Abstract
We hypothesized that parents of infants prefer growth at higher percentiles and are averse to growth at lower percentiles. Of 279 participating parents, only 10% desired their child’s weight to be in the lowest quartile. For children weighing in the lowest quartile, 57% of parents thought their child’s weight was “too low.” In contrast, 66% of parents whose child’s weight was in the top quartile preferred their child weigh that much. When viewing hypothetical infant growth trajectories, 47% ranked a growth chart demonstrating growth along the 10th percentile for weight as “least healthy” of 6 growth patterns, and 29% chose charts showing an infant at the 90th percentile for weight at age 1 as “healthiest.” In conclusion, parents are averse to growth at the bottom of the weight growth chart but are much less likely to feel negatively about growth at higher percentiles. This is troubling given the childhood obesity epidemic.
Keywords: infant, growth, growth chart, obesity
Introduction
The World Health Organization recently estimated that 22 million children below the age of 5 are overweight.1 In the United States, 1 in every 4 children between ages 2 and 5 are either overweight or obese.2 Because infancy is a time of rapid growth for cells and tissues, including adipocytes, overnutrition during this crucial period may lead to future obesity.3 Numerous reports support this concept as the relationship between growth during infancy and subsequent weight later during childhood and adult life is well established.4–7
It is the responsibility of health care providers to communicate child weight status, discuss healthy patterns of growth, and explain infant growth charts at health maintenance visits. Most often, however, parents are given their child’s growth chart information with little, if any, explanation. During infancy, physicians are more likely to raise concerns over slower growth and downward crossing of weight-for-age percentile lines than they are for rapid growth with upward crossing of percentile lines. Additionally, although in nearly every life circumstance scoring high on a percentile ranking is desirable and lower percentiles are undesirable, such values related to weight status should be interpreted differently, but parents may not understand this unique circumstance.
Because infant overweight and rapid weight gain during infancy are both associated with later obesity,8–11 parental interpretation of infant growth requires further study. Therefore, we sought to determine parent preferences for weight percentiles and how these preferences relate to their child’s actual weight percentile. Additionally, we aimed to assess parent perceptions of weight-for-age growth chart appearance for infants up to 1 year of age. We hypothesized that parents would prefer their children to be above the 50th percentile for weight and that weight in the lowest quartile would be perceived negatively. Regarding parent perception of weight-for-age growth charts, we hypothesized that parents would prefer their infants to be at higher percentiles and not growing along curves near the bottom of the growth chart.
Methods
Participants
A convenience sample of 279 parent–child pairs attending a single pediatric outpatient office (Penn State Hershey Pediatrics, Hershey, PA) were recruited for this study. Eligible participants were parent–child pairs presenting for the child’s health maintenance visits when the children were between 6 and 27 months of age. Information about parental age, sex, education, and self-reported race and ethnicity were collected. Infant sex was also recorded. This study was approved by the Human Subjects Protection Office of the Penn State College of Medicine.
Data Collection
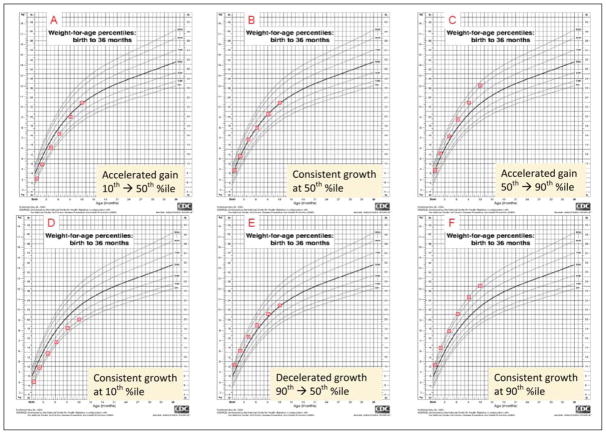
After weight and length measurements were obtained by clinic nurses, plotted on the child’s clinic growth chart from the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention,12 and reported to parents, the parents were asked a series of questions regarding children’s weights and growth charts. First, they were asked whether they felt that their child’s weight was much too low, low, just right, high, or much too high. Parents then chose the weight percentile range in which they preferred their child to fall (<10th percentile, 10th to 25th, 25th to 50th, 50th to 75th, 75th to 90th, or >90th percentile). They were then shown a composite of 6 weight-for-age growth curves (Figure 1). Each chart illustrated different patterns of weight gain between birth and 1 year of age. Three of the charts showed consistent growth along a percentile curve (10th, 50th, 90th), 2 displayed upward crossing of major percentile lines (10th to 50th, 50th to 90th), and 1 had downward crossing of percentile lines (90th to 50th). Parents were asked to rank these curves from “healthiest” to “least healthy.”
