Abstract
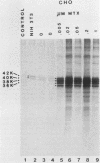
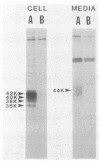
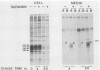
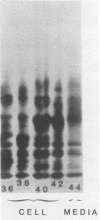
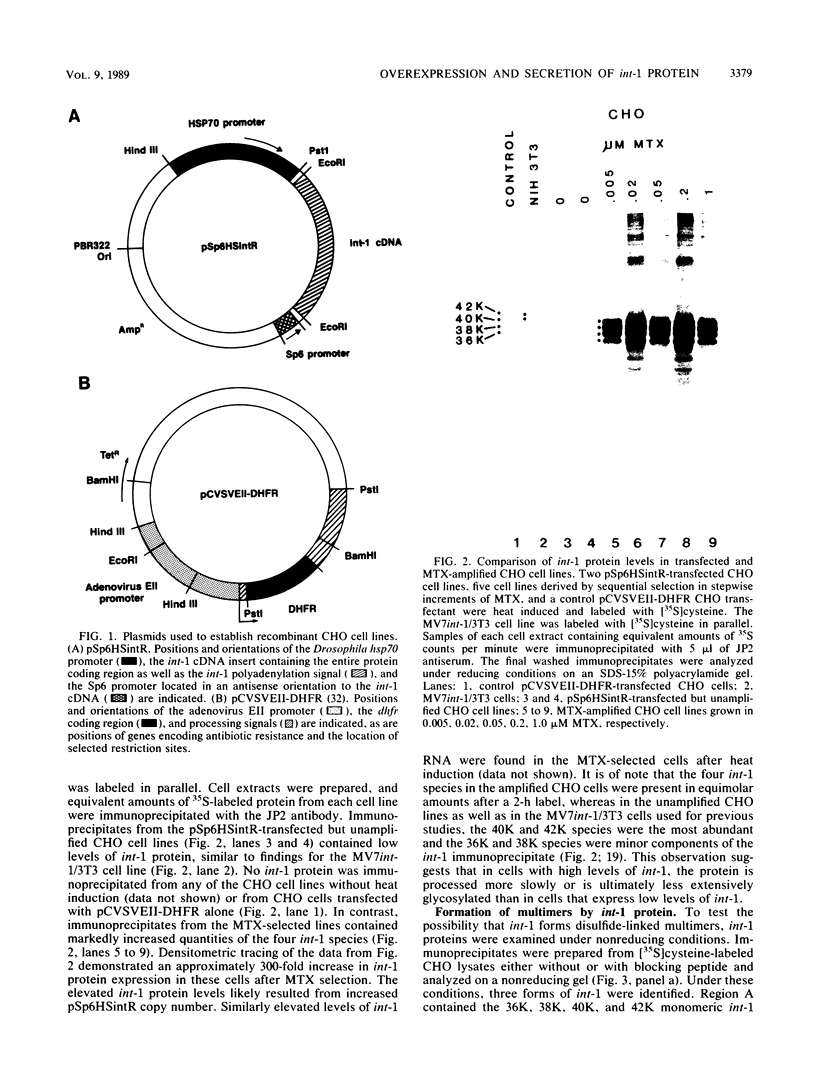
The int-1 proto-oncogene is a target for insertional activation of transcription by mouse mammary tumor virus in many murine mammary tumors. Whereas no expression of int-1 is seen in normal mammary tissue, int-1 RNA can be detected in normal mice in the neural tubes of midgestation embryos and in postmeiotic spermatocytes from adult testes. I report here the results of a study in which several different antibodies against synthetic peptides were produced and used to characterize the processing and secretion of int-1 protein. CHO cells were transfected with an inducible int-1 expression vector that was subsequently amplified to generate cell lines expressing very high levels of int-1 protein. Immunoprecipitation of [35S]cysteine-labeled cell lysates from these CHO cells yielded large amounts of four immature forms of int-1 glycoprotein (molecular weights of 36,000, 38,000, 40,000, and 42,000). A significant fraction of these int-1 species formed disulfide-linked multimers. Pulse-chase and glycosidase digestion studies demonstrated that some of the immature species of int-1 protein move through the secretory pathway and are processed to a mature heterogeneous glycoprotein with a molecular weight of about 44,000. Suramin treatment of the CHO cells during pulse-chase experiments increased the amount of 44,000-molecular-weight int-1 protein in the culture medium.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker N. E. Molecular cloning of sequences from wingless, a segment polarity gene in Drosophila: the spatial distribution of a transcript in embryos. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1765–1773. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsholtz C., Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Efficient reversion of simian sarcoma virus-transformation and inhibition of growth factor-induced mitogenesis by suramin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6440–6444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Papkoff J., Fung Y. K., Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E. Identification of protein products encoded by the proto-oncogene int-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3971–3977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Wildin R. S., Prendergast T. J., Varmus H. E. A retrovirus vector expressing the putative mammary oncogene int-1 causes partial transformation of a mammary epithelial cell line. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90699-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera C. V., Alonso M. C., Johnston P., Phillips R. G., Lawrence P. A. Phenocopies induced with antisense RNA identify the wingless gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):659–663. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corless C. L., Matzuk M. M., Ramabhadran T. V., Krichevsky A., Boime I. Gonadotropin beta subunits determine the rate of assembly and the oligosaccharide processing of hormone dimer in transfected cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1173–1181. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Shackleford G. M., Brown A. M., Sanders G. S., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence and expression in vitro of cDNA derived from mRNA of int-1, a provirally activated mouse mammary oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3337–3344. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. E., Webb N. R., Lim G. J., Brunner A. M., Ranchalis J. E., Twardzik D. R., Lioubin M. N., Marquardt H., Purchio A. F. Type 1 transforming growth factor beta: amplified expression and secretion of mature and precursor polypeptides in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3418–3427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E., Martin G. R. Two proto-oncogenes implicated in mammary carcinogenesis, int-1 and int-2, are independently regulated during mouse development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7806–7810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Spiliotes A. J., Gossels S. D., Latt S. A., Larsen G. R., Kay R. M. Coamplification and coexpression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator and murine dihydrofolate reductase sequences in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1750–1759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G., Shinnick T. M. Antibodies to chemically synthesized peptides predicted from DNA sequences as probes of gene expression. