi N., Myer A., Liou H. C., Shen F. W., Gillis S., Bonventre J. V., Glimcher L. H. Differential induction of class II gene expression in murine pre-B-cell lines by B-cell stimulatory factor-1 and by antibodies to B-cell surface antigens. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1988;3(6):363–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polla B. S., Poljak A., Geier S. G., Nathenson S. G., Ohara J., Paul W. E., Glimcher L. H. Three distinct signals can induce class II gene expression in a murine pre-B-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4878–4882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polla B. S., Poljak A., Ohara J., Paul W. E., Glimcher L. H. Regulation of class II gene expression: analysis in B cell stimulatory factor 1-inducible murine pre-B cell lines. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3332–3337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Harth N., Eades A. M., Litfin M., Steinmetz M., Forni L., Herrlich P. Interferon-gamma, mitomycin C, and cycloheximide as regulatory agents of MHC class II-associated invariant chain expression. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2293–2299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. T-lymphocyte recognition of antigen in association with gene products of the major histocompatibility complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:237–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkewitz A. P., Sullivan C. P., Mescher M. F. Large-scale purification of murine I-Ak and I-Ek antigens and characterization of the purified proteins. Mol Immunol. 1983 Nov;20(11):1139–1147. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner F. R., Czaja M. J., Jefferson D. M., Giambrone M. A., Tur-Kaspa R., Reid L. M., Zern M. A. The effects of dexamethasone on in vitro collagen gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6955–6958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]