Figure 1.
Growth chart choices for parents to rank from “healthiest” to “least healthy”
Data Analysis
Demographic comparisons between quartiles of child’s weight-for-age percentile were made using χ2 tests or Fisher’s exact tests as needed for categorical characteristics and Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient for continuous characteristics. Logistic regression was used to test contrasts of quartiles of child’s weight-for-age percentile. Mantel-Haenszel χ2 tests were used to compare quartiles of child’s weight-for-age percentile with respect to parent’s feeling about child’s weight-for-age percentile and parent’s preference for child’s weight-for-age percentile.
Results
Of the 279 participating parents, 238 (87.2%) were self-described as white, most were female, and the mean parental age was 30.3 years (Table 1). Of the participating parents, 72.1% had at least some college or technical school training. For the children, there was an even distribution between male (n = 139) and female (n = 140) children, and a relatively even distribution of children at each age where health maintenance visits occur between 6 months and 2 years of age. The median weight-for-age percentile for children was 45.
Table 1.
Demographics of Study Parents and Their Children (N = 279)
| Characteristic | |
|---|---|
| Parent characteristics | |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Female | 239 (85.7) |
| Male | 40 (14.3) |
| Age (years), mean ± standard deviation | 30.3±6.5 |
| Hispanic ethnicity, n (%) | 22 (7.9) |
| Race, N (%) | |
| White | 238 (87.2) |
| Black | 19 (7.0) |
| Asian | 14 (5.1) |
| Other | 2 (0.7) |
| Education, n (%) | |
| Eighth grade or less | 1 (0.4) |
| Some high school | 13 (4.7) |
| High school graduate | 64 (22.9) |
| Some college/technical school | 68 (24.4) |
| College graduate | 85 (30.5) |
| Postgraduate training/degree | 48 (17.2) |
| Child characteristics | |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Female | 140 (50.2) |
| Male | 139 (49.8) |
| Age at health maintenance visit, n (%) | |
| 6–8 Months | 53 (19.2) |
| 9–11 Months | 54 (19.6) |
| 12–14 Months | 49 (17.68) |
| 15–17 Months | 47 (17.0) |
| 18–23 Months | 36 (13.0) |
| 24 to <27 Months | 37 (13.4) |
| Weight-for-age perecentile, median (intraquartile range) | 45 (20–73) |
Perception of Current Weight
When asked about their child’s current weight, for the entire cohort, 200 of 279 (71.7%) parents felt their child’s weight was “just right” (Table 2). However, significant differences existed depending on the child’s current weight percentile. Whereas the vast majority of parents whose children weighed between the 25th and 75th percentile and greater than the 75th percentile thought their child’s weight was just right, less than half of those whose children were in the lowest quartile for weight felt the same (P<.0001). Instead, the majority of those whose children were in the lowest quartile felt that their child’s weight was low or much too low, whereas very few with children weighing in the middle or highest quartiles answered this way (P<.0001). In contrast to the dissatisfaction regarding their child’s weight for parents of lighter children, only 21.2% of parents whose child weighed in the highest quartile felt that their child’s weight was “too high.”
Table 2.