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):309–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. The TGF-beta family of growth and differentiation factors. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):437–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90443-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morata G., Lawrence P. A. The development of wingless, a homeotic mutation of Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1977 Apr;56(2):227–240. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90266-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):899–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., van Ooyen A., Cox D., Fung Y. K., Varmus H. Mode of proviral activation of a putative mammary oncogene (int-1) on mouse chromosome 15. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):131–136. doi: 10.1038/307131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Brown A. M., Varmus H. E. The int-1 proto-oncogene products are glycoproteins that appear to enter the secretory pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3978–3984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petcu D. J., Aldrich C. E., Coates L., Taylor J. M., Mason W. S. Suramin inhibits in vitro infection by duck hepatitis B virus, Rous sarcoma virus, and hepatitis delta virus. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):385–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsewijk F., Schuermann M., Wagenaar E., Parren P., Weigel D., Nusse R. The Drosophila homolog of the mouse mammary oncogene int-1 is identical to the segment polarity gene wingless. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsewijk F., van Deemter L., Wagenaar E., Sonnenberg A., Nusse R. Transfection of the int-1 mammary oncogene in cuboidal RAC mammary cell line results in morphological transformation and tumorigenicity. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):127–131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04729.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Antoniades H. N., Devare S. G., Hunkapiller M. W., Aaronson S. A. Structural and immunological similarities between simian sarcoma virus gene product(s) and human platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):605–608. doi: 10.1038/305605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Protein sorting by selective retention in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi stack. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):521–522. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90024-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to postmeiotic male germ cells and the neural tube of mid-gestational embryos. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto A. S., Grosschedl R., Guzman R. C., Parslow T., Varmus H. E. Expression of the int-1 gene in transgenic mice is associated with mammary gland hyperplasia and adenocarcinomas in male and female mice. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzvölgyi E., Kiss I., Pitt A., Arsenian S., Ingvarsson S., Udvardy A., Hamada M., Klein G., Sümegi J. Drosophila homolog of the murine Int-1 protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3034–3038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bailes J. A., McMahon A. P. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to specific neural cells in the developing mouse embryo. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90664-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Tremble P. M., Lavin M. F., Sunday M. E. Platelet-derived growth factor receptors form a high affinity state in membrane preparations. Kinetics and affinity cross-linking studies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5287–5294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurm F. M., Gwinn K. A., Kingston R. E. Inducible overproduction of the mouse c-myc protein in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ooyen A., Nusse R. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the putative mammary oncogene int-1; proviral insertions leave the protein-encoding domain intact. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]