Abstract
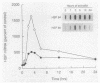
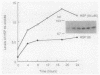
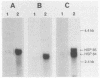
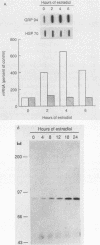
Murine uterine steady-state protein levels of the 90-kilodalton heat shock protein (HSP90) have been demonstrated recently to be increased by estrogen in a target tissue- and steroid-specific manner (C. Ramachandran, M.G. Catelli, W. Schneider, and G. Shyamala, Endocrinology 123:956-961, 1988). We now report that this regulation occurred with both the HSP86 and HSP84 forms of HSP90 as well as with the 94-kilodalton glucose-regulated protein. At the mRNA level, this response was greatest for HSP86 (15-fold). In contrast, estradiol had no significant effect on HSP70.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baez M., Sargan D. R., Elbrecht A., Kulomaa M. S., Zarucki-Schulz T., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Steroid hormone regulation of the gene encoding the chicken heat shock protein hsp 108. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6582–6588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnier J. V., Bensaude O., Morange M., Babinet C. Mouse 89 kD heat shock protein. Two polypeptides with distinct developmental regulation. Exp Cell Res. 1987 May;170(1):186–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baulieu E. E. Steroid hormone antagonists at the receptor level: a role for the heat-shock protein MW 90,000 (hsp 90). J Cell Biochem. 1987 Oct;35(2):161–174. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240350209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon R. H. Heat shock and the heat shock proteins. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2400313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catelli M. G., Binart N., Jung-Testas I., Renoir J. M., Baulieu E. E., Feramisco J. R., Welch W. J. The common 90-kd protein component of non-transformed '8S' steroid receptors is a heat-shock protein. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3131–3135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. P., Weigel N. L., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W., McGuire W. L. Structural analysis of chicken oviduct progesterone receptor using monoclonal antibodies to the subunit B protein. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 11;23(19):4427–4435. doi: 10.1021/bi00314a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhart J. C., Duthu A., Ullrich S., Appella E., May P. Specific interaction between a subset of the p53 protein family and heat shock proteins hsp72/hsc73 in a human osteosarcoma cell line. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):595–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joab I., Radanyi C., Renoir M., Buchou T., Catelli M. G., Binart N., Mester J., Baulieu E. E. Common non-hormone binding component in non-transformed chick oviduct receptors of four steroid hormones. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):850–853. doi: 10.1038/308850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarella R. A., Green M. ERp99, an abundant, conserved glycoprotein of the endoplasmic reticulum, is homologous to the 90-kDa heat shock protein (hsp90) and the 94-kDa glucose regulated protein (GRP94). J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8875–8883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Bodwell J. E., Gametchu B., Harrison R. W., Munck A. Molybdate-stabilized nonactivated glucocorticoid-receptor complexes contain a 90-kDa non-steroid-binding phosphoprotein that is lost on activation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3758–3763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. K., Kozak C., Robinson E. A., Ullrich S. J., Appella E. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the murine hsp84 cDNA and chromosome assignment of related sequences. Gene. 1987;56(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. K., Kozak C., Robinson E. A., Ullrich S. J., Appella E. Murine 86- and 84-kDa heat shock proteins, cDNA sequences, chromosome assignments, and evolutionary origins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5343–5351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Two signals mediate hormone-dependent nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3333–3340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran C., Catelli M. G., Schneider W., Shyamala G. Estrogenic regulation of uterine 90-kilodalton heat shock protein. Endocrinology. 1988 Aug;123(2):956–961. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-2-956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebbe N. F., Ware J., Bertina R. M., Modrich P., Stafford D. W. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA for a member of the human 90-kDa heat-shock protein family. Gene. 1987;53(2-3):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Toft D. O., Schlesinger M. J., Pratt W. B. Evidence that the 90-kDa phosphoprotein associated with the untransformed L-cell glucocorticoid receptor is a murine heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12398–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. The glucose-regulated protein grp94 is related to heat shock protein hsp90. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 20;194(2):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S. J., Moore S. K., Appella E. Transcriptional and translational analysis of the murine 84- and 86-kDa heat shock proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6810–6816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S. J., Robinson E. A., Law L. W., Willingham M., Appella E. A mouse tumor-specific transplantation antigen is a heat shock-related protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3121–3125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]