Parent Impression of Their Own Child’s Weight and Desired Weight Percentile Range
| Entire Cohort, N = 279 | Children <25th Percentile, n = 83 | Children 25th to 75th Percentile, n = 144 | Children >75th Percentile, n = 52 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parent’s feeling about child’s weight, n (%) | <.0001 | ||||
| Much too low | 6 (2.2) | 5 (6.0) | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0) | |
| Low | 60 (21.5) | 42 (50.6) | 17 (11.8) | 1 (1.9) | |
| Just right | 200 (71.7) | 36 (43.4) | 124 (86.1) | 40 (76.9) | |
| High | 13 (4.7) | 0 (0) | 2 (1.4) | 11 (21.2) | |
| Much too high | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Parent preference for child’s weight-for-age percentilea | <.0001 | ||||
| <10th | 4 (1.4) | 4 (4.9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| 10th to 24th | 25 (9.0) | 23 (28.4) | 2 (1.4) | 0 (0) | |
| 25th to 49th | 67 (24.2) | 28 (34.6) | 38 (26.4) | 1 (1.9) | |
| 50th to 74th | 122 (44.0) | 20 (24.7) | 85 (59.0) | 17 (32.7) | |
| 75th to 90th | 48 (17.3) | 6 (7.4) | 19 (13.2) | 23 (44.2) | |
| ≥90th | 11 (4.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 11 (21.2) | |
| Parent choice as “least healthy” growth chartb | .84 | ||||
| A | 14 (5.2) | 5 (6.3) | 7 (5.0) | 2 (4.1) | |
| B | 2 (0.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.7) | 1 (2.0) | |
| C | 42 (15.7) | 12 (15.0) | 21 (15.1) | 9 (18.4) | |
| D | 125 (46.6) | 32 (40.0) | 69 (49.6) | 24 (49.0) | |
| E | 27 (10.1) | 9 (11.3) | 13 (9.4) | 5 (10.2) | |
| F | 58 (21.6) | 22 (27.5) | 28 (20.1) | 8 (16.3) | |
| Parent choiceas “healthiest” growth chartc | .35 | ||||
| A | 7 (2.6) | 2 (2.4) | 5 (3.6) | 0 (0) | |
| B | 154 (57.3) | 52 (63.4) | 78 (56.6) | 24 (49.0) | |
| C | 26 (9.7) | 5 (6.1) | 15 (10.9) | 6 (12.2) | |
| D | 10 (3.7) | 6 (7.3) | 3 (2.2) | 1 (2.0) | |
| E | 20 (7.4) | 4 (4.9) | 11 (8.0) | 5 (10.2) | |
| F | 52 (19.3) | 13 (15.9) | 26 (18.8) | 13 (26.5) |
2 Participants did not answer this question.
11 Participants did not answer this question.
10 Participants did not answer this question.
Desired Weight Percentile Range
Regarding parents’ desired weight percentile range for their child, only 10% of parents desired their child’s weight to be in the lowest quartile, whereas 21% desired their child’s weight be in the highest quartile. These preferences were related to the child’s actual weight-forage percentile (P < .0001). Of parents whose child’s actual weight was in the highest quartile, 65.7% preferred their child’s weight to be in that range. In contrast, for parents of children in the lower 3 quartiles, only 11.0% desired their child’s weight to be in the top quartile range. Parental preference for higher weight-for-age percentile was associated with not having a college education (P = .04) but not with the child’s sex, race, ethnicity, or age at the visit.
Growth Chart Preference
When parents were asked to rank their preferences for the 6 patterns of growth seen in the figure, nearly half ranked the growth chart demonstrating consistent growth along the 10th percentile as the “least healthy” choice making it the lowest ranked choice overall. Parents without any college education were more likely to rank this choice as the “least healthy” option (P = .03), but no other demographic variable was associated with their choice. As for parents’ views of the healthiest growth pattern, 57% chose the chart with steady growth along the 50th percentile, and 29% chose either growth chart C or F (each with weights at the 90th percentile at age 1 year). For these rankings, significant differences were associated with the child’s weight status (P = .03). Specifically, whereas only about 25% of parents with children whose weight-for-age was less than the 75th percentile chose charts ending at the 90th percentile as the most preferred, that pattern was chosen by nearly 40% of parents with children in the top weight-for-age quartile.
Discussion
During the first 2 years after birth, growth charts are typically used by health care providers to ensure adequate and proportional growth with respect to weight, length, and head circumference, but information is usually communicated to parents without significant explanation so long as the child does not (a) raise concern for failure to thrive or (b) demonstrate disproportionate or very excessive growth on 1 of the 3 measurements. The results of this study suggest that improved communication between health care providers and parents about normal infant growth is necessary. These data suggest that many parents are averse to their children growing in the lowest quartile for weight. In contrast, many parents have a preference for their child’s weight to show progression toward the higher percentiles on the growth chart despite evidence that during infancy, weight in the higher percentiles and rapid patterns of growth elevate the risk for obesity and its comorbidi-ties.4–7,13–23 Parents’ bias in favor of higher percentiles may reflect their response to the use of percentiles as a way of presenting their infant’s growth relative to others because in nearly every other life circumstance, higher percentiles are better, as for example, in the case of academic achievement.
Overall, parents tended to have negative perceptions of patterns of early life growth in the lower percentiles. These negative perceptions may have negative consequences; parents who perceive their children as too thin are more likely to pressure them into eating.24 This hinders children’s ability to recognize internal cues for hunger and satiety.25 Furthermore, parents often perceive their children as picky eaters even when their weight gain is progressing normally,26 and infants and children perceived as too small are often given developmentally inappropriate nutrition, including the early introduction of solids and/or table foods.27,28 This, combined with findings that parents tend to underestimate rather than overestimate their child’s weight, might create a major obesogenic force.17,29–35
Many parents believe that greater infant weight is an indicator of good infant health and higher levels of parenting competence.27,28,36–40 Furthermore, parents may not value their child’s weight status as a health indicator but, rather, may refer to their ability to perform activities accomplished by their peers or the lack of chronic medical illness.41 Whereas in the past these findings have been shown in low-income or minority populations where there is often an association of food with love,42 the current results show general preferences for higher weight infants in a mostly white, well-educated, middle class community.
The results of this study are limited by several factors. First, the participants were from a single, suburban, outpatient office, and the population was homogeneous, with limited minority group representation. This is important to note because ethnicity has been demonstrated to play a significant role in parental assessment of child weight status.27,28,40,42 Nonetheless, the current data suggest that the phenomenon of “more is better” regarding infant weight is not limited to minority groups. A second limitation is that the results rely solely on weight percentiles, not weight-for-length percentiles, which may better represent infant adiposity.43 Despite this, weight-for-length percentiles are much less commonly used by clinicians in day-to-day practice and may be a more difficult measurement for parents to understand. Furthermore, the accuracy of length measurements in the clinic setting may be questionable.44 Whereas weight measures can be obtained accurately if proper quality control is practiced, length measures are more difficult to obtain accurately.
In conclusion, this sample of parents perceived infant and toddler growth at lower percentiles on the weight-for-age growth chart more negatively than growth in the upper percentile range. In the midst of a childhood obesity epidemic, the reasons for such parental preferences require further exploration, as does study in differing population groups. Because early life overweight and obesity are increasingly common, children currently considered “normal” may include infants and toddlers who are larger than those in the past. Clinicians must recognize that parents may have potentially unhealthy preferences for their infant’s weight as well as perceptions of normal that are different from those in previous generations and educate families on what constitutes a healthy growth pattern.
Acknowledgments
Funding
This work was supported by Grant DK72996 from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). Additional support was received from the Children’s Miracle Network. Dr Paul had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Footnotes
Reprints and permission: http://www.sagepub.com/journalsPermissions.nav
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
References
- 1.World Health Organization. [Accessed October 31, 2008];Obesity and overweight. http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/publications/facts/obesity/en. Updated 2009.
- 2.Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. High body mass index for age among US children and adolescents, 2003–2006. JAMA. 2008;299:2401–2405. doi: 10.1001/jama.299.20.2401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lederman SA, Akabas SR, Moore BJ. Editors’ overview of the conference on preventing childhood obesity. Pediatrics. 2004;114:1139–1145. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Reilly JJ, Armstrong J, Dorosty AR, et al. Early life risk factors for obesity in childhood: cohort study. BMJ. 2005;330:1358–1360. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38470.670903.E0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Monteiro PO, Victora CG, Barros FC, Monteiro LM. Birth size, early childhood growth, and adolescent obesity in a Brazilian birth cohort. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003;27:1274–1282. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Charney E, Goodman HC, McBride M, Lyon B, Pratt R. Childhood antecedents of adult obesity: do chubby infants become obese adults? N Engl J Med. 1976;295:6–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197607012950102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Whitaker RC, Wright JA, Pepe MS, Seidel KD, Dietz WH. Predicting obesity in young adulthood from childhood and parental obesity. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:869–873. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199709253371301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ong KK, Ahmed ML, Emmett PM, Preece MA, Dunger DB. Association between postnatal catch-up growth and obesity in childhood: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2000;320:967–971. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7240.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Stettler N, Zemel BS, Kumanyika S, Stallings VA. Infant weight gain and childhood overweight status in a multi-center, cohort study. Pediatrics. 2002;109:194–199. doi: 10.1542/peds.109.2.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stettler N, Kumanyika SK, Katz SH, Zemel BS, Stallings VA. Rapid weight gain during infancy and obesity in young adulthood in a cohort of African Americans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003;77:1374–1378. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/77.6.1374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.von Kries R, Toschke AM, Wurmser H, Sauerwald T, Koletzko B. Reduced risk for overweight and obesity in 5- and 6-y-old children by duration of sleep: a cross-sectional study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2002;26:710–716. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.National Center for Health Statistics. [Accessed July 16, 2009];CDC growth charts: United States. 2000 http://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/. Updated June 4, 2009.
- 13.Jaffe M, Kosakov C. The motor development of fat babies. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1982;21:619–621. doi: 10.1177/000992288202101011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shibli R, Rubin L, Akons H, Shaoul R. Morbidity of overweight (>or=85th percentile) in the first 2 years of life. Pediatrics. 2008;122:267–272. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-2867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wake M, Hardy P, Sawyer MG, Carlin JB. Comorbidities of overweight/obesity in Australian preschoolers: a cross- sectional population study. Arch Dis Child. 2008;93:502–507. doi: 10.1136/adc.2007.128116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Taveras EM, Rifas-Shiman SL, Camargo CA, Jr, et al. Higher adiposity in infancy associated with recurrent wheeze in a prospective cohort of children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121:1161–1166. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.03.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lucas P, Arai L, Baird J, Kleijnen J, Law C, Roberts H. A systematic review of lay views about infant size and growth. Arch Dis Child. 2007;92:120–127. doi: 10.1136/adc.2005.087288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Singhal A, Cole TJ, Fewtrell M, Deanfield J, Lucas A. Is slower early growth beneficial for long-term cardiovascular health? Circulation. 2004;109:1108–1113. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000118500.23649.DF. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Huxley RR, Shiell AW, Law CM. The role of size at birth and postnatal catch-up growth in determining systolic blood pressure: a systematic review of the literature. J Hypertens. 2000;18:815–831. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200018070-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Law CM, Shiell AW, Newsome CA, et al. Fetal, infant, and childhood growth and adult blood pressure: a longitudinal study from birth to 22 years of age. Circulation. 2002;105:1088–1092. doi: 10.1161/hc0902.104677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Parker L, Lamont DW, Unwin N, et al. A lifecourse study of risk for hyperinsulinaemia, dyslipidaemia and obesity (the central metabolic syndrome) at age 49–51 years. Diabet Med. 2003;20:406–415. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.00949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Eriksson JG, Forsen T, Tuomilehto J, Winter PD, Osmond C, Barker DJ. Catch-up growth in childhood and death from coronary heart disease: longitudinal study. BMJ. 1999;318:427–431. doi: 10.1136/bmj.318.7181.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Barker DJ, Osmond C, Forsen TJ, Kajantie E, Eriksson JG. Trajectories of growth among children who have coronary events as adults. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1802–1809. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa044160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Heird WC. Parental feeding behavior and children’s fat mass. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;75:451–452. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/75.3.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Faith MS, Scanlon KS, Birch LL, Francis LA, Sherry B. Parent–child feeding strategies and their relationships to child eating and weight status. Obes Res. 2004;12:1711–1722. doi: 10.1038/oby.2004.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Birch LL, Fisher JO. Development of eating behaviors among children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 1998;101:539–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bentley M, Gavin L, Black MM, Teti L. Infant feeding practices of low-income, African-American, adolescent mothers: an ecological, multigenerational perspective. Soc Sci Med. 1999;49:1085–1100. doi: 10.1016/s0277-9536(99)00198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Boyington JA, Johnson AA. Maternal perception of body size as a determinant of infant adiposity in an African-American community. J Natl Med Assoc. 2004;96:351–362. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jain A, Sherman SN, Chamberlin LA, Carter Y, Powers SW, Whitaker RC. Why don’t low-income mothers worry about their preschoolers being overweight? Pediatrics. 2001;107:1138–1146. doi: 10.1542/peds.107.5.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Baughcum AE, Chamberlin LA, Deeks CM, Powers SW, Whitaker RC. Maternal perceptions of overweight pre-school children. Pediatrics. 2000;106:1380–1386. doi: 10.1542/peds.106.6.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Maynard LM, Galuska DA, Blanck HM, Serdula MK. Maternal perceptions of weight status of children. Pediatrics. 2003;111:1226–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Carnell S, Edwards C, Croker H, Boniface D, Wardle J. Parental perceptions of overweight in 3–5 y olds. Int J Obes (Lond) 2005;29:353–355. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Campbell MW, Williams J, Hampton A, Wake M. Maternal concern and perceptions of overweight in Australian preschool-aged children. Med J Aust. 2006;184:274–277. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.2006.tb00236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jackson J, Strauss CC, Lee AA, Hunter K. Parents’ accuracy in estimating child weight status. Addict Behav. 1990;15:65–68. doi: 10.1016/0306-4603(90)90007-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Towns N, D’Auria J. Parental perceptions of their child’s overweight: an integrative review of the literature. J Pediatr Nurs. 2009;24:115–130. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2008.02.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kramer MS, Barr RG, Leduc DG, Boisjoly C, Pless IB. Maternal psychological determinants of infant obesity: development and testing of two new instruments. J Chronic Dis. 1983;36:329–335. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(83)90118-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Baughcum AE, Burklow KA, Deeks CM, Powers SW, Whitaker RC. Maternal feeding practices and childhood obesity: a focus group study of low-income mothers. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1998;152:1010–1014. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.152.10.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Contento IR, Basch C, Zybert P. Body image, weight, and food choices of Latina women and their young children. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2003;35:236–248. doi: 10.1016/s1499-4046(06)60054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sherry B, McDivitt J, Birch LL, et al. Attitudes, practices, and concerns about child feeding and child weight status among socioeconomically diverse white, Hispanic, and African-American mothers. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004;104:215–221. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2003.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Reifsnider E, Flores-Vela AR, Beckman-Mendez D, Nguyen H, Keller C, Dowdall-Smith S. Perceptions of children’s body sizes among mothers living on the Texas-Mexico border (La Frontera) Public Health Nurs. 2006;23:488–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1446.2006.00588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Borra ST, Kelly L, Shirreffs MB, Neville K, Geiger CJ. Developing health messages: qualitative studies with children, parents, and teachers help identify communications opportunities for healthful lifestyles and the prevention of obesity. J Am Diet Assoc. 2003;103:721–728. doi: 10.1053/jada.2003.50140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bruss MB, Morris J, Dannison L. Prevention of childhood obesity: sociocultural and familial factors. J Am Diet Assoc. 2003;103:1042–1045. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8223(03)00472-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Belfort MB, Rifas-Shiman SL, Rich-Edwards J, Kleinman KP, Gillman MW. Size at birth, infant growth, and blood pressure at three years of age. J Pediatr. 2007;151:670–674. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.05.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Johnson TS, Engstrom JL, Warda JA, Kabat M, Peters B. Reliability of length measurements in full-term neonates. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 1998;27:270–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6909.1998.tb02649